|
Indonesian Government
The term Government of the Republic of Indonesia (, GOI, sometimes also referred to as Government of Indonesia or the Central Government () especially in laws) can have a number of different meanings. At its widest, it can refer collectively to the three traditional branches of government – the executive branch, legislative branch and judicial branch. The term is also used colloquially to mean the executive and legislature together, as these are the branches of government responsible for day-to-day governance of the nation and lawmaking. At its narrowest, the term is used to refer to the executive branch in the form of the President of Indonesia, as assisted by the Vice President and the Cabinet, as this is the branch of government responsible for day-to-day governance. History Liberal democracy phase An era of Liberal Democracy () in Indonesia began on August 17, 1950, following the dissolution of the federal United States of Indonesia less than a year after its for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
National Emblem Of Indonesia Garuda Pancasila
National may refer to: Common uses * Nation or country ** Nationality – a ''national'' is a person who is subject to a nation, regardless of whether the person has full rights as a citizen Places in the United States * National, Maryland, census-designated place * National, Nevada, ghost town * National, Utah, ghost town * National, West Virginia, unincorporated community Commerce * National (brand), a brand name of electronic goods from Panasonic * National Benzole (or simply known as National), former petrol station chain in the UK, merged with BP * National Book Store, a bookstore and office supplies chain in the Philippines * National Car Rental, an American rental car company * National Energy Systems, a former name of Eco Marine Power * National Entertainment Commission, a former name of the Media Rating Council * National Motor Vehicle Company, Indianapolis, Indiana, USA 1900–1924 * National Radio Company, Malden, Massachusetts, USA 1914–1991 * National Supermarke ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Legislative Branch
A legislature (, ) is a deliberative assembly with the authority, legal authority to make laws for a Polity, political entity such as a Sovereign state, country, nation or city on behalf of the people therein. They are often contrasted with the Executive (government), executive and Judiciary, judicial powers of government. Legislatures can exist at different levels of government–national, state/provincial/regional, local, even supranational (such as the European Parliament). Countries differ as to what extent they grant deliberative assemblies at the subnational law-making power, as opposed to purely administrative responsibilities. Laws enacted by legislatures are usually known as Primary and secondary legislation, primary legislation. In addition, legislatures may observe and steer governing actions, with authority to amend the budget involved. The members of a legislature are called legislators. In a democracy, legislators are most commonly popularly Election, elected, al ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dhalang
The dhalang or dalang (; ) is the puppeteer in an Indonesian performance. In a performance of , the dalang sits behind a screen () made of white cotton stretched on a wooden frame. Above his head, hanging from beams attached to the top of the screen is the lamp (), which projects the shadows onto the screen. In front of the dhalang is a stage (), traditionally made from the trunk of a banana tree, into which the sharpened control rods of the puppets can be pushed to keep them in position during the performance. To his left is the puppet chest (), and to his right is the puppet chest's lid, on which the puppets sit ready for use. In addition to moving the puppets and speaking their lines, the dalang is also responsible for giving cues to the gamelan. This is done principally by playing the kepyak, a metal plate or set of plates played with his foot, or by rapping on the puppet chest () with a wooden mallet held in the left hand. The art of puppetry () was traditionally hande ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Suharto
Suharto (8 June 1921 – 27 January 2008) was an Indonesian Officer (armed forces), military officer and politician, and dictator, who was the second and longest serving president of Indonesia, serving from 1967 to 1998. His 32 years rule, characterised as authoritarian and kleptocratic, was marked by widespread corruption, political repression, and human rights abuses. Suharto's regime Fall of Suharto, ultimately collapsed in 1998 amid May 1998 riots of Indonesia, mass protests, violent unrest, and the fallout of the 1997 Asian financial crisis, leading to his resignation. Suharto was born in Kemusuk, near the city of Yogyakarta, during the Dutch East Indies, Dutch colonial era. He grew up in humble circumstances. His Javanese people, Javanese Muslim parents divorced not long after his birth, and he lived with foster parents for much of his childhood. During the Japanese occupation of the Dutch East Indies, Japanese occupation, Suharto served in the Japanese-organized Indones ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
History Of Indonesia
The history of Indonesia has been shaped by its geographic position, natural resources, a series of human migrations and contacts, wars and conquests, as well as by trade, economics and politics. Indonesia is an archipelagic country of 17,000 to 18,000 islands stretching along the equator in Southeast Asia and Oceania. The country's strategic sea-lane position fostered inter-island and international trade; trade has since fundamentally shaped Indonesian history. The area of Indonesia is populated by peoples of various migrations, creating a diversity of cultures, ethnicities, and languages. The archipelago's landforms and climate significantly influenced agriculture and trade, and the formation of states. The boundaries of the state of Indonesia match the 20th-century borders of the Dutch East Indies. Fossilised remains of ''Homo erectus'', popularly known as " Java Man", and their tools suggest the Indonesian archipelago was inhabited at least 1.5 million years ago. Austron ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sukarno
Sukarno (6 June 1901 – 21 June 1970) was an Indonesian statesman, orator, revolutionary, and nationalist who was the first president of Indonesia, serving from 1945 to 1967. Sukarno was the leader of the Indonesian struggle for independence from the Dutch East Indies, Dutch colonialists. He was a prominent leader of Indonesian National Party, Indonesia's nationalist movement during the colonial period and spent over a decade under Dutch detention until released by the Dutch East Indies campaign, invading Empire of Japan, Japanese forces in World War II. Sukarno and his fellow nationalists Collaboration with Imperial Japan#Dutch East Indies (Indonesia), collaborated to garner support for the Japanese war effort from the population, in exchange for Japanese aid in spreading nationalist ideas. Upon Surrender of Japan, Japanese surrender, Sukarno and Mohammad Hatta Proclamation of Indonesian Independence, declared Indonesian independence on 17 August 1945, and Sukarno was appoin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
New Order (Indonesia)
The New Order (, abbreviated ''Orba'') describes the regime of the second Indonesian President Suharto from his rise to power in 1966 until his resignation in 1998. Suharto coined the term upon his accession and used it to contrast his presidency with that of his predecessor Sukarno (retroactively dubbed the "Old Order" or ). Immediately following the attempted coup in 1965, the political situation was uncertain, and Suharto's New Order found much popular support from groups wanting a separation from Indonesia's problems since its independence. The 'generation of 66' ('' Angkatan 66'') epitomised talk of a new group of young leaders and new intellectual thought. Following Indonesia's communal and political conflicts, and its economic collapse and social breakdown of the late 1950s through to the mid-1960s, the "New Order" was committed to achieving and maintaining political order, economic development, and the removal of mass participation in the political process. The featu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
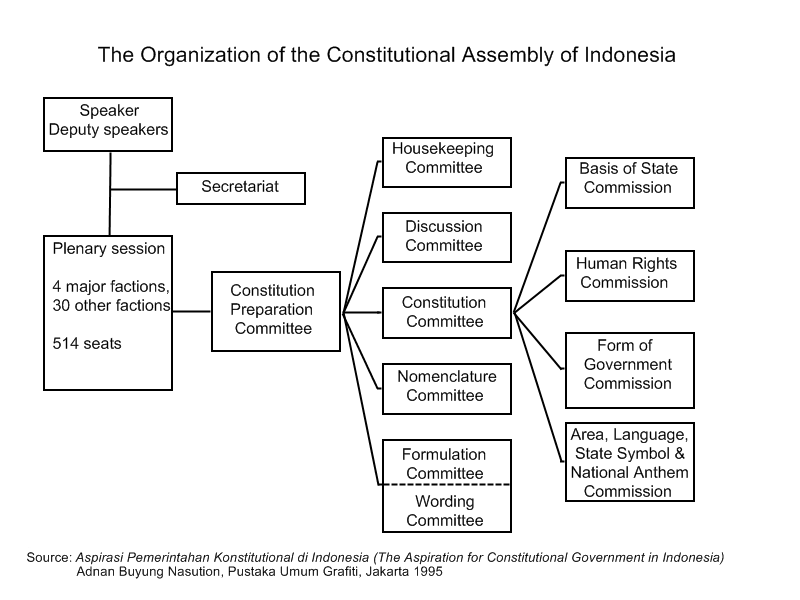
Constitutional Assembly Of Indonesia
The Constitutional Assembly () was a body elected in 1955 to draw up a permanent constitution for the Republic of Indonesia. It sat between 10 November 1956 and 2 July 1959. It was dissolved by then President Sukarno in a decree issued on 5 July 1959 which reimposed the 1945 Constitution. Background On 17 August 1945, Sukarno proclaimed the independence of the Republic of Indonesia. The next day, a meeting of the Preparatory Committee for Indonesian Independence chaired by President Sukarno officially adopted the Constitution of Indonesia, which had been drawn up by the Investigating Committee for Preparatory Work for Independence in the months leading up to the Japanese surrender. In a speech, Sukarno stated that the constitution was "a temporary constitution... a lightning constitution", and that a more permanent version would be drawn up when circumstances permitted. It was not until 1949 that the Netherlands formally transferred sovereignty to Indonesia, and the Unit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bandung Conference
The first large-scale Asian–African or Afro–Asian Conference (), also known as the Bandung Conference, was a meeting of Asian and African states, most of which were newly independent, which took place on 18–24 April 1955 in Bandung, West Java, Indonesia. The twenty-nine countries that participated represented a total population of 1.5 billion people, 54% of the world's population. The conference was organized by Indonesia, Burma (Myanmar), India, Ceylon (Sri Lanka), and Pakistan and was coordinated by Ruslan Abdulgani, secretary general of the Ministry of Foreign Affairs of the Republic of Indonesia. The conference's stated aims were to promote Afro-Asian economic and cultural cooperation and to oppose colonialism or neocolonialism by any nation. The conference was a step towards the eventual creation of the Non-Aligned Movement (NAM) yet the two initiatives ran in parallel during the 1960s, even coming in confrontation with one another prior to the 2nd Cairo NAM C ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Guided Democracy In Indonesia
Guided Democracy (), also called the Old Order (), was the political system in place in Indonesia from 1959 until the New Order began in 1966. This period followed the dissolution of the liberal democracy period in Indonesia by President Sukarno, who centralized control in the name of political stability. He claimed to have based the system on the traditional village system of discussion and consensus, which occurred under the guidance of village elders. On the national level, however, this meant centralized rule under Sukarno: martial law, a massive reduction in civil liberties and democratic norms, and the Republic of Indonesia Armed Forces (in particular the Indonesian Army) and Communist Party of Indonesia acting as major power blocs. Sukarno proposed a threefold blend of nationalism, religion, and communism into a co-operative or governmental concept. This was intended to satisfy the four main factions in Indonesian politics—the army, the secular nationalists, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
President Sukarno's 1959 Decree
The Presidential Decree of 5 July 1959 (legally the Decree of the President of the Republic of Indonesia Number 150 of 1959 on the Return to the Constitution of 1945, ) was issued by President Sukarno Sukarno (6 June 1901 – 21 June 1970) was an Indonesian statesman, orator, revolutionary, and nationalist who was the first president of Indonesia, serving from 1945 to 1967. Sukarno was the leader of the Indonesian struggle for independenc ... in the face of the inability of the Constitutional Assembly of Indonesia to achieve the two-thirds majority to reimpose the 1945 Constitution. It was army chief of staff Abdul Haris Nasution who concluded that this would be the only way to bring about the reintroduction of a constitution that paved the way for the military to play a greater role in the running of the state, ushering in the period known as the " guided democracy" (1959–1966). The Decree The decree, which was read by Sukarno at the Merdeka Palace reads as follows ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Martial Law
Martial law is the replacement of civilian government by military rule and the suspension of civilian legal processes for military powers. Martial law can continue for a specified amount of time, or indefinitely, and standard civil liberties may be suspended for as long as martial law continues. Most often, martial law is declared in times of war or emergencies such as civil unrest and natural disasters. Alternatively, martial law may be declared in instances of Coup d'état, military coups d'état. Overview Despite the fact that it has been declared frequently throughout history, martial law is still often described as largely elusive as a legal entity. References to martial law date back to 1628 England, when Matthew Hale (jurist), Sir Matthew Hale described martial law as, "no Law, but something indulged rather than allowed as a Law." Despite being centuries old, this quote remains true in many countries around the world today. Most often, the implementation of martial l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |