|
Inda Sillasie
Inda Sillasie is a ''tabia'' or municipality in the Dogu'a Tembien district of the Tigray Region of Ethiopia. The ''tabia'' centre is in Migichi village, located approximately 13 km to the south-southeast of the ''woreda'' town Hagere Selam. Geography The ''tabia'' stretches down from the foot of the Tsatsen ridge to Giba River, over a long ledge between the Inda Sillasie and Gra Agiam/Bitchoqo rivers. The highest peak is a hill at May Ch’elaqo (2330 m a.s.l.) and the lowest place is the confluence between Giba and Bitchoqo rivers (1440 m a.s.l.). Geology From the higher to the lower locations, the following geological formations are present: * Antalo Limestone * Adigrat Sandstone * Quaternary alluvium and freshwater tufa Geomorphology and soils The main geomorphic unit, with corresponding soil types is the gently rolling Antalo Limestone plateau, holding cliffs and valley bottoms. * Associated soil types ** shallow stony soils with a dark surface horizo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ethiopia
Ethiopia, , om, Itiyoophiyaa, so, Itoobiya, ti, ኢትዮጵያ, Ítiyop'iya, aa, Itiyoppiya officially the Federal Democratic Republic of Ethiopia, is a landlocked country in the Horn of Africa. It shares borders with Eritrea to the Eritrea–Ethiopia border, north, Djibouti to the Djibouti–Ethiopia border, northeast, Somalia to the Ethiopia–Somalia border, east and northeast, Kenya to the Ethiopia–Kenya border, south, South Sudan to the Ethiopia–South Sudan border, west, and Sudan to the Ethiopia–Sudan border, northwest. Ethiopia has a total area of . As of 2022, it is home to around 113.5 million inhabitants, making it the List of countries and dependencies by population, 13th-most populous country in the world and the List of African countries by population, 2nd-most populous in Africa after Nigeria. The national capital and largest city, Addis Ababa, lies several kilometres west of the East African Rift that splits the country into the African Plate, Africa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Waterlogging (agriculture)
Waterlogging water is the saturation of soil with water. Soil may be regarded as waterlogged when it is nearly saturated with water much of the time such that its air phase is restricted and anaerobic conditions prevail. In extreme cases of prolonged waterlogging, anaerobiosis occurs, the roots of mesophytes suffer, and the subsurface reducing atmosphere leads to such processes as denitrification, methanogenesis, and the reduction of iron and manganese oxides. All plants, including crops require air (specifically, oxygen) to respire, produce energy and keep their cells alive. In agriculture, waterlogging of the soil typically blocks air from getting in to the roots. With the exception of rice (''Oryza sativa''), most crops like maize and potato, are therefore highly intolerant to waterlogging. Plant cells use a variety of signals such the oxygen concentration, plant hormones like ethylene, energy and sugar status to acclimate to waterlogging-induced oxygen deprivation. In ir ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flash Flood
A flash flood is a rapid flooding of low-lying areas: washes, rivers, dry lakes and depressions. It may be caused by heavy rain associated with a severe thunderstorm, hurricane, or tropical storm, or by meltwater from ice or snow flowing over ice sheets or snowfields. Flash floods may also occur after the collapse of a natural ice or debris dam, or a human structure such as a man-made dam, as occurred before the Johnstown Flood of 1889. Flash floods are distinguished from regular floods by having a timescale of fewer than six hours between rainfall and the onset of flooding. Flash floods are a significant hazard, causing more fatalities in the U.S. in an average year than lightning, tornadoes, or hurricanes. Flash floods can also deposit large quantities of sediments on floodplains and can be destructive of vegetation cover not adapted to frequent flood conditions. Causes Flash floods most often occur in dry areas that have recently received precipitation, but th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mika'el Abiy
Mika’el Abiy is a ''tabia'' or municipality in the Dogu’a Tembien district of the Tigray Region of Ethiopia. The ''tabia'' centre is in Megesta village, located approximately 7 km to the southeast of the ''woreda'' town Hagere Selam. Geography The ''tabia'' stretches down south of the main road towards Rubaksa, which is a wider area with several springs and traditional irrigation. The highest peak is Gumawta (2815 m a.s.l.) on the Tsatsen plateau and the lowest place Rubaksa (1920 m a.s.l.). Geology and soils Geological formations From the higher to the lower locations, the following geological formations are present: * Upper basalt * Interbedded lacustrine deposits * Lower basalt * Amba Aradam Formation * Antalo Limestone * Quaternary alluvium and freshwater tufa Soilscape The main geomorphic units, with corresponding soil types are: * Hagere Selam Highlands, along the basalt and sandstone ridge ** Associated soil types *** shallow soils with high s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ayninbirkekin
Ayninbirkekin is a ''tabia'' or municipality in the Dogu'a Tembien district of the Tigray Region of Ethiopia. Literal meaning of Ayninbirkekin in Tigrinya is "We will not bend". The ''tabia'' centre is in Halah village, located approximately 8 km to the east of the ''woreda'' town Hagere Selam. Main town is Ala'isa, situated on the ridge overseeing the Giba valley. Geography The ''tabia'' is located astride a main water divide (that is followed by the main road) and stretches down towards May Zegzeg river at the south and upper Tsaliet River at the north. Three highest places (at around 2600 m a.s.l.) are Meri’a Ziban in the west, Imba Ra’isot in the centre and the escarpment to Arebay at the north. The lowest places are the confluence of May Zegzeg and May Be’ati Rivers (1970 m a.s.l.) in the south and in the north May Leiba River near Iyesus church (2240 m a.s.l.). Geology From the higher to the lower locations, the following geological form ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
May Zegzeg
May Zegzeg is a river of the Nile basin. Rising in the mountains of Dogu’a Tembien in northern Ethiopia, it flows southward to empty finally in Giba and Tekezé River. Characteristics It is a confined river, locally meandering in its narrow alluvial plain, with an average slope gradient of 43 metres per kilometre. With its tributaries May Sho'ate and May Harena, the river has cut a gorge. Jointly with adjacent May Be’ati River, this river is the source of Rubaksa River. Flash floods and flood buffering Runoff mostly happens in the form of high runoff discharge events that occur in a very short period (called flash floods). These are related to the steep topography, often little vegetation cover and intense convective rainfall. The peaks of such flash floods have often a 50 to 100 times larger discharge than the preceding baseflow. The magnitude of floods in this river has however been decreased due to interventions in the catchment. At Habdi Luqmuts and on other stee ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amanit
Amanit is a ''tabia'' or municipality in the Dogu'a Tembien district of the Tigray Region of Ethiopia. The ''tabia'' centre is Addi Qeshofo village, located approximately 15 km to the southeast of the ''woreda'' town Hagere Selam (as the crow flies). Geography The ''tabia'' stretches down southbound over an elongated ridge between Inda Sillasie River and Addi Keshofo River towards Giba River. The highest place is a hill east of Gudeli (2230 m a.s.l.) and the lowest place at the junction of Inda Sillasie and Giba Rivers (1448 m a.s.l.). Geology The two main geological formations are Antalo Limestone in most of the ''tabia'', and Adigrat Sandstone on the slopes towards the river gorges. Quaternary alluvium and freshwater tufa occur in the valley bottoms. Geomorphology and soils The main geomorphic units, with corresponding soil types are: * Gently rolling Antalo Limestone plateau, holding cliffs and valley bottoms on limestone ** Associated soil types *** shallow st ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
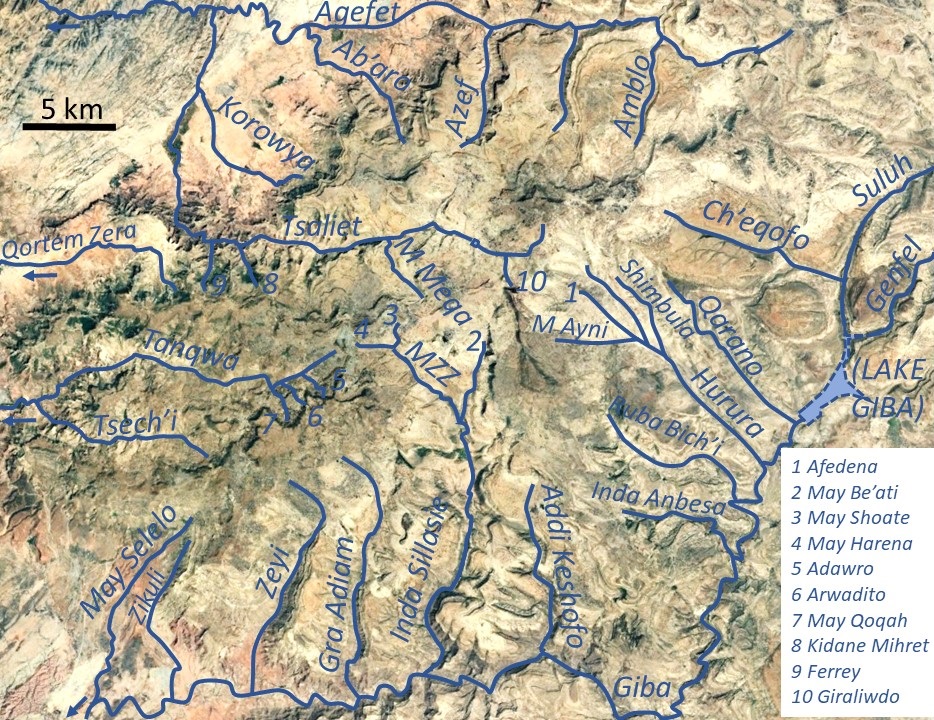
Giba River
Giba is a river of northern Ethiopia. It starts at the confluence of Genfel and Sulluh (which rises in the mountains of Mugulat) (3298 metres above sea level) and flows westward to the Tekezé River. Future Lake Giba will occupy the plain where Sulluh, Genfel and Agula'i Rivers meet, and hence be the future source of Giba River. Hydrography It is a confined river, locally meandering in its narrow alluvial plain, with a slope gradient of 7 metres per kilometre. With its tributaries, the river has cut a deep gorge. Tributaries Main tributaries, from downstream to upstream, are * Tanqwa ** Tsech'i River ** May Qoqah ** Arwadito ** Adawro River * May Selelo * Zikuli River * Gra Adiam River, also called Bitchoqo River * Zeyi River * Inda Sillasie River ** May Zegzeg *** May Harena *** May Sho'ate ** May Be'ati River * Addi Keshofo River * May Gabat * Inda Anbesa * Ruba Bich'i River * Hurura ** Afedena River *** May Ayni ** Shimbula * Ilala River * Qarano ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
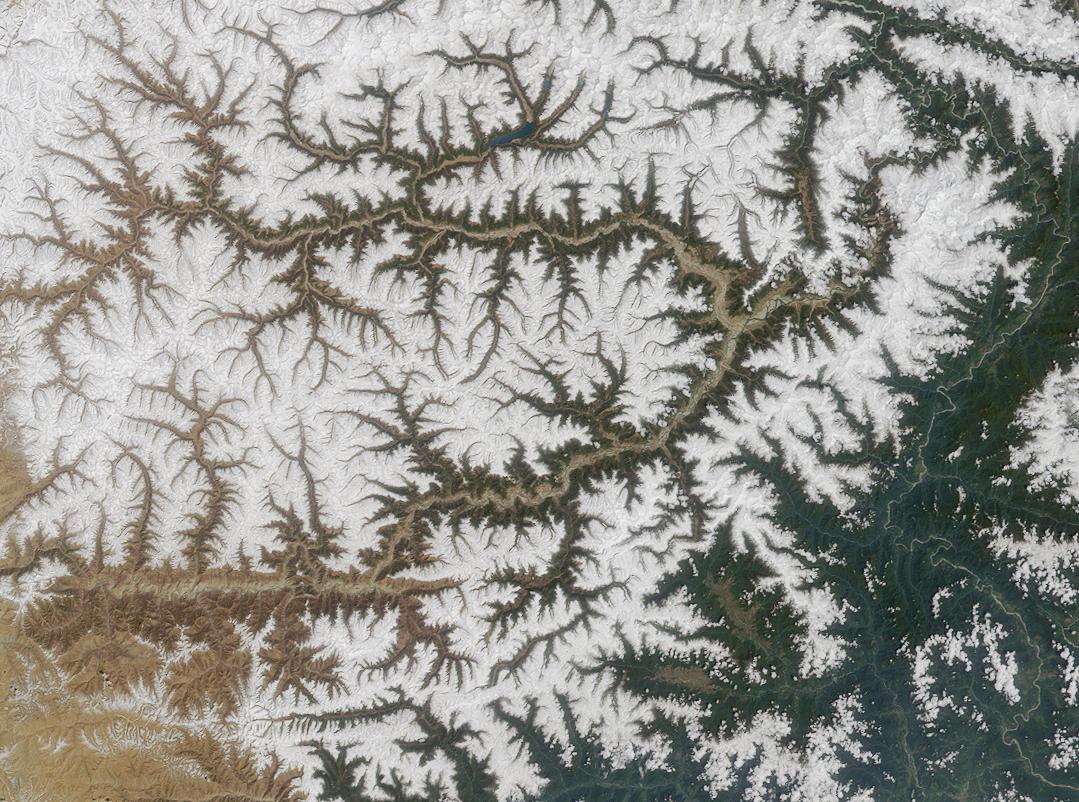
Drainage System (geomorphology)
In geomorphology, drainage systems, also known as river systems, are the patterns formed by the streams, rivers, and lakes in a particular drainage basin. They are governed by the topography of land, whether a particular region is dominated by hard or soft rocks, and the gradient of the land. Geomorphologists and hydrologists often view streams as part of drainage basins (and sub-basins). This is the topographic region from which a stream receives runoff, throughflow, and its saturated equivalent, groundwater flow. The number, size, and shape of the drainage basins varies and the larger and more detailed the topographic map, the more information is available. Drainage patterns Per the lie of channels, drainage systems can fall into one of several categories, known as drainage patterns. These depend on the topography and geology of the land. All forms of transitions can occur between parallel, dendritic, and trellis patterns. Accordant versus discordant drainage patterns ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nile
The Nile, , Bohairic , lg, Kiira , Nobiin language, Nobiin: Áman Dawū is a major north-flowing river in northeastern Africa. It flows into the Mediterranean Sea. The Nile is the longest river in Africa and has historically been considered the List of rivers by length, longest river in the world, though this has been contested by research suggesting that the Amazon River is slightly longer.Amazon Longer Than Nile River, Scientists Say Of the world's major rivers, the Nile is one of the smallest, as measured by annual flow in cubic metres of water. About long, its drainage basin covers eleven countries: the Democratic Republic of the Congo, Tanzania, Burundi, Rwanda, Uganda, Kenya, Ethiopia, Erit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tekezé River
The Tekezé or Täkkäze River ( amh, ተከዜ, ti, ተከዘ; originally meaning "river" in Ge’ez, ), also spelled Takkaze, is a major river of Ethiopia. For part of its course it forms a section of the westernmost border of Ethiopia and Eritrea. The river is also known as the Setit () in Eritrea, western Ethiopia, and eastern Sudan. According to materials published by the Ethiopian Central Statistical Agency, the Tekezé River is long. The canyon which it has created is the deepest in Africa and one of the deepest in the world, at some points having a depth of over 2000 meters (6,562 feet). Course The Tekezé River rises in the central Ethiopian Highlands near Mount Qachen within Lasta, from where it flows west, north, then west again, forming the westernmost border of Ethiopia and Eritrea from the confluence of the Tomsa with the Tekezé at to the tripoint between the two countries and Sudan at . After entering northeastern Sudan at the tripoint it joins the Atbara ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



.jpg)