|
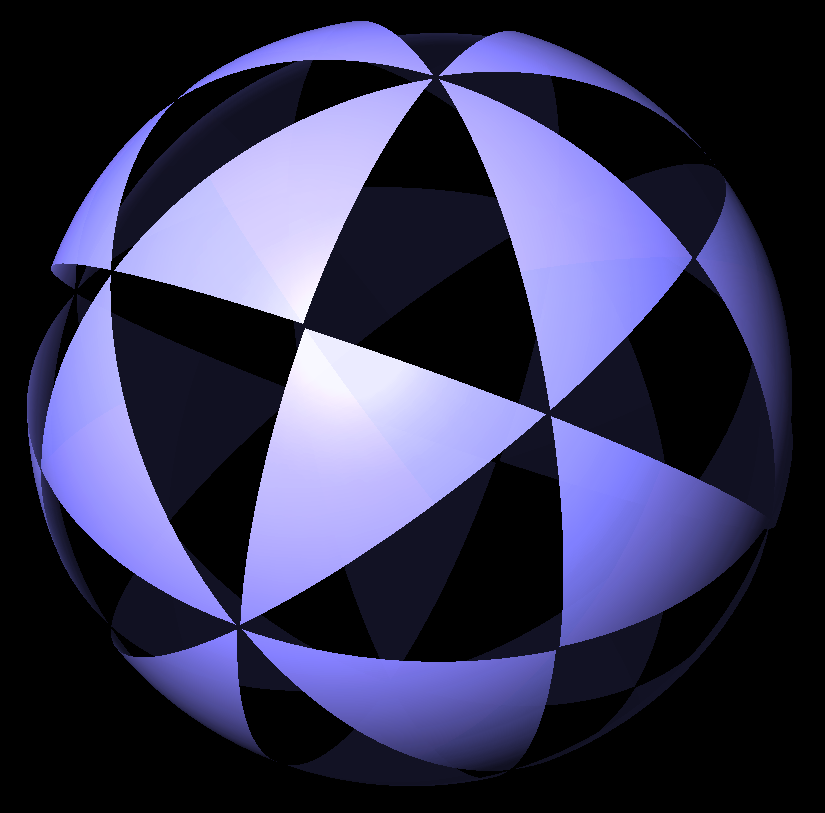
Icosahedral Symmetry
In mathematics, and especially in geometry, an object has icosahedral symmetry if it has the same symmetries as a regular icosahedron. Examples of other polyhedra with icosahedral symmetry include the regular dodecahedron (the dual polyhedron, dual of the icosahedron) and the rhombic triacontahedron. Every polyhedron with icosahedral symmetry has 60 Rotational symmetry, rotational (or orientation-preserving) symmetries and 60 orientation-reversing symmetries (that combine a rotation and a Reflection symmetry, reflection), for a total symmetry order of 120. The full symmetry group is the Coxeter group of type . It may be represented by Coxeter notation and Coxeter diagram . The set of rotational symmetries forms a subgroup that is isomorphic to the alternating group on 5 letters. As point group Apart from the two infinite series of prismatic and antiprismatic symmetry, rotational icosahedral symmetry or chiral icosahedral symmetry of chiral objects and full icosahedra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Icosahedral Reflection Domains
In geometry, an icosahedron ( or ) is a polyhedron with 20 faces. The name comes . The plural can be either "icosahedra" () or "icosahedrons". There are infinitely many non-similarity (geometry), similar shapes of icosahedra, some of them being more symmetrical than others. The best known is the (convex polyhedron, convex, non-stellation, stellated) regular icosahedron—one of the Platonic solids—whose faces are 20 equilateral triangles. Regular icosahedra There are two objects, one convex and one nonconvex, that can both be called regular icosahedra. Each has 30 edges and 20 equilateral triangle faces with five meeting at each of its twelve vertices. Both have icosahedral symmetry. The term "regular icosahedron" generally refers to the convex variety, while the nonconvex form is called a ''great icosahedron''. Convex regular icosahedron The convex regular icosahedron is usually referred to simply as the ''regular icosahedron'', one of the five regular Platonic solids, a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Point Groups In Three Dimensions
In geometry, a point group in three dimensions is an isometry group in three dimensions that leaves the origin fixed, or correspondingly, an isometry group of a sphere. It is a subgroup of the orthogonal group O(3), the group (mathematics), group of all isometry, isometries that leave the origin fixed, or correspondingly, the group of orthogonal matrix, orthogonal matrices. O(3) itself is a subgroup of the Euclidean group E(3) of all isometries. Symmetry groups of geometric objects are isometry groups. Accordingly, analysis of isometry groups is analysis of possible symmetry, symmetries. All isometries of a Bounded set, bounded (finite) 3D object have one or more common fixed points. We follow the usual convention by choosing the Origin (mathematics), origin as one of them. The symmetry group of an object is sometimes also called its full symmetry group, as opposed to its proper symmetry group, the intersection of its full symmetry group with Euclidean group#Direct and indirect is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Philosophical Magazine
The ''Philosophical Magazine'' is one of the oldest scientific journals published in English. It was established by Alexander Tilloch in 1798;John Burnett"Tilloch, Alexander (1759–1825)" Dictionary of National Biography#Oxford Dictionary of National Biography, Oxford Dictionary of National Biography, Oxford University Press, Sept 2004; online edn, May 2006, accessed 17 Feb 2010 in 1822 Richard Taylor (editor), Richard Taylor became joint editor and it has been published continuously by Taylor & Francis ever since. Early history The name of the journal dates from a period when "natural philosophy" embraced all aspects of science. The very first paper published in the journal carried the title "Account of Mr Cartwright's Patent Steam Engine". Other articles in the first volume include "Methods of discovering whether Wine has been adulterated with any Metals prejudicial to Health" and "Description of the Apparatus used by Lavoisier to produce Water from its component Parts, Oxyg ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Icosian Calculus
The icosian calculus is a non-commutative algebraic structure discovered by the Irish mathematician William Rowan Hamilton in 1856. In modern terms, he gave a group presentation of the icosahedral group, icosahedral rotation group by Generating set of a group, generators and relations. Hamilton's discovery derived from his attempts to find an algebra of tuple, "triplets" or 3-tuples that he believed would reflect the three Cartesian coordinate system#Cartesian coordinates in three dimensions, Cartesian axes. The symbols of the icosian calculus correspond to moves between vertices on a dodecahedron. (Hamilton originally thought in terms of moves between the faces of an icosahedron, which is equivalent by Platonic solid#Dual polyhedra, duality. This is the origin of the name "icosian".) Hamilton's work in this area resulted indirectly in the terms Hamiltonian circuit and Hamiltonian path in graph theory. He also invented the icosian game as a means of illustrating and popularising hi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
William Rowan Hamilton
Sir William Rowan Hamilton (4 August 1805 – 2 September 1865) was an Irish astronomer, mathematician, and physicist who made numerous major contributions to abstract algebra, classical mechanics, and optics. His theoretical works and mathematical equations are considered fundamental to modern theoretical physics, particularly Hamiltonian mechanics, his reformulation of Lagrangian mechanics. His career included the analysis of geometrical optics, Fourier analysis, and quaternions, the last of which made him one of the founders of modern linear algebra. Hamilton was Andrews Professor of Astronomy at Trinity College Dublin. He was also the third director of Dunsink Observatory from 1827 to 1865. The Hamilton Institute at Maynooth University is named after him. Early life Hamilton was the fourth of nine children born to Sarah Hutton (1780–1817) and Archibald Hamilton (1778–1819), who lived in Dublin at 29 Dominick Street, Dublin, Dominick Street, later renumbered to 36. Ham ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Triangle Group
In mathematics, a triangle group is a group that can be realized geometrically by sequences of reflections across the sides of a triangle. The triangle can be an ordinary Euclidean triangle, a triangle on the sphere, or a hyperbolic triangle. Each triangle group is the symmetry group of a tiling of the Euclidean plane, the sphere, or the hyperbolic plane by congruent triangles called Möbius triangles, each one a fundamental domain for the action. Definition Let ''l'', ''m'', ''n'' be integers greater than or equal to 2. A triangle group Δ(''l'',''m'',''n'') is a group of motions of the Euclidean plane, the two-dimensional sphere, the real projective plane, or the hyperbolic plane generated by the reflections in the sides of a triangle with angles π/''l'', π/''m'' and π/''n'' (measured in radians). The product of the reflections in two adjacent sides is a rotation by the angle which is twice the angle between those sides, 2π/''l'', 2π/''m'' and 2π/''n''. Therefo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Presentation Of A Group
In mathematics, a presentation is one method of specifying a group. A presentation of a group ''G'' comprises a set ''S'' of generators—so that every element of the group can be written as a product of powers of some of these generators—and a set ''R'' of relations among those generators. We then say ''G'' has presentation :\langle S \mid R\rangle. Informally, ''G'' has the above presentation if it is the "freest group" generated by ''S'' subject only to the relations ''R''. Formally, the group ''G'' is said to have the above presentation if it is isomorphic to the quotient of a free group on ''S'' by the normal subgroup generated by the relations ''R''. As a simple example, the cyclic group of order ''n'' has the presentation :\langle a \mid a^n = 1\rangle, where 1 is the group identity. This may be written equivalently as :\langle a \mid a^n\rangle, thanks to the convention that terms that do not include an equals sign are taken to be equal to the group identity ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alternating Group
In mathematics, an alternating group is the Group (mathematics), group of even permutations of a finite set. The alternating group on a set of elements is called the alternating group of degree , or the alternating group on letters and denoted by or Basic properties For , the group A''n'' is the commutator subgroup of the symmetric group S''n'' with Index of a subgroup, index 2 and has therefore factorial, ''n''!/2 elements. It is the kernel (algebra), kernel of the signature group homomorphism explained under symmetric group. The group A''n'' is abelian group, abelian if and only if and simple group, simple if and only if or . A5 is the smallest non-abelian simple group, having order of a group, order 60, and thus the smallest non-solvable group. The group A4 has the Klein four-group V as a proper normal subgroup, namely the identity and the double transpositions , that is the kernel of the surjection of A4 onto . We have the exact sequence . In Galois theory, this m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Symmetry Order
The symmetry number or symmetry order of an object is the number of different but indistinguishable (or equivalent) arrangements (or views) of the object, that is, it is the order of its symmetry group. The object can be a molecule, crystal lattice, lattice, tiling, or in general any kind of mathematical object that admits symmetries. In statistical thermodynamics, the symmetry number corrects for any overcounting of equivalent molecular conformations in the partition function. In this sense, the symmetry number depends upon how the partition function is formulated. For example, if one writes the partition function of ethane so that the integral includes full rotation of a methyl, then the 3-fold rotational symmetry of the methyl group contributes a factor of 3 to the symmetry number; but if one writes the partition function so that the integral includes only one rotational energy well of the methyl, then the methyl rotation does not contribute to the symmetry number. Symmetry ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Orbifold Notation
In geometry, orbifold notation (or orbifold signature) is a system, invented by the mathematician William Thurston and promoted by John Horton Conway, John Conway, for representing types of symmetry groups in two-dimensional spaces of constant curvature. The advantage of the notation is that it describes these groups in a way which indicates many of the groups' properties: in particular, it follows William Thurston in describing the orbifold obtained by taking the quotient of Euclidean space by the group under consideration. Groups representable in this notation include the point groups in three dimensions, point groups on the sphere (S^2), the frieze groups and wallpaper groups of the Euclidean plane (E^2), and their analogues on the hyperbolic geometry, hyperbolic plane (H^2). Definition of the notation The following types of Euclidean transformation can occur in a group described by orbifold notation: * reflection through a line (or plane) * translation by a vector * rotati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arthur Moritz Schönflies
Arthur Moritz Schoenflies (; 17 April 1853 – 27 May 1928), sometimes written as Schönflies, was a German mathematician, known for his contributions to the application of group theory to crystallography, and for work in topology. Schoenflies was born in Landsberg an der Warthe (modern Gorzów, Poland). Arthur Schoenflies married Emma Levin (1868–1939) in 1896. He studied under Ernst Kummer and Karl Weierstrass, and was influenced by Felix Klein. The Schoenflies problem is to prove that an (n - 1)-sphere in Euclidean ''n''-space bounds a topological ball, however embedded. This question is much more subtle than it initially appears. He studied at the University of Berlin from 1870 to 1875. He obtained a doctorate in 1877, and in 1878 he was a teacher at a school in Berlin. In 1880, he went to Colmar to teach. Schoenflies was a frequent contributor to Klein's ''Encyclopedia of Mathematical Sciences'': In 1898 he wrote on set theory, in 1902 on kinematics, and on project ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Space Group
In mathematics, physics and chemistry, a space group is the symmetry group of a repeating pattern in space, usually in three dimensions. The elements of a space group (its symmetry operations) are the rigid transformations of the pattern that leave it unchanged. In three dimensions, space groups are classified into 219 distinct types, or 230 types if chiral copies are considered distinct. Space groups are discrete cocompact groups of isometries of an oriented Euclidean space in any number of dimensions. In dimensions other than 3, they are sometimes called Bieberbach groups. In crystallography, space groups are also called the crystallographic or Fedorov groups, and represent a description of the symmetry of the crystal. A definitive source regarding 3-dimensional space groups is the ''International Tables for Crystallography'' . History Space groups in 2 dimensions are the 17 wallpaper groups which have been known for several centuries, though the proof that the list ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |