|
Ideal Solution
An ideal solution or ideal mixture is a solution that exhibits thermodynamic properties analogous to those of a mixture of ideal gases. The enthalpy of mixing is zero as is the volume change on mixing. The vapor pressures of all components obey Raoult's law across the entire range of concentrations, and the activity coefficient (which measures deviation from ideality) is equal to one for each component. The concept of an ideal solution is fundamental to both thermodynamics and chemical thermodynamics and their applications, such as the explanation of colligative properties. Physical origin Ideality of solutions is analogous to ideality for gases, with the important difference that intermolecular interactions in liquids are strong and cannot simply be neglected as they can for ideal gases. Instead we assume that the mean strength of the interactions are the same between all the molecules of the solution. More formally, for a mix of molecules of A and B, then the interacti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Solution (chemistry)
In chemistry, a solution is defined by IUPAC as "A liquid or solid phase containing more than one substance, when for convenience one (or more) substance, which is called the solvent, is treated differently from the other substances, which are called solutes. When, as is often but not necessarily the case, the sum of the mole fractions of solutes is small compared with unity, the solution is called a dilute solution. A superscript attached to the ∞ symbol for a property of a solution denotes the property in the limit of infinite dilution." One important parameter of a solution is the concentration, which is a measure of the amount of solute in a given amount of solution or solvent. The term " aqueous solution" is used when one of the solvents is water. Types ''Homogeneous'' means that the components of the mixture form a single phase. ''Heterogeneous'' means that the components of the mixture are of different phase. The properties of the mixture (such as concentration, temp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Activity (chemistry)
In thermodynamics, activity (symbol ) is a measure of the "effective concentration" of a species in a mixture, in the sense that the species' chemical potential depends on the activity of a real solution in the same way that it would depend on concentration for an ideal solution. The term "activity" in this sense was coined by the American chemist Gilbert N. Lewis in 1907. By convention, activity is treated as a dimensionless quantity, although its value depends on customary choices of standard state for the species. The activity of pure substances in condensed phases (solids and liquids) is taken as = 1. Activity depends on temperature, pressure and composition of the mixture, among other things. For gases, the activity is the effective partial pressure, and is usually referred to as fugacity. The difference between activity and other measures of concentration arises because the interactions between different types of molecules in non-ideal gases or solutions are differen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Regular Solution
In chemistry, a regular solution is a solution whose entropy of mixing is equal to that of an ideal solution with the same composition, but is non-ideal due to a nonzero enthalpy of mixing.P. Atkins and J. de Paula, ''Atkins' Physical Chemistry'' (8th ed. W.H. Freeman 2006) p.149P.A. Rock, ''Chemical Thermodynamics. Principles and Applications'' (Macmillan 1969) p.263 Such a solution is formed by random mixing of components of similar molar volume and without strong specific interactions, and its behavior diverges from that of an ideal solution by showing phase separation at intermediate compositions and temperatures (a miscibility gap). Its entropy of mixing is equal to that of an ideal solution with the same composition, due to random mixing without strong specific interactions. For two components :\Delta S_ = -nR(x_1\ln x_1 + x_2\ln x_2)\, where R\, is the gas constant, n\, the total number of mole (unit), moles, and x_i\, the mole fraction of each component. Only the enthalpy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Entropy Of Mixing
In thermodynamics, the entropy of mixing is the increase in the total entropy when several initially separate systems of different composition, each in a thermodynamic state of internal equilibrium, are mixed without chemical reaction by the thermodynamic operation of removal of impermeable partition(s) between them, followed by a time for establishment of a new thermodynamic state of internal equilibrium in the new unpartitioned closed system. In general, the mixing may be constrained to occur under various prescribed conditions. In the customarily prescribed conditions, the materials are each initially at a common temperature and pressure, and the new system may change its volume, while being maintained at that same constant temperature, pressure, and chemical component masses. The volume available for each material to explore is increased, from that of its initially separate compartment, to the total common final volume. The final volume need not be the sum of the initially se ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Activity Coefficient
In thermodynamics, an activity coefficient is a factor used to account for deviation of a mixture of chemical substances from ideal behaviour. In an ideal mixture, the microscopic interactions between each pair of chemical species are the same (or macroscopically equivalent, the enthalpy change of solution and volume variation in mixing is zero) and, as a result, properties of the mixtures can be expressed directly in terms of simple concentrations or partial pressures of the substances present e.g. Raoult's law. Deviations from ideality are accommodated by modifying the concentration by an ''activity coefficient''. Analogously, expressions involving gases can be adjusted for non-ideality by scaling partial pressures by a fugacity coefficient. The concept of activity coefficient is closely linked to that of activity in chemistry. Thermodynamic definition The chemical potential, \mu_\mathrm, of a substance B in an ideal mixture of liquids or an ideal solution is given ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thermodynamic Activity
In thermodynamics, activity (symbol ) is a measure of the "effective concentration" of a species in a mixture, in the sense that the species' chemical potential depends on the activity of a real solution in the same way that it would depend on concentration for an ideal solution. The term "activity" in this sense was coined by the American chemist Gilbert N. Lewis in 1907. By convention, activity is treated as a dimensionless quantity, although its value depends on customary choices of standard state for the species. The activity of pure substances in condensed phases (solids and liquids) is taken as = 1. Activity depends on temperature, pressure and composition of the mixture, among other things. For gases, the activity is the effective partial pressure, and is usually referred to as fugacity. The difference between activity and other measures of concentration arises because the interactions between different types of molecules in non-ideal gases or solutions are different ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Solubility
In chemistry, solubility is the ability of a chemical substance, substance, the solute, to form a solution (chemistry), solution with another substance, the solvent. Insolubility is the opposite property, the inability of the solute to form such a solution. The extent of the solubility of a substance in a specific solvent is generally measured as the concentration of the solute in a wikt:saturated#Chemistry, saturated solution, one in which no more solute can be dissolved. At this point, the two substances are said to be at the solubility equilibrium. For some solutes and solvents, there may be no such limit, in which case the two substances are said to be "miscibility, miscible in all proportions" (or just "miscible"). The solute can be a solid, a liquid, or a gas, while the solvent is usually solid or liquid. Both may be pure substances, or may themselves be solutions. Gases are always miscible in all proportions, except in very extreme situations,J. de Swaan Arons and G. A. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Regular Solution
In chemistry, a regular solution is a solution whose entropy of mixing is equal to that of an ideal solution with the same composition, but is non-ideal due to a nonzero enthalpy of mixing.P. Atkins and J. de Paula, ''Atkins' Physical Chemistry'' (8th ed. W.H. Freeman 2006) p.149P.A. Rock, ''Chemical Thermodynamics. Principles and Applications'' (Macmillan 1969) p.263 Such a solution is formed by random mixing of components of similar molar volume and without strong specific interactions, and its behavior diverges from that of an ideal solution by showing phase separation at intermediate compositions and temperatures (a miscibility gap). Its entropy of mixing is equal to that of an ideal solution with the same composition, due to random mixing without strong specific interactions. For two components :\Delta S_ = -nR(x_1\ln x_1 + x_2\ln x_2)\, where R\, is the gas constant, n\, the total number of mole (unit), moles, and x_i\, the mole fraction of each component. Only the enthalpy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Margules Function
The Margules activity model is a simple thermodynamic model for the excess Gibbs free energy of a liquid mixture introduced in 1895 by Max Margules. After Lewis had introduced the concept of the activity coefficient, the model could be used to derive an expression for the activity coefficients \gamma_i of a compound i in a liquid, a measure for the deviation from ideal solubility, also known as Raoult's law Raoult's law ( law) is a relation of physical chemistry, with implications in thermodynamics. Proposed by French chemist François-Marie Raoult in 1887, it states that the partial pressure of each component of an ideal mixture of ''liquids'' is .... In 1900, Jan Zawidzki proved the model via determining the composition of binary mixtures condensed at different temperatures by their refractive indices. In chemical engineering the Margules Gibbs free energy model for liquid mixtures is better known as the Margules activity or activity coefficient model. Although the model ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
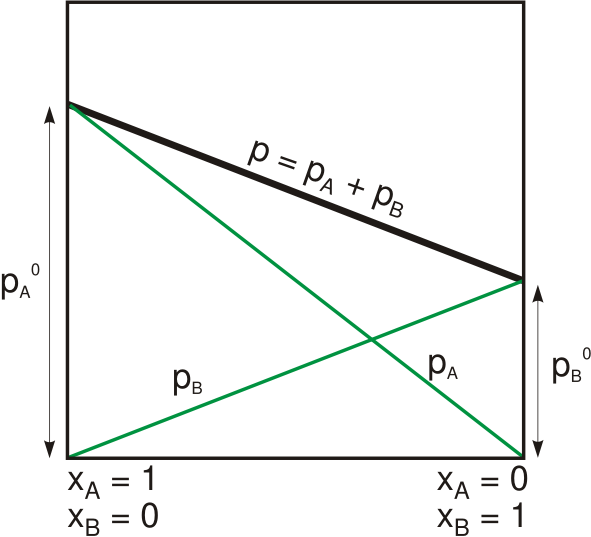
Raoult's Law
Raoult's law ( law) is a relation of physical chemistry, with implications in thermodynamics. Proposed by French chemist François-Marie Raoult in 1887, it states that the partial pressure of each component of an ideal mixture of ''liquids'' is equal to the vapor pressure of the pure component (liquid or solid) multiplied by its mole fraction in the mixture. In consequence, the relative lowering of vapor pressure of a dilute solution of nonvolatile solute is equal to the mole fraction of solute in the solution. Mathematically, Raoult's law for a single component in an ideal solution is stated as : p_i = p_i^\star x_i where p_i is the partial pressure of the component i in the gaseous mixture above the solution, p_i^\star is the equilibrium vapor pressure of the pure component i, and x_i is the mole fraction of the component i in the liquid or solid solution. Where two volatile liquids A and B are mixed with each other to form a solution, the vapor phase consists of both compo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gibbs Free Energy
In thermodynamics, the Gibbs free energy (or Gibbs energy as the recommended name; symbol is a thermodynamic potential that can be used to calculate the maximum amount of Work (thermodynamics), work, other than Work (thermodynamics)#Pressure–volume work, pressure–volume work, that may be performed by a closed system, thermodynamically closed system at constant temperature and pressure. It also provides a necessary condition for processes such as chemical reactions that may occur under these conditions. The Gibbs free energy is expressed as G(p,T) = U + pV - TS = H - TS where: * U is the internal energy of the system * H is the enthalpy of the system * S is the entropy of the system * T is the temperature of the system * V is the volume of the system * p is the pressure of the system (which must be equal to that of the surroundings for mechanical equilibrium). The Gibbs free energy change (, measured in joules in International System of Units, SI) is the ''maximum'' amount of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Entropy Of Mixing
In thermodynamics, the entropy of mixing is the increase in the total entropy when several initially separate systems of different composition, each in a thermodynamic state of internal equilibrium, are mixed without chemical reaction by the thermodynamic operation of removal of impermeable partition(s) between them, followed by a time for establishment of a new thermodynamic state of internal equilibrium in the new unpartitioned closed system. In general, the mixing may be constrained to occur under various prescribed conditions. In the customarily prescribed conditions, the materials are each initially at a common temperature and pressure, and the new system may change its volume, while being maintained at that same constant temperature, pressure, and chemical component masses. The volume available for each material to explore is increased, from that of its initially separate compartment, to the total common final volume. The final volume need not be the sum of the initially se ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |