air data computer on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
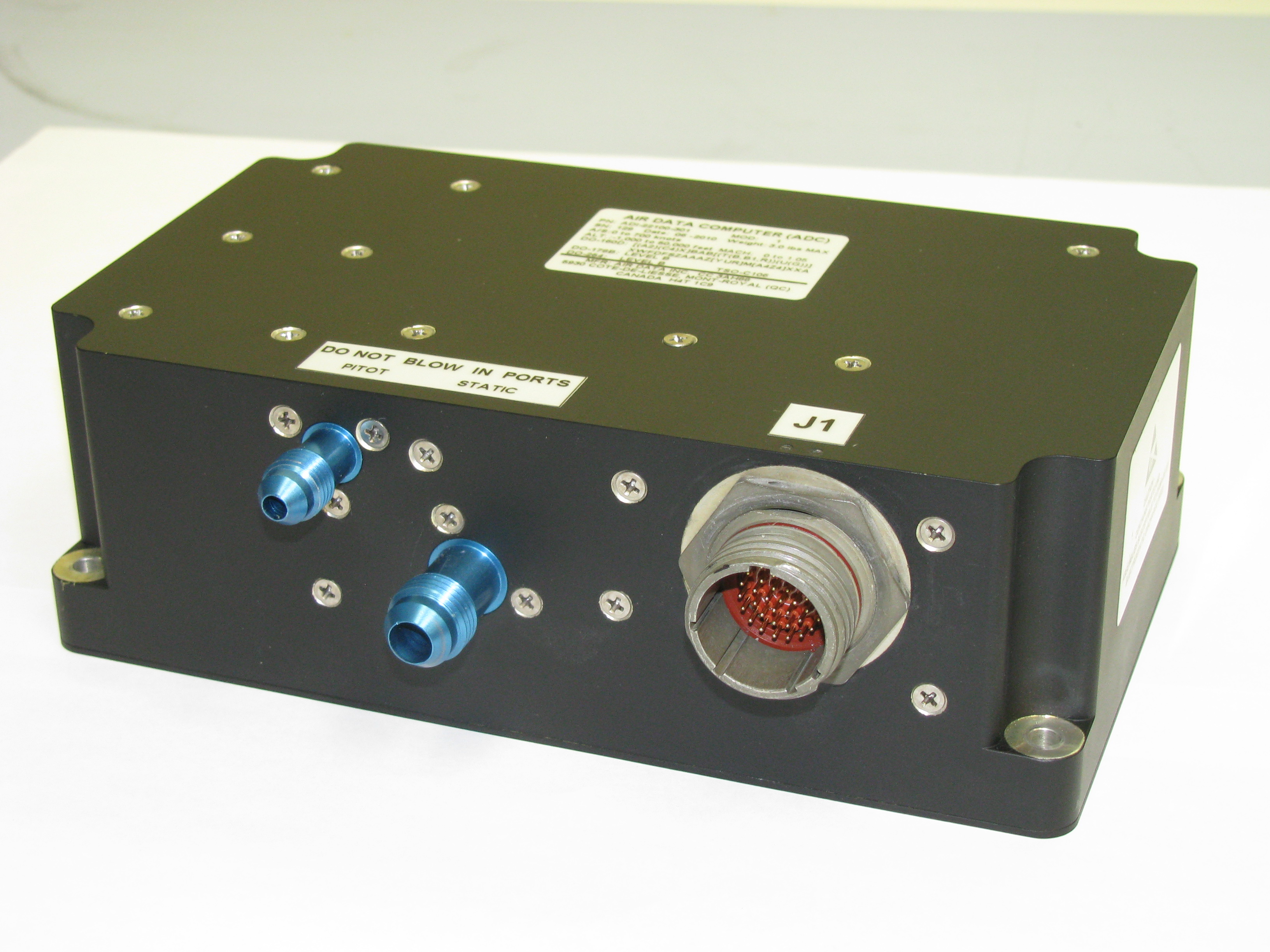 An air data computer (ADC) or central air data computer (CADC) computes
An air data computer (ADC) or central air data computer (CADC) computes
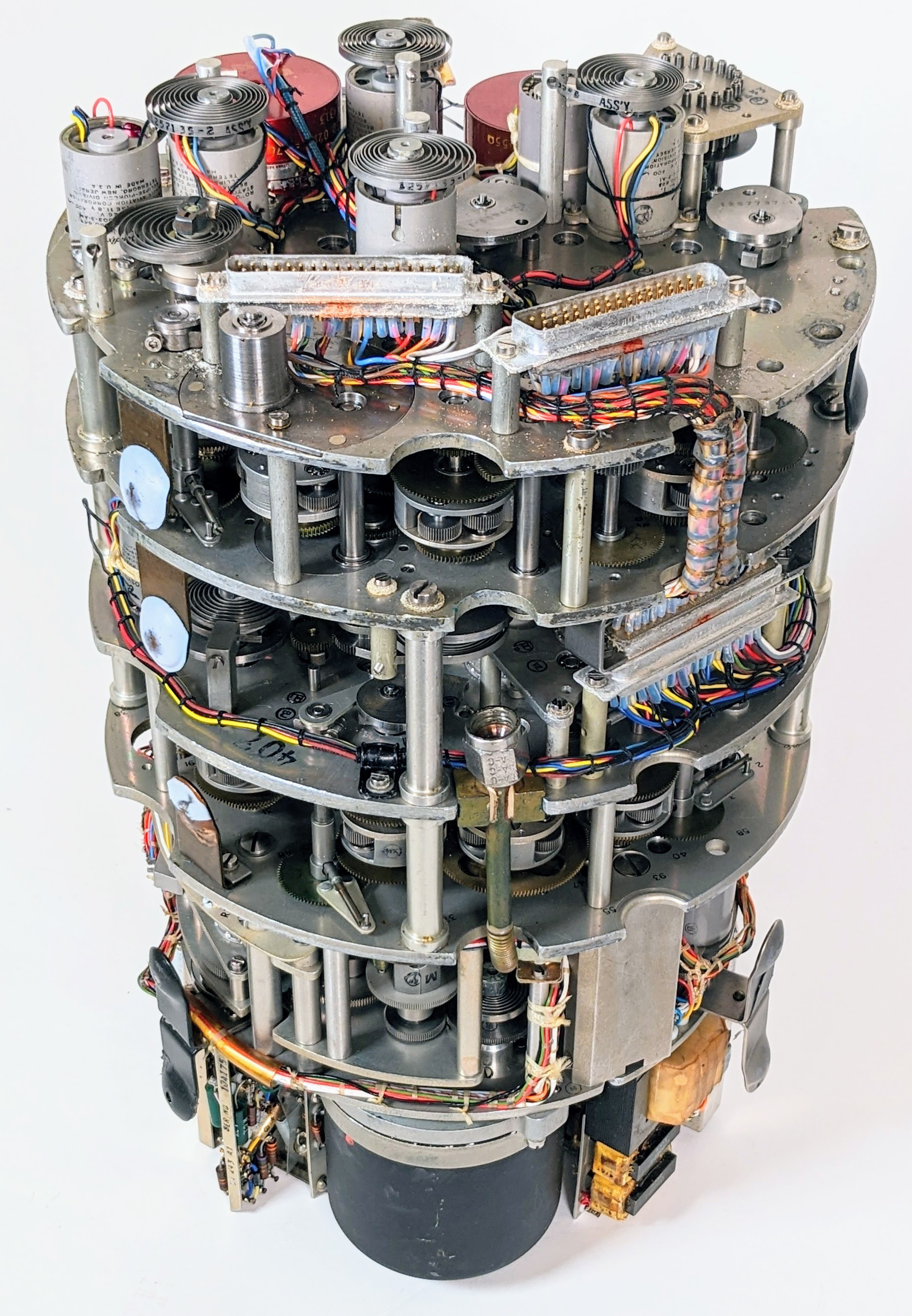 Electrical-mechanical air data computers were developed in the early 1950s to provide a central source of airspeed, altitude, and other signals to avionic systems that needed this data. A central air data computer avoided duplication of sensing equipment and could be more sophisticated and accurate. The first air data computer was built by Kollsman Instruments for the B-52 bomber. Bendix started producing a central air data computer in 1956 for use on US Air Force jet fighters. Garrett AiResearch developed early central air data computer systems that integrated pneumatic, electrical, and electronic components.
The late 1960s saw the introduction of digital air data computers. In 1967, Garrett AiResearch's ILAAS air data computer was the first all-digital unit. The DC-10 used Honeywell's digital air data system in 1969 and the F-14 CADC used on the F-14 in 1970 used custom
Electrical-mechanical air data computers were developed in the early 1950s to provide a central source of airspeed, altitude, and other signals to avionic systems that needed this data. A central air data computer avoided duplication of sensing equipment and could be more sophisticated and accurate. The first air data computer was built by Kollsman Instruments for the B-52 bomber. Bendix started producing a central air data computer in 1956 for use on US Air Force jet fighters. Garrett AiResearch developed early central air data computer systems that integrated pneumatic, electrical, and electronic components.
The late 1960s saw the introduction of digital air data computers. In 1967, Garrett AiResearch's ILAAS air data computer was the first all-digital unit. The DC-10 used Honeywell's digital air data system in 1969 and the F-14 CADC used on the F-14 in 1970 used custom
 An air data computer (ADC) or central air data computer (CADC) computes
An air data computer (ADC) or central air data computer (CADC) computes altitude
Altitude is a distance measurement, usually in the vertical or "up" direction, between a reference datum (geodesy), datum and a point or object. The exact definition and reference datum varies according to the context (e.g., aviation, geometr ...
, vertical speed, air speed, and Mach number from pressure and temperature inputs. It is an essential avionics
Avionics (a portmanteau of ''aviation'' and ''electronics'') are the Electronics, electronic systems used on aircraft. Avionic systems include communications, Air navigation, navigation, the display and management of multiple systems, and the ...
component found in modern aircraft. This computer, rather than individual instruments, can determine the calibrated airspeed, Mach number, altitude, and altitude trend data from an aircraft's pitot-static system. In some very high-speed aircraft such as the Space Shuttle
The Space Shuttle is a retired, partially reusable launch system, reusable low Earth orbital spacecraft system operated from 1981 to 2011 by the U.S. National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA) as part of the Space Shuttle program. ...
, equivalent airspeed is calculated instead of calibrated airspeed. Air data computers usually also have an input of total air temperature. This enables the computation of static air temperature and true airspeed.
Models
InAirbus
Airbus SE ( ; ; ; ) is a Pan-European aerospace corporation. The company's primary business is the design and manufacturing of commercial aircraft but it also has separate Airbus Defence and Space, defence and space and Airbus Helicopters, he ...
aircraft the air data computer is combined with attitude, heading and navigation sources in a single unit known as the Air Data Inertial Reference Unit (ADIRU) which has now been replaced by the Global Navigation Air Data Inertial Reference System (GNADIRS).
On the Embraer Embraer E-Jet family the concept has been refined further by splitting air data acquisition and measuring – performed by combined pitot/static "air data smart probes" with integrated sensors – and computation of parameters performed by "air data applications" (ADA) executed on non-dedicated processing units. As all information from the sensors is transmitted electrically, routing of pitot and static pressure lines through the aircraft and associated maintenance tasks is avoided.
In simpler aircraft and helicopters, the air data computers, generally two in number, and smaller, lighter and simpler than an ADIRU, may be called air data units, although their internal computational power is still significant. They commonly have the pitot and static pressure inputs, as well as outside air temperature from a platinum resistance thermometer and may control heating of the pitot tube and static vent to prevent blockage due to ice. On simpler aircraft, there is usually not a fly-by-wire system so the outputs are typically to the cockpit altimeters or display system, flight data recorder and autopilot system. Output interfaces typically are ARINC 429, Gillham or even IEEE 1394 (Firewire). The data provided may be true airspeed, pressure altitude, density altitude and Outside Air Temperature (OAT), but with no involvement in aircraft attitude or heading, as there are no gyroscope
A gyroscope (from Ancient Greek γῦρος ''gŷros'', "round" and σκοπέω ''skopéō'', "to look") is a device used for measuring or maintaining Orientation (geometry), orientation and angular velocity. It is a spinning wheel or disc in ...
s or accelerometer
An accelerometer is a device that measures the proper acceleration of an object. Proper acceleration is the acceleration (the rate of change (mathematics), rate of change of velocity) of the object relative to an observer who is in free fall (tha ...
s fitted internally. These devices are usually autonomous and do not require pilot input, merely sending continuously updated data to the recipient systems while the aircraft is powered up. Some, like the Enhanced Software Configurable Air Data Unit (ESCADU) are software configurable to suit many different aircraft applications.
Apart from commercial ADCs, there are available do-it-yourself, and open-source implementations.
History
 Electrical-mechanical air data computers were developed in the early 1950s to provide a central source of airspeed, altitude, and other signals to avionic systems that needed this data. A central air data computer avoided duplication of sensing equipment and could be more sophisticated and accurate. The first air data computer was built by Kollsman Instruments for the B-52 bomber. Bendix started producing a central air data computer in 1956 for use on US Air Force jet fighters. Garrett AiResearch developed early central air data computer systems that integrated pneumatic, electrical, and electronic components.
The late 1960s saw the introduction of digital air data computers. In 1967, Garrett AiResearch's ILAAS air data computer was the first all-digital unit. The DC-10 used Honeywell's digital air data system in 1969 and the F-14 CADC used on the F-14 in 1970 used custom
Electrical-mechanical air data computers were developed in the early 1950s to provide a central source of airspeed, altitude, and other signals to avionic systems that needed this data. A central air data computer avoided duplication of sensing equipment and could be more sophisticated and accurate. The first air data computer was built by Kollsman Instruments for the B-52 bomber. Bendix started producing a central air data computer in 1956 for use on US Air Force jet fighters. Garrett AiResearch developed early central air data computer systems that integrated pneumatic, electrical, and electronic components.
The late 1960s saw the introduction of digital air data computers. In 1967, Garrett AiResearch's ILAAS air data computer was the first all-digital unit. The DC-10 used Honeywell's digital air data system in 1969 and the F-14 CADC used on the F-14 in 1970 used custom integrated circuit
An integrated circuit (IC), also known as a microchip or simply chip, is a set of electronic circuits, consisting of various electronic components (such as transistors, resistors, and capacitors) and their interconnections. These components a ...
s.
From the late 1980s much of the USAF
The United States Air Force (USAF) is the Air force, air service branch of the United States Department of Defense. It is one of the six United States Armed Forces and one of the eight uniformed services of the United States. Tracing its ori ...
and USN aircraft fleets were retrofitted with the GEC Avionics Rochester-developed Standard Central Air Data Computer (SCADC). Aircraft fitted included the A-4 Skyhawk, A-6 Intruder, A-7 Corsair, C-5A/B Galaxy, EA-6B Prowler, F-111 Aardvark, F-4 Phantom, S-3 Viking, C-141 Starlifter, C-135 Stratolifter, C-2 Greyhound, and E-2 Hawkeye, for which the company received the Queen's Award for Technological Achievement.
See also
* Acronyms and abbreviations in avionics * F-14 Central Air Data Computer, used on the F-14References
{{DEFAULTSORT:Air Data Computer Avionics Aircraft instruments Glass cockpit