|
Ichirai Hōshi
Ichirai (一来, died 1180) was a Japanese warrior monk who supported the Minamoto clan of samurai against their rivals, the Taira clan The was one of the four most important Japanese clans, clans that dominated Japanese politics during the Heian period, Heian period of History of Japan, Japanese history – the others being the Minamoto clan, Minamoto, the Fujiwara clan, Fuji .... Ichirai-hōshi is best known for his part in the battle of Uji. He was fighting behind Tsutsui Jōmyō Meishū on the Uji bridge, but he could not fight alongside his ally as the beams were so narrow. He is said to have leapt over the other monk, taken over the brunt of the fighting, and continued until he fell. References *Turnbull, Stephen. ''Warriors of Medieval Japan.'' Oxford: Osprey Publishing, 2005 Japanese warrior monks 1180 deaths People of the Heian period Buddhist clergy of the Heian period Year of birth unknown {{Japan-mil-bio-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sōhei
were Buddhist warrior monks of both classical and feudal Japan. At certain points in history, they held considerable power, obliging the imperial and military governments to collaborate. The prominence of the ''sōhei'' rose in parallel with the ascendancy of the Tendai school's influence between the 10th and 17th centuries. The warriors protected land and intimidated rival schools of Buddhism, becoming a significant factor in the spread of Buddhism and the development of different schools during the Kamakura period. The ''sōhei'' shared many similarities with the European lay brothers, members of a monastic order who might not have been ordained. Much like the Teutonic Order, the warrior monks of the Holy Roman Empire, and the crusading orders, ''sōhei'' did not operate as individuals, or even as members of small, individual temples, but rather as warriors in a large extended brotherhood or monastic order. The home temple of a ''sōhei'' monastic order might have h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
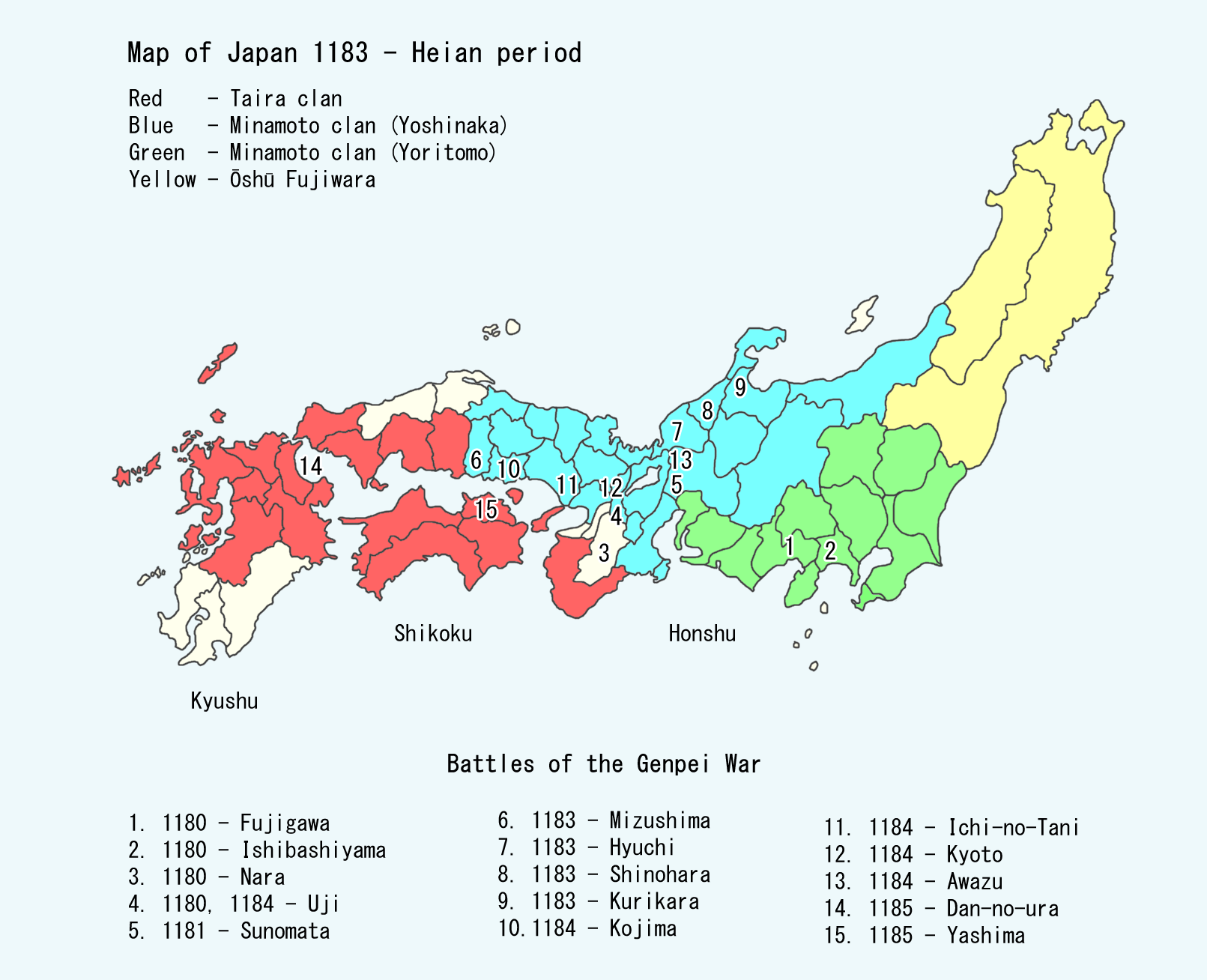
Minamoto Clan
was a Aristocracy (class), noble surname bestowed by the Emperors of Japan upon members of the Imperial House of Japan, imperial family who were excluded from the List of emperors of Japan, line of succession and demoted into the ranks of Nobility, the nobility since 814."...the Minamoto (1192-1333)". ''Warrior Rule in Japan'', page 11. Cambridge University Press. Several noble lines were bestowed the surname, the most notable of which was the Seiwa Genji, whose descendants established the Kamakura shogunate, Kamakura and Ashikaga shogunate, Ashikaga Shogun, shogunates following the Heian era. The Minamoto was one of the four great Japanese clans, clans that dominated Japanese politics during the Heian period, Heian period in History of Japan, Japanese history—the other three were the Fujiwara clan, Fujiwara, the Taira clan, Taira, and the Tachibana clan (kuge), Tachibana. In the late Heian period, Minamoto rivalry with the Taira culminated in the Genpei War (1180–1185 AD). T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Samurai
The samurai () were members of the warrior class in Japan. They were originally provincial warriors who came from wealthy landowning families who could afford to train their men to be mounted archers. In the 8th century AD, the imperial court downsized the national army and delegated the security of the countryside to these privately trained warriors. Eventually the samurai clans grew so powerful that they became the ''de facto'' rulers of the country. In the aftermath of the Gempei War (1180-1185), Japan formally passed into military rule with the founding of the first shogunate. The status of samurai became heredity by the mid-eleventh century. By the start of the Edo period, the shogun had disbanded the warrior-monk orders and peasant conscript system, leaving the samurai as the only men in the country permitted to carry weapons at all times. Because the Edo period was a time of peace, many samurai neglected their warrior training and focused on peacetime activities such as a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Taira Clan
The was one of the four most important Japanese clans, clans that dominated Japanese politics during the Heian period, Heian period of History of Japan, Japanese history – the others being the Minamoto clan, Minamoto, the Fujiwara clan, Fujiwara, and the Tachibana clan (kuge), Tachibana. The clan is divided into four major groups, named after the Emperor of Japan, emperors they descended from: Emperor Kanmu, Kanmu Heishi, Emperor Ninmyō, Ninmyō Heishi, Emperor Montoku, Montoku Heishi, and Emperor Kōkō, Kōkō Heishi, the most influential of which was the Kanmu Heishi line. In the twilight of the Heian period, the Taira controlled the boy emperor Emperor Antoku, Antoku (himself the grandson of the powerful ''Kugyō'' Taira no Kiyomori) and had effectively dominated the Imperial capital of Heian-kyō, Heian. However, they were opposed by their rivals the Minamoto clan (the Genji), which culminated in the Genpei War (1180–1185 AD). The five-year-long war concluded with a d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Uji (1180)
The , alternatively known as "Mochihitos Raising of an Army" in Japan is a battle which took place on June 20, 1180, following Prince Mochihito and Minamoto no Yorimasa's plan to raise an army to overthrow the Taira clan and the issuing of an edict urging the Minamoto clan, major temples, and shrines in the country to revolt. Due to lack of preparation, the plan was discovered by the Taira, and Prince Mochihito and Yorimasa were defeated, dying at the battle. However, this triggered multiple anti-Taira forces to raise their armies. The battle is famous for having begun the Genpei War. Background Prince Mochihito, having been passed over twice in the succession of the Imperial Throne and believing Taira no Kiyomori was causing suffering in the country, coordinated with Minamoto no Yorimasa, who believed Mochihito to be the legitimate heir to the successors, and urged him to rebel. Minamoto no Yorimasa was an Kuge, aristocrat, who dominated the Imperial Court in Kyoto. He was the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tsutsui Jōmyō Meishū
Tsutsui no Jōmyō Meishū (筒井浄妙明秀) was a warrior monk (''sōhei'') from Mii-dera who fought alongside Minamoto no Yorimasa and his fellow monks at the Battle of Uji in 1180, defending the Byōdō-in and Prince Mochihito from the Taira clan. Later, in the same account, Gochi-in no Tajima is replaced on the bridge by his comrade, Tsutsui. Standing upon the broken bridge of Uji, Kyoto, Tsutsui fought off the Taira samurai The samurai () were members of the warrior class in Japan. They were originally provincial warriors who came from wealthy landowning families who could afford to train their men to be mounted archers. In the 8th century AD, the imperial court d ... with bow and arrow, '' naginata'', sword, and dagger. According to '' The Tale of the Heike'': References *Turnbull, Stephen. ''Japanese Warrior Monks AD 949–1603.'' Oxford: Osprey Publishing, 2003. {{DEFAULTSORT:Tsutsui, Jomyo Meishu Japanese warrior monks Buddhist clergy of the Heian peri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Japanese Warrior Monks
Japanese may refer to: * Something from or related to Japan, an island country in East Asia * Japanese language, spoken mainly in Japan * Japanese people, the ethnic group that identifies with Japan through ancestry or culture ** Japanese diaspora, Japanese emigrants and their descendants around the world * Japanese citizens, nationals of Japan under Japanese nationality law ** Foreign-born Japanese, naturalized citizens of Japan * Japanese writing system, consisting of kanji and kana * Japanese cuisine, the food and food culture of Japan See also * List of Japanese people * * Japonica (other) * Japanese studies , sometimes known as Japanology in Europe, is a sub-field of area studies or East Asian studies involved in social sciences and humanities research on Japan. It incorporates fields such as the study of Japanese language, history, culture, litera ... {{disambiguation Language and nationality disambiguation pages ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1180 Deaths
Year 1180 ( MCLXXX) was a leap year starting on Tuesday of the Julian calendar. Events By place Byzantine Empire * September 24 – Emperor Manuel I Komnenos dies in Constantinople after a 37-year reign. He is succeeded by his 11-year-old son, Alexios II Komnenos, who will reign briefly as emperor of the Byzantine Empire under the regency of his mother, Maria of Antioch. Maria assumes power as regent (until 1183) and takes as her advisor and lover, Alexios Komnenos (protosebastos), a nephew of Manuel I, which causes scandal and unrest among the Byzantine populace. Europe * January 13 – Henry the Lion, Duke of Saxony and Bavaria, is stripped of his duchies and all his imperial fiefs at an Imperial Diet in Würzburg for violating the king's peace. On April 13, Emperor Frederick I Barbarossa issues the Gelnhausen Charter, formally dissolving Henry's former domains. A portion of Saxony is reorganized as the Duchy of Westphalia, while other territories are gran ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
People Of The Heian Period
The term "the people" refers to the public or common mass of people of a polity. As such it is a concept of human rights law, international law as well as constitutional law, particularly used for claims of popular sovereignty. In contrast, a people is any plurality of persons considered as a whole. Used in politics and law, the term "a people" refers to the collective or community of an ethnic group or nation. Concepts Legal Chapter One, Article One of the Charter of the United Nations states that "peoples" have the right to self-determination. Though the mere status as peoples and the right to self-determination, as for example in the case of Indigenous peoples (''peoples'', as in all groups of indigenous people, not merely all indigenous persons as in ''indigenous people''), does not automatically provide for independent sovereignty and therefore secession. Indeed, judge Ivor Jennings identified the inherent problems in the right of "peoples" to self-determination, as i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Buddhist Clergy Of The Heian Period
Buddhism, also known as Buddhadharma and Dharmavinaya, is an Indian religion and List of philosophies, philosophical tradition based on Pre-sectarian Buddhism, teachings attributed to the Buddha, a wandering teacher who lived in the 6th or 5th century Before the Common Era, BCE. It is the Major religious groups, world's fourth-largest religion, with about 500 million followers, known as Buddhists, who comprise four percent of the global population. It arose in the eastern Gangetic plain as a movement in the 5th century BCE, and gradually spread throughout much of Asia. Buddhism has subsequently played a major role in Asian culture and spirituality, eventually spreading to Western world, the West in the 20th century. According to tradition, the Buddha instructed his followers in a path of bhavana, development which leads to Enlightenment in Buddhism, awakening and moksha, full liberation from ''Duḥkha, dukkha'' (). He regarded this path as a Middle Way between extremes su ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |