|
Idun Peak
Idun Peak () is a small peak between Mount Thundergut and Veli Peak in the Asgard Range of Victoria Land, Antarctica. The name, recommended by the Advisory Committee on Antarctic Names in consultation with the New Zealand Antarctic Place-Names Committee, is one in a group of names in the Asgard Range derived from Norse mythology Norse, Nordic, or Scandinavian mythology is the body of myths belonging to the North Germanic peoples, stemming from Old Norse religion and continuing after the Christianization of Scandinavia, and into the Nordic folklore of the modern period ..., Idun ( Iðunn) being a Norse goddess. References Mountains of the Asgard Range McMurdo Dry Valleys {{McMurdoDryValleys-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Summit (topography)
A summit is a point on a surface that is higher in elevation than all points immediately adjacent to it. The topographic terms acme, apex, peak (mountain peak), and zenith are synonymous. The term (mountain top) is generally used only for a mountain peak that is located at some distance from the nearest point of higher elevation. For example, a big, massive rock next to the main summit of a mountain is not considered a summit. Summits near a higher peak, with some prominence or isolation, but not reaching a certain cutoff value for the quantities, are often considered ''subsummits'' (or ''subpeaks'') of the higher peak, and are considered part of the same mountain. A pyramidal peak is an exaggerated form produced by ice erosion of a mountain top. Summit may also refer to the highest point along a line, trail, or route. The highest summit in the world is Mount Everest with a height of above sea level. The first official ascent was made by Tenzing Norgay and Sir Edmund Hill ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mount Thundergut
The Inland Forts () are a line of peaks extending between Northwest Mountain and Saint Pauls Mountain, in the Asgard Range of Victoria Land, Antarctica. Taylor Glacier lies to the south. The peaks were discovered and so named by the British National Antarctic Expedition, 1901–04. Peaks * Mattox Bastion * Sutherland Peak * Wolak Peak The Inland Forts () are a line of peaks extending between Northwest Mountain and Saint Pauls Mountain, in the Asgard Range of Victoria Land, Antarctica. Taylor Glacier lies to the south. The peaks were discovered and so named by the British Nationa ... References Further reading * James G. Bockheim, editorThe Soils of Antarctica p. 133 US Antarctic Program Continuation: Environmental Impact Statement p. 36 * David R. Marchant, George H. Denton, David E. Sugden and Carl C. Swisher, IIIMiocene Glacial Stratigraphy and Landscape Evolution of the Western Asgard Range, Antarctica Asgard Range Mountain ranges of Victoria Land McMurdo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Veli Peak
Mount Odin () is the most prominent peak, though not the highest, in the Asgard Range, of Victoria Land, Antarctica. It rises over just south of Lake Vanda. It was named by the Victoria University of Wellington Antarctic Expedition (VUWAE) (1958–59) for the Norse god Odin. Location Mount Odin lies to the south of Lake Vanda in the Wright Valley. The Odin Valley is to its east, and Obelisk Mountain to its south. Junction Knob is to the southwest. A study of soil microbiology from sites in the Odin valley down to the Onyx River in the Wright Valley, published in 1972, showed that despite the cold and dry conditions, there was active in-situ microbial life in all the soils examined. Features Features in the region around the mountain include Odin Valley, Tiw Valley, Mime Glacier, Siegfried Peak, Siegmund Peak, Heimdall Glacier, Mount Beowulf, Beowulf Glacier,, Mount Valhalla, Valhalla Glacier, Obelisk Mountain, Hind Turret, Junction Knob, Odin Glacier, Alberich Glacier, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
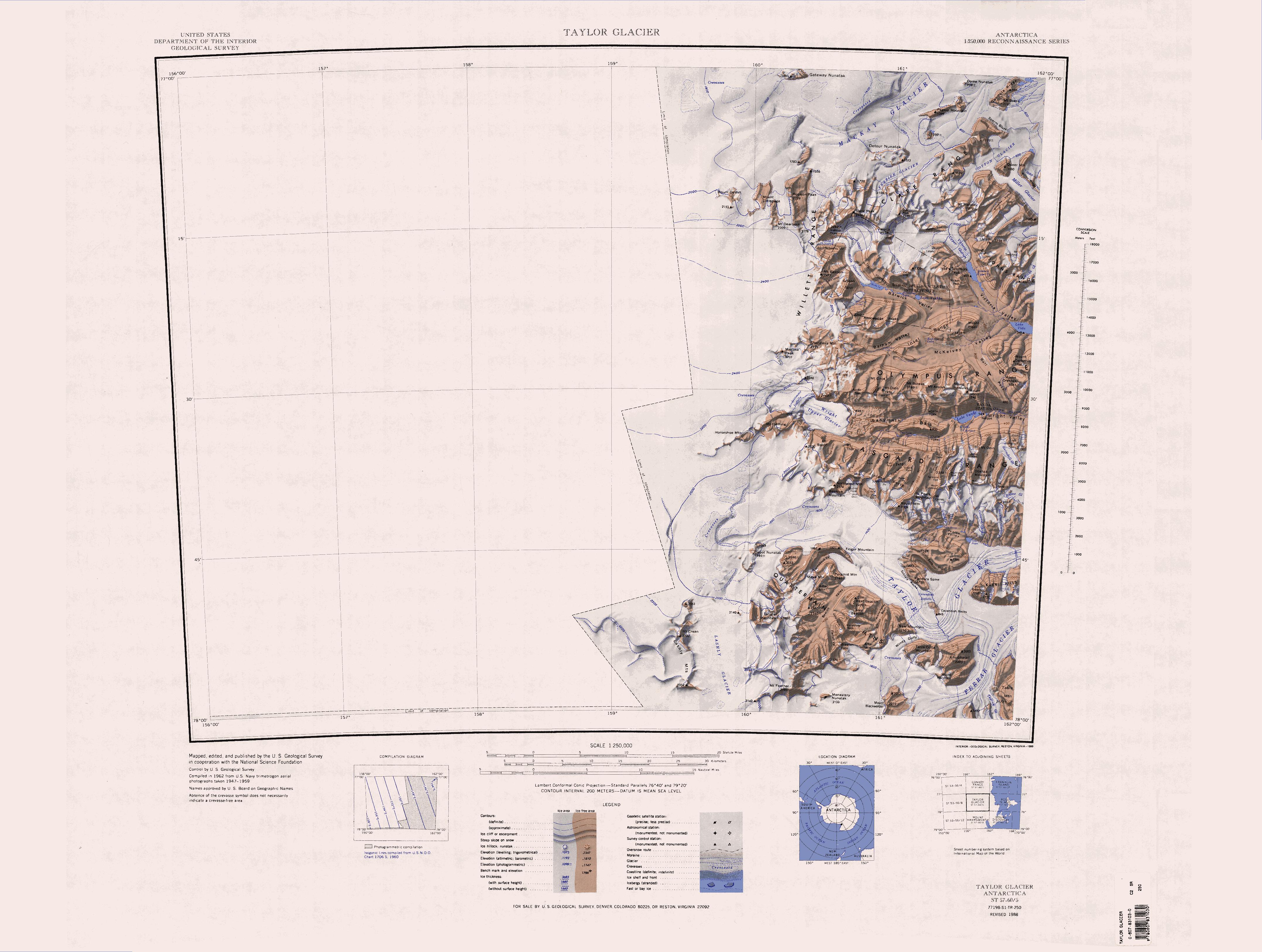
Asgard Range
The Asgard Range is a mountain range in Victoria Land, Antarctica. It divides Wright Valley from Taylor Glacier and Taylor Valley, and was named by the Victoria University of Wellington Antarctic Expedition (1958–59) after Asgard, the home of the Norse gods. Geography The Asgard Range contains numerous named features such as peaks, valleys, and glaciers, and even some sub-ranges. Many are named after Norse gods and mythological figures, in keeping with the name of the range itself. Mountains * Ball Peak * Mount Beowulf * Bromley Peak * Brunhilde Peak * Mount Carnes * Mount Darby * Mount Feola * Mount Freya * Mount Holm-Hansen * Mount Grendal * Mount Hall * Harp Hill * Harris Peak * Hetha Peak * Hind Turret * Hoehn Peak * Hoffman Peak * Idun Peak * Mount Irvine * Mount Jord * Mount Knox * Mount Loke * Lyons Cone * Matterhorn * Mattox Bastion * Mount Newall * Obelisk Mountain * Mount Odin * Oliver Peak * Panorama Peak * Perk Summit * Ponder Peak * Mount S ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Victoria Land
Victoria Land is a region in eastern Antarctica which fronts the western side of the Ross Sea and the Ross Ice Shelf, extending southward from about 70°30'S to 78°00'S, and westward from the Ross Sea to the edge of the Antarctic Plateau. It was discovered by Captain James Clark Ross in January 1841 and named after Queen Victoria. The rocky promontory of Minna Bluff is often regarded as the southernmost point of Victoria Land, and separates the Scott Coast to the north from the Hillary Coast of the Ross Dependency to the south. The region includes ranges of the Transantarctic Mountains and the McMurdo Dry Valleys (the highest point being Mount Abbott in the Northern Foothills), and the flatlands known as the Labyrinth. The Mount Melbourne is an active volcano in Victoria Land. Early explorers of Victoria Land include James Clark Ross and Douglas Mawson. In 1979, scientists discovered a group of 309 meteorites A meteorite is a solid piece of debris from an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Advisory Committee On Antarctic Names
The Advisory Committee on Antarctic Names (ACAN or US-ACAN) is an advisory committee of the United States Board on Geographic Names responsible for recommending commemorative names for features in Antarctica. History The committee was established in 1943 as the Special Committee on Antarctic Names (SCAN). It became the Advisory Committee on Antarctic Names in 1947. Fred G. Alberts was Secretary of the Committee from 1949 to 1980. By 1959, a structured nomenclature was reached, allowing for further exploration, structured mapping of the region and a unique naming system. A 1990 ACAN gazeeter of Antarctica listed 16,000 names. Description The United States does not recognise territorial boundaries within Antarctica, so ACAN assigns names to features anywhere within the continent, in consultation with other national nomenclature bodies where appropriate, as defined by the Antarctic Treaty System. The research and staff support for the ACAN is provided by the United States Geolog ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
New Zealand Antarctic Place-Names Committee
New Zealand Antarctic Place-Names Committee (NZ-APC) is an adjudicating committee established to authorize the naming of features in the Ross Dependency on the Antarctic continent. It is composed of the members of the New Zealand Geographic Board plus selected specialists on Antarctica. This committee works in collaboration with similar place-naming authorities in Australia, Great Britain and the United States to reach concurrence on each decision. The NZ-APC committee was established in 1956. Names attributed by the committee * Alberich Glacier, named after Alberich, king of the elves and chief of the Nibelungen * Arena Saddle, named in conjunction with Arena Valley * Brawhm Pass, named after the six party members of the University of New South Wales expeditions of 1964–65 and 1966–67 * Caliper Cove, named for descriptive features * Canada Stream, named in conjunction with Canada Glacier * Cape Crossfire, named for descriptive features * Cuneiform Cliffs, named for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Norse Mythology
Norse, Nordic, or Scandinavian mythology is the body of myths belonging to the North Germanic peoples, stemming from Old Norse religion and continuing after the Christianization of Scandinavia, and into the Nordic folklore of the modern period. The northernmost extension of Germanic mythology and stemming from Proto-Germanic folklore, Norse mythology consists of tales of various deities, beings, and heroes derived from numerous sources from both before and after the pagan period, including medieval manuscripts, archaeological representations, and folk tradition. The source texts mention numerous gods such as the thunder-god Thor, the raven-flanked god Odin, the goddess Freyja, and numerous other deities. Most of the surviving mythology centers on the plights of the gods and their interaction with several other beings, such as humanity and the jötnar, beings who may be friends, lovers, foes, or family members of the gods. The cosmos in Norse mythology consists of Nine ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Iðunn
In Norse mythology, Iðunn is a goddess associated with apples and youth. Iðunn is attested in the ''Poetic Edda'', compiled in the 13th century from earlier traditional sources, and the ''Prose Edda'', written in the 13th century by Snorri Sturluson. In both sources, she is described as the wife of the skaldic god Bragi, and in the ''Prose Edda'', also as a keeper of apples and granter of eternal youthfulness. The ''Prose Edda'' relates how Loki was once forced by the jötunn Þjazi to lure Iðunn out of Asgard and into a wood with the promise of apples even fairer than her own. Þjazi, in the form of an eagle, abducts Iðunn from the wood, bearing her off to his home. Iðunn's absence causes the gods to grow old and grey, and they realize that Loki is responsible for her disappearance. Under duress, Loki promises to bring her back and, setting out in the form of a falcon, eventually finds her alone at Þjazi's home. He turns her into a nut and flies back toward Asgard. W ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mountains Of The Asgard Range
A mountain is an elevated portion of the Earth's crust, generally with steep sides that show significant exposed bedrock. Although definitions vary, a mountain may differ from a plateau in having a limited summit area, and is usually higher than a hill, typically rising at least 300 metres (1,000 feet) above the surrounding land. A few mountains are isolated summits, but most occur in mountain ranges. Mountains are formed through tectonic forces, erosion, or volcanism, which act on time scales of up to tens of millions of years. Once mountain building ceases, mountains are slowly leveled through the action of weathering, through slumping and other forms of mass wasting, as well as through erosion by rivers and glaciers. High elevations on mountains produce colder climates than at sea level at similar latitude. These colder climates strongly affect the ecosystems of mountains: different elevations have different plants and animals. Because of the less hospitable terrain and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



_by_H._W._Bissen_-_angle.jpg)
