 |
Inertial Reference System
An inertial navigation system (INS; also inertial guidance system, inertial instrument) is a navigation device that uses motion sensors (accelerometers), rotation sensors ( gyroscopes) and a computer to continuously calculate by dead reckoning the position, the orientation, and the velocity (direction and speed of movement) of a moving object without the need for external references. Often the inertial sensors are supplemented by a barometric altimeter and sometimes by magnetic sensors ( magnetometers) and/or speed measuring devices. INSs are used on mobile robots and on vehicles such as ships, aircraft, submarines, guided missiles, and spacecraft. Older INS systems generally used an inertial platform as their mounting point to the vehicle and the terms are sometimes considered synonymous. Design Inertial navigation is a self-contained navigation technique in which measurements provided by accelerometers and gyroscopes are used to track the position and orientation of an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
Project SPIRE Inertial Navigation Control
A project is a type of assignment, typically involving research or design, that is carefully plan, planned to achieve a specific objective. An alternative view sees a project managerialism, managerially as a sequence of events: a "set of interrelated tasks to be executed over a fixed period and within certain cost and other limitations". A project may be a temporary (rather than a permanent) social system (work systems, work system), possibly staffed by teams (within or across organizations) to accomplish particular Task (project management), tasks under Time limit, time constraints. A project may form a part of wider programme management or function as an ''ad hoc'' system. Open-source software "projects" or artists' musical "projects" (for example) may lack defined team-membership, precise planning and/or time-limited durations. Overview The word ''project'' comes from the Latin word ''projectum'' from the Latin verb ''proicere'', "before an action", which in turn comes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
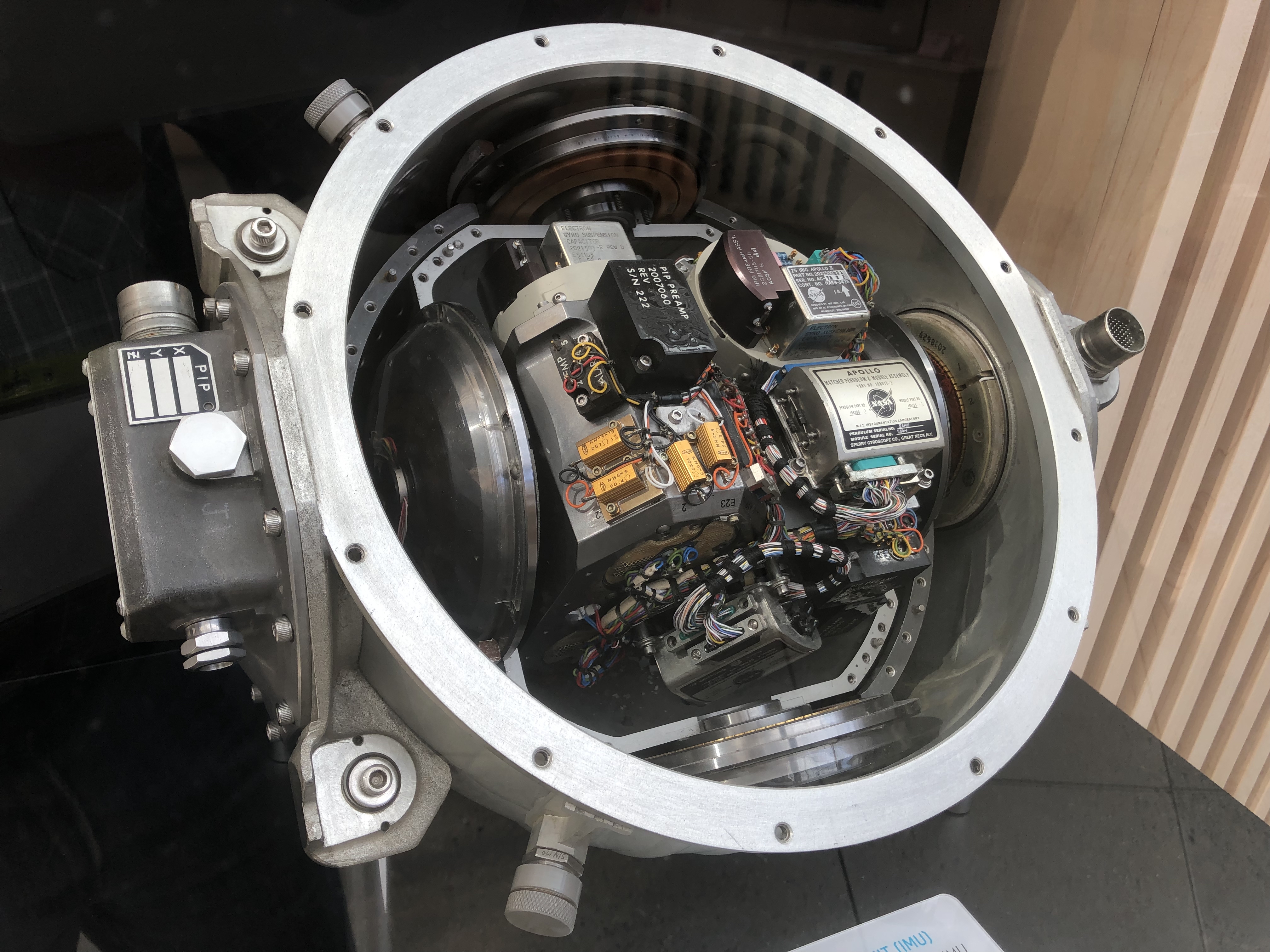 |
Inertial Measurement Unit
An inertial measurement unit (IMU) is an electronic device that measures and reports a body's specific force, angular rate, and sometimes the Orientation (geometry), orientation of the body, using a combination of accelerometers, gyroscopes, and sometimes magnetometers. When the magnetometer is included, IMUs are referred to as IMMUs. IMUs are typically used to maneuver modern vehicles including motorcycles, missiles, aircraft (an attitude and heading reference system), including uncrewed aerial vehicles (UAVs), among many others, and spacecraft, including satellites and Lander (spacecraft), landers. Recent developments allow for the production of IMU-enabled GPS devices. An IMU allows a GPS receiver to work when GPS-signals are unavailable, such as in tunnels, inside buildings, or when electronic interference is present. IMUs are used in VR headsets and smartphones, and also in motion tracked game controllers like the Wii Remote. Operational principles file:Centrale-intert ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
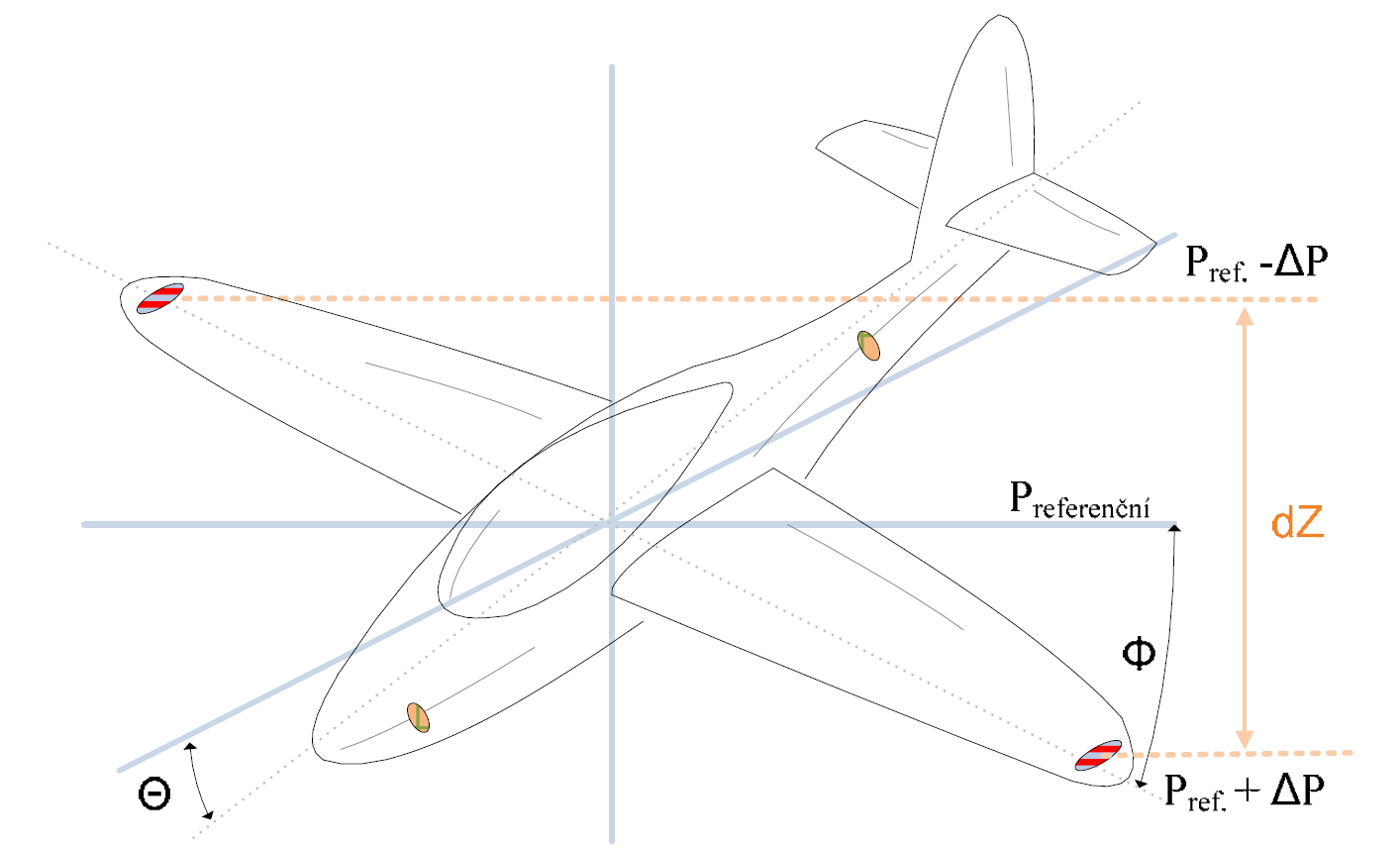 |
Pressure Reference System
Pressure reference system (PRS) is an enhancement of the inertial reference system and attitude and heading reference system designed to provide position angles measurements which are stable in time and do not suffer from long term drift caused by the sensor imperfections. The measurement system uses behavior of the International Standard Atmosphere where atmospheric pressure descends with increasing altitude and two pairs of measurement units. Each pair measures pressure at two different positions that are mechanically connected with known distance between units, e.g. the units are mounted at the tips of the wing. In horizontal flight, there is no pressure difference measured by the measurement system which means the position angle is zero. In case the airplane banks (to turn), the tips of the wings mutually change their positions, one is going up and the second one is going down, and the pressure sensors in every unit measure different values which are translated into a positio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
Numerical Integration
In analysis, numerical integration comprises a broad family of algorithms for calculating the numerical value of a definite integral. The term numerical quadrature (often abbreviated to quadrature) is more or less a synonym for "numerical integration", especially as applied to one-dimensional integrals. Some authors refer to numerical integration over more than one dimension as cubature; others take "quadrature" to include higher-dimensional integration. The basic problem in numerical integration is to compute an approximate solution to a definite integral :\int_a^b f(x) \, dx to a given degree of accuracy. If is a smooth function integrated over a small number of dimensions, and the domain of integration is bounded, there are many methods for approximating the integral to the desired precision. Numerical integration has roots in the geometrical problem of finding a square with the same area as a given plane figure ('' quadrature'' or ''squaring''), as in the quadrature of t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
 |
Required Navigation Performance
Required navigation performance (RNP) is a type of performance-based navigation (PBN) that allows an aircraft to fly a specific path between two 3D-defined points in space. Navigation precision Area navigation, Area navigation (RNAV) and RNP systems are fundamentally similar. The key difference between them is the requirement for on-board performance monitoring and alerting. A navigation specification that includes a requirement for on-board navigation performance monitoring and alerting is referred to as an RNP specification. One not having such a requirement is referred to as an RNAV specification. Therefore, if ATC radar monitoring is not provided, safe navigation in respect to terrain shall be self-monitored by the pilot and RNP shall be used instead of RNAV. RNP also refers to the level of performance required for a specific procedure or a specific block of airspace. An RNP of 10 means that a navigation system must be able to calculate its position to within a circle with ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
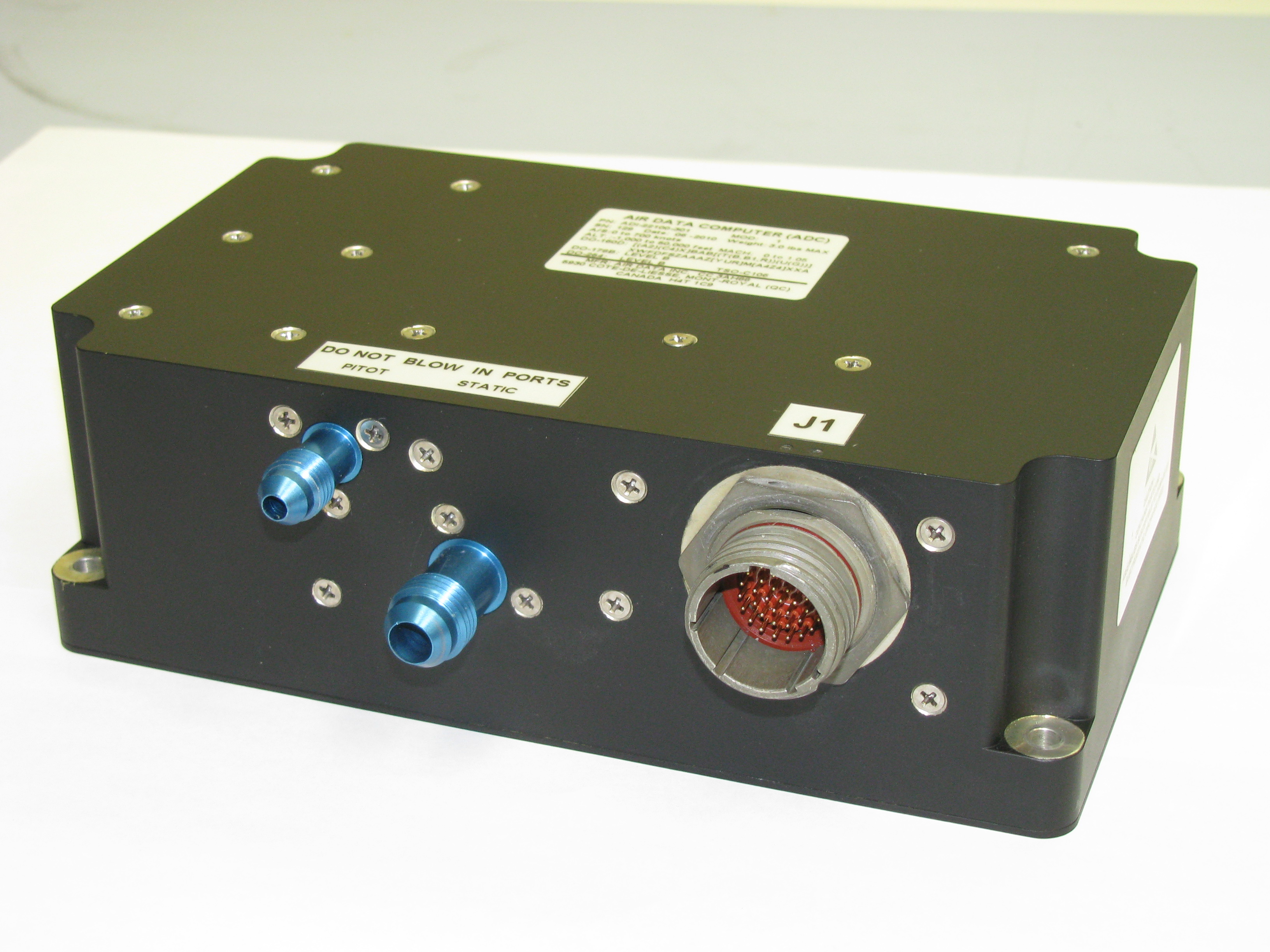 |
Air Data Computer
An air data computer (ADC) or central air data computer (CADC) computes altitude, vertical speed, air speed, and Mach number from pressure and temperature inputs. It is an essential avionics component found in modern aircraft. This computer, rather than individual flight instruments, instruments, can determine the calibrated airspeed, Mach number, altitude, and vertical speed indicator, altitude trend data from an aircraft's pitot-static system. In some very high-speed aircraft such as the Space Shuttle, equivalent airspeed is calculated instead of calibrated airspeed. Air data computers usually also have an input of total air temperature. This enables the computation of static air temperature and true airspeed. Models In Airbus aircraft the air data computer is combined with attitude, heading and navigation sources in a single unit known as the Air Data Inertial Reference Unit (ADIRU) which has now been replaced by the Global Navigation Air Data Inertial Reference System (GNADI ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
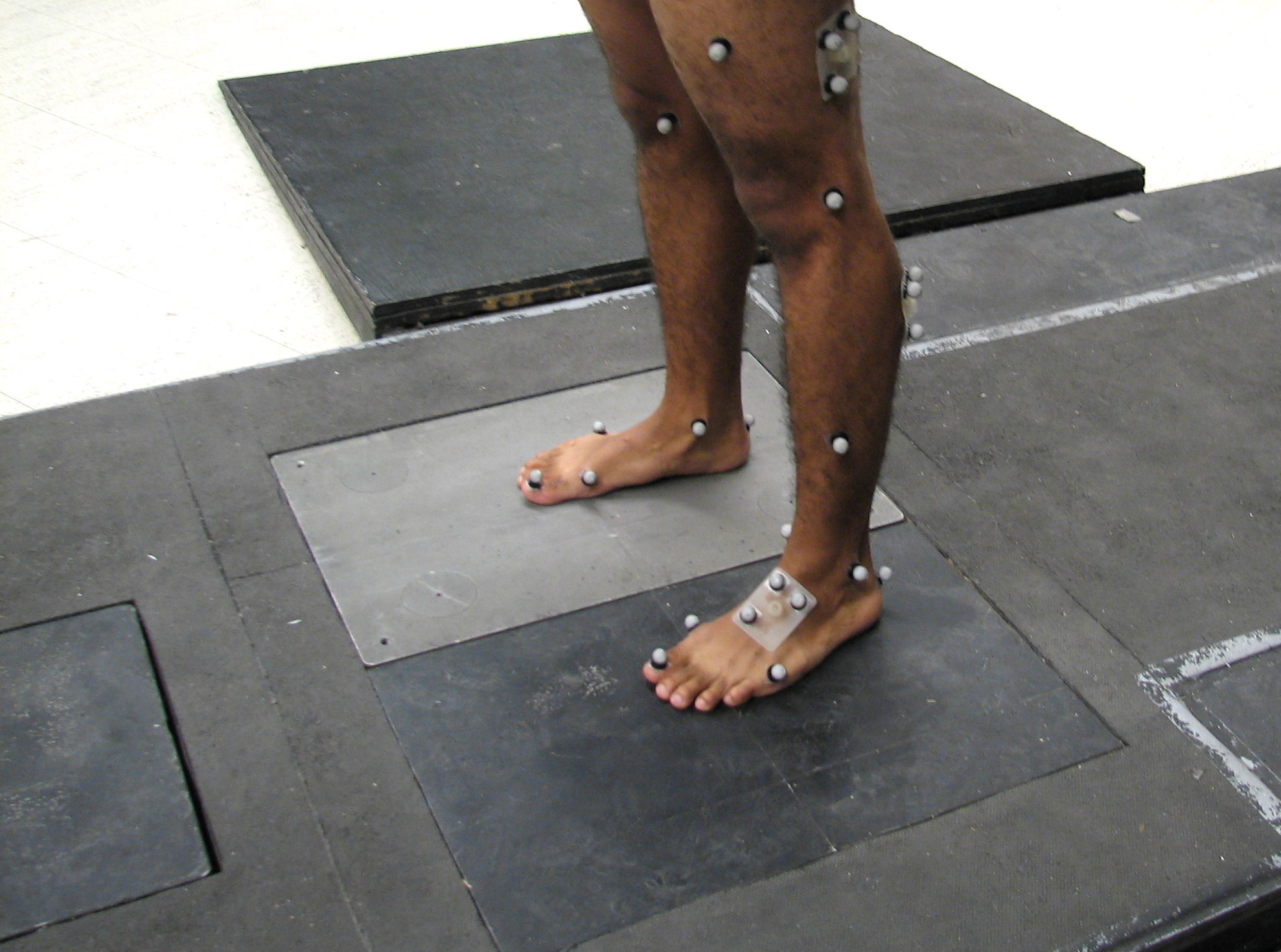 |
Motion Capture
Motion capture (sometimes referred as mocap or mo-cap, for short) is the process of recording high-resolution motion (physics), movement of objects or people into a computer system. It is used in Military science, military, entertainment, sports, medical applications, and for validation of computer vision and robots. In films, television shows and video games, motion capture refers to recording actions of Motion-capture acting, human actors and using that information to animate Character animation, digital character models in 2D or 3D computer animation. When it includes face and fingers or captures subtle expressions, it is often referred to as performance capture. In many fields, motion capture is sometimes called motion tracking, but in filmmaking and games, motion tracking usually refers more to match moving. In motion capture sessions, movements of one or more actors are sampled many times per second. Whereas early techniques used 3D reconstruction from multiple images, ima ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
 |
Microelectromechanical Systems
MEMS (micro-electromechanical systems) is the technology of microscopic devices incorporating both electronic and moving parts. MEMS are made up of components between 1 and 100 micrometres in size (i.e., 0.001 to 0.1 mm), and MEMS devices generally range in size from 20 micrometres to a millimetre (i.e., 0.02 to 1.0 mm), although components arranged in arrays (e.g., digital micromirror devices) can be more than 1000 mm2. They usually consist of a central unit that processes data (an integrated circuit chip such as microprocessor) and several components that interact with the surroundings (such as microsensors). Because of the large surface area to volume ratio of MEMS, forces produced by ambient electromagnetism (e.g., electrostatic charges and magnetic moments), and fluid dynamics (e.g., surface tension and viscosity) are more important design considerations than with larger scale mechanical devices. MEMS technology is distinguished from molecular nanotechnol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
Kinematics
In physics, kinematics studies the geometrical aspects of motion of physical objects independent of forces that set them in motion. Constrained motion such as linked machine parts are also described as kinematics. Kinematics is concerned with systems of specification of objects' positions and velocities and mathematical transformations between such systems. These systems may be rectangular like Cartesian coordinate system, cartesian, Curvilinear coordinates like polar coordinates or other systems. The object trajectories may be specified with respect to other objects which may themselve be in motion relative to a standard reference. Rotating systems may also be used. Numerous practical problems in kinematics involve constraints, such as mechanical linkages, ropes, or rolling disks. Overview Kinematics is a subfield of physics and mathematics, developed in classical mechanics, that describes the motion of points, Physical object, bodies (objects), and systems of bodies (group ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
|
Angular Velocity
In physics, angular velocity (symbol or \vec, the lowercase Greek letter omega), also known as the angular frequency vector,(UP1) is a pseudovector representation of how the angular position or orientation of an object changes with time, i.e. how quickly an object rotates (spins or revolves) around an axis of rotation and how fast the axis itself changes direction. The magnitude of the pseudovector, \omega=\, \boldsymbol\, , represents the '' angular speed'' (or ''angular frequency''), the angular rate at which the object rotates (spins or revolves). The pseudovector direction \hat\boldsymbol=\boldsymbol/\omega is normal to the instantaneous plane of rotation or angular displacement. There are two types of angular velocity: * Orbital angular velocity refers to how fast a point object revolves about a fixed origin, i.e. the time rate of change of its angular position relative to the origin. * Spin angular velocity refers to how fast a rigid body rotates around a f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
|
Integral
In mathematics, an integral is the continuous analog of a Summation, sum, which is used to calculate area, areas, volume, volumes, and their generalizations. Integration, the process of computing an integral, is one of the two fundamental operations of calculus,Integral calculus is a very well established mathematical discipline for which there are many sources. See and , for example. the other being Derivative, differentiation. Integration was initially used to solve problems in mathematics and physics, such as finding the area under a curve, or determining displacement from velocity. Usage of integration expanded to a wide variety of scientific fields thereafter. A definite integral computes the signed area of the region in the plane that is bounded by the Graph of a function, graph of a given Function (mathematics), function between two points in the real line. Conventionally, areas above the horizontal Coordinate axis, axis of the plane are positive while areas below are n ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |