|
Indonesian State Intelligence Agency
Badan Intelijen Negara ("State Intelligence Agency"), commonly referred to as BIN, is Indonesia's primary intelligence agency. Prior to 2001, it was known as Bakin (''Badan Koordinasi Intelijen Negara'', "State Intelligence Coordinating Agency"); its name was changed as part of a general restructuring of the agency. BIN is responsible for co-ordinating information sharing and operations among Indonesia's other intelligence agencies, as well as for mounting operations on its own. At the time of its name change in 2001, BIN's role in co-ordinating was de-emphasised. However, in the wake of the 2002 Bali bombing, the co-ordinating function was strengthened as part of an all-around expansion of the agency's mandate, which included an expanded budget. Since 9 September 2016, the agency has been headed by Budi Gunawan. History 1943–1965 The origin of the state intelligence agency can be traced to Japanese occupation, in 1943,at which time Japan established a local version ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
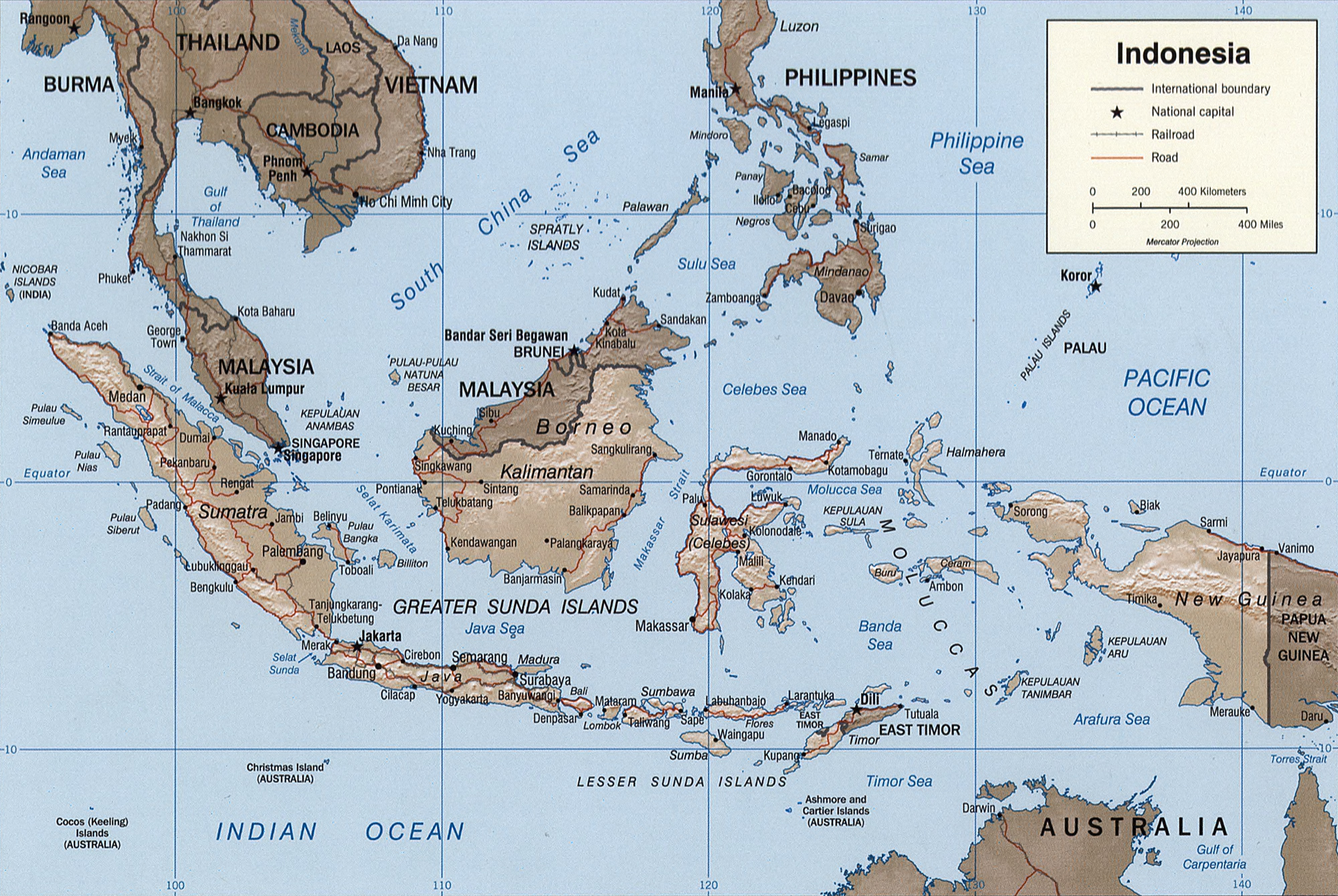
Indonesia
Indonesia, officially the Republic of Indonesia, is a country in Southeast Asia and Oceania between the Indian and Pacific oceans. It consists of over 17,000 islands, including Sumatra, Java, Sulawesi, and parts of Borneo and New Guinea. Indonesia is the world's largest archipelagic state and the 14th-largest country by area, at . With over 275 million people, Indonesia is the world's fourth-most populous country and the most populous Muslim-majority country. Java, the world's most populous island, is home to more than half of the country's population. Indonesia is a presidential republic with an elected legislature. It has 38 provinces, of which nine have special status. The country's capital, Jakarta, is the world's second-most populous urban area. Indonesia shares land borders with Papua New Guinea, East Timor, and the East Malaysia, eastern part of Malaysia, as well as maritime borders with Singapore, Vietnam, Thailand, the Philippines, Australia, Palau, an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Operation Trikora
Operation Trikora was an Indonesian military operation which aimed to seize and annex the Dutch overseas territory of Netherlands New Guinea in 1961 and 1962. After negotiations, the Netherlands signed the New York Agreement with Indonesia on 15 August 1962, relinquishing control of Western New Guinea to the United Nations. Background When the rest of the Dutch East Indies became fully independent as Indonesia in December 1949, the Dutch retained sovereignty over the western part of the island of New Guinea and took steps to prepare it for independence as a separate country. The Dutch and some West Papuan leaders argued that the territory did not belong to Indonesia because the West Papuans were ethnically and geographically separated from Indonesians, had always been administrated separately, and that the West Papuans did not want to be under Indonesian control.Ron Crocombe, 282 From its independence in 1949 until 1961, Indonesia attempted to gain control of Western N ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Abdurrahman Wahid
Abdurrahman Wahid ( ; born Abdurrahman ad-Dakhil; 7 September 1940 – 30 December 2009), though more colloquially known as Gus Dur (), was an Indonesian politician and Islamic religious leader who served as the 4th president of Indonesia, from his election in 1999 until his removal from power in 2001. A long time leader within the Nahdlatul Ulama organization, he was the founder of the National Awakening Party (PKB). He was the son of Minister of Religious Affairs Wahid Hasyim, and the grandson of Nahdatul Ulama founder Hasyim Asy'ari. He had a visual impairment caused by glaucoma. He was blind on the left eye and partially blind on his right eye. He was the first and as of 2022 the only president of Indonesia to have had physical disabilities. His popular nickname 'Gus Dur' is derived from ''Gus'', a common honorific for a son of kyai, and from the short-form of ''bagus'' ('handsome lad' in Javanese); and ''Dur'', short-form of his name, Abdurrahman. Early life Abdur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Golongan Karya
) , foundation = , youth = AMPG (Golkar Party Young Force) , women = KPPG (Golkar Party Women's Corps) , newspaper = ''Suara Karya'' (1971–2016) , headquarters = Jakarta , ideology = PancasilaConservatismNational conservatismEconomic liberalismIndonesian nationalismSecularism SuhartoismCatch-all party During the New Order:Big tentRight-wing authoritarianism , political_position = , anthem = ''Mars Partai Golkar'' , national = Onward Indonesia CoalitionUnited Indonesia Coalition , BallNo = 4 , DPRseats = , DPRD1seats = , labour = , website = , footnotes = The Party of Functional Groups ( id, Partai Golongan Karya), often known by its abbreviation Golkar, is a political party in Indonesia. It was founded as the Joint Secretariat of Functional Groups ( id, Sekretariat Bersama Golongan Karya, links=no, Sekber Golkar) in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
West Irian
Western New Guinea, also known as Papua, Indonesian New Guinea, or Indonesian Papua, is the western half of the Melanesian island of New Guinea which is administered by Indonesia. Since the island is alternatively named as Papua, the region is also called West Papua ( id, Papua Barat). Lying to the west of Papua New Guinea and considered a part of the Australian continent, the territory is almost entirely in the Southern Hemisphere and includes the Schouten and Raja Ampat archipelagoes. The region is predominantly covered with ancient rainforest where numerous traditional tribes live such as the Dani of the Baliem Valley although a large proportion of the population live in or near coastal areas with the largest city being Jayapura. Within five years following its proclamation of independence in 1945, the Republic of Indonesia (for a time part of the United States of Indonesia) took over all the former territories of the Dutch East Indies except Western New Guinea, accor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Act Of Free Choice
The Act of Free Choice ( id, Penentuan Pendapat Rakyat, PEPERA, Determination of the People's Opinion) was a controversial plebiscite held between 14 July and 2 August 1969 in which 1,025 people selected by the Indonesian military in Western New Guinea voted unanimously in favor of Indonesian control. The event was mentioned by the United Nations in General Assembly resolution 2504 (XXIV) without giving an opinion whether it complied with the authorizing New York Agreement, and without giving an opinion whether it was an act of "self-determination" as referred to and described in United Nations General Assembly resolutions 1514 and 1541 (XV) respectively. The event is sometimes disparagingly referred to as the "Act of No Choice" because of its controversial process. Background The referendum and its conduct had been specified in the New York Agreement; Article 17 of which in part says: "Indonesia will invite the Secretary-General to appoint a Representative who" ... "will car ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fort Gordon
Fort Gordon, formerly known as Camp Gordon, is a United States Army installation established in October 1941. It is the current home of the United States Army Signal Corps, United States Army Cyber Command, and the Cyber Center of Excellence. It was once the home of The Provost Marshal General School and Civil Affairs School. The fort is located southwest of Augusta, Georgia. One of the major components of the installation is Advanced Individual Training for Signal Corps military occupational specialties. Signals Intelligence has become more visible and comprises more and more of the fort's duties. The installation was recommended for renaming to Fort Eisenhower by The Naming Commission. Etymology It is named after John Brown Gordon, a major general in the Confederate army during the Civil War. Fort Gordon is one of the U.S. Army installations named for Confederate soldiers to be recommended for renaming by The Naming Commission. Their recommendation is that the post be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Leonardus Benjamin Moerdani
General (Ret.) Leonardus Benjamin Moerdani (also publicly known as LB Moerdani or Benny Moerdani and in foreign media as Murdani; 2 October 1932 – 29 August 2004) was the ABRI Commander from 1983 to 1988 and also served as Indonesia's Minister of Defense and Security. He is famous due to his strong stance in many decisive situations in Indonesian political and social life. He was also significant as a leader who was Catholic in a predominantly Muslim community. Early life Moerdani was born on 2 October 1932 at Cepu, in the Blora Regency in Central Java, to R.G. Moerdani Sosrodirjo, a railway worker and his Indo Eurasian wife Jeanne Roech, who was half German. Moerdani was the 3rd out of 11 children. Although a Muslim, Moerdani Sosrodirjo tolerated his wife's and in their turn, his children's Catholic faith. Military career Early Military Career After the Indonesian Declaration of Independence on 17 August 1945, Moerdani was caught up in the wave of nationalism. In Oc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ali Moertopo
Ali Murtopo (23 September 1924 – 15 May 1984) was a prominent Indonesian general and political figure during the first half of General Suharto's New Order regime. Early life Ali Murtopo was born on 23 September 1924 in Kebumen, Central Java and received his education in Central Java and West Java. He met his wife, Wastoeti, in Yogyakarta and they were married in May 1956. Military career As a teenager, Ali joined Hizbullah but would eventually join the Indonesian military. During the Indonesian National Revolution, Ali became a staff member in a brigade led by Ahmad Yani. In 1952, Ali became a company Commander in Ahmad Yani's Banteng Raiders, an elite group of soldiers formed to chase away the remnants of the Darul Islam movement. In 1956, whilst still in command of his Banteng Raider unit, Ali was involved in the lobbying to decide who should become the Commander of the 4th Military Territory (TT IV) Diponegoro, which supervised the security of the Provinces of Centra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kopkamtib
The Operational Command for the Restoration of Security and Order ( id, Komando Operasi Pemulihan Keamanan dan Ketertiban), or Kopkamtib, was a military body established to deal with the 1965 coup attempt operation in Indonesia, and was subsequently used by President Suharto's New Order regime to suppress dissent. Origins of Kopkamtib Kopkamtib was established on 10 October 1965, ten days after the 30 September Movement killed six senior army generals in a failed coup attempt. Surviving general, Suharto, accepted President Sukarno's order to take control of the army on condition that he be handed full authority to restore order and security, an arrangement that was formalised by creating Kopkamtib.Cribb & Kahin (2004) p218 The conflict between the forces of the military and their rivals the Communist Party of Indonesia (PKI), had predated the setting up of the organisation. The formation of Kopkamtib was a legitimisation of military and the New Order governments determination ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Soeharto
Suharto (; ; 8 June 1921 – 27 January 2008) was an Indonesian army officer and politician, who served as the second and the longest serving president of Indonesia. Widely regarded as a military dictator by international observers, Suharto led Indonesia through a dictatorship for 31 years, from the fall of Sukarno in 1967 until his own resignation in 1998. The legacy of his 31-year rule, and his US$38 billion net worth, is still debated at home and abroad. Suharto was born in the small village of Kemusuk, in the Godean area near the city of Yogyakarta, during the Dutch colonial era. He grew up in humble circumstances. His Javanese Muslim parents divorced not long after his birth, and he lived with foster parents for much of his childhood. During the Japanese occupation era, Suharto served in the Japanese-organized Indonesian security forces. During Indonesia's independence struggle, he joined the newly formed Indonesian Army. There, Suharto rose to the rank of major ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
New Order (Indonesia)
The New Order ( id, Orde Baru, abbreviated ''Orba'') is the term coined by the second Indonesian President Suharto to characterise his administration as he came to power in Transition to the New Order, 1966 until his Fall of Suharto, resignation in 1998. Suharto used this term to contrast his presidency with that of his predecessor Sukarno (retroactively dubbed the "Old Order," or ''Orde Lama''). Immediately following the 30 September Movement, attempted coup in 1965, the political situation was uncertain, Suharto's New Order found much popular support from groups wanting a separation from Indonesia's problems since its independence. The 'generation of 66' (''Angkatan 66'') epitomised talk of a new group of young leaders and new intellectual thought. Following Indonesia's communal and political conflicts, and its economic collapse and social breakdown of the late 1950s through to the mid-1960s, the "New Order" was committed to achieving and maintaining political order, econom ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |