|
Ibn Al‐Ha'im Al‐Ishbili
} Abu Muhammad Abd al-Haqq al‐Ghafiqi al‐Ishbili (), also known as Ibn al‐Hāʾim (fl. was a medieval Muslim astronomer and mathematician from Seville. He is known to modern scholars for his (1204/5), which was had a great influence on the development of Islamic astronomy and which has provided important information on astronomers from Al-Andalus, including the instrument maker and astrologer Al-Zarqali. Life Ibn al‐Hāʾim originated from Seville in Al-Andalus. As a student, he learnt mathematics using the works of the scholars Al-Jayyani and Jabir ibn Aflah. He probably worked in North Africa, at a time when the Almohad Caliphate ruled the region. Ibn al‐Hāʾim became proficient at mathematics and was familiar with the trigonometrical concepts introduced into al‐Andalus by the scholar Ibn Mu'adh al-Jayyani in the 11th century and developed during the next century by the astronomer and mathematician Jābir ibn Aflaḥ. In 1204/5 Ibn al‐Hāʾim wrote ("'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Seville
Seville ( ; , ) is the capital and largest city of the Spain, Spanish autonomous communities of Spain, autonomous community of Andalusia and the province of Seville. It is situated on the lower reaches of the Guadalquivir, River Guadalquivir, in the southwest of the Iberian Peninsula. Seville has a municipal population of about 701,000 , and a Seville metropolitan area, metropolitan population of about 1.5 million, making it the largest city in Andalusia and the List of metropolitan areas in Spain, fourth-largest city in Spain. Its old town, with an area of , contains a UNESCO World Heritage Site comprising three buildings: the Alcázar of Seville, Alcázar palace complex, the Seville Cathedral, Cathedral and the General Archive of the Indies. The Seville harbour, located about from the Atlantic Ocean, is the only river port in Spain. The capital of Andalusia features hot temperatures in the summer, with daily maximums routinely above in July and August. Seville was founded ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Maghreb
The Maghreb (; ), also known as the Arab Maghreb () and Northwest Africa, is the western part of the Arab world. The region comprises western and central North Africa, including Algeria, Libya, Mauritania, Morocco, and Tunisia. The Maghreb also includes the territorial dispute, disputed territory of Western Sahara. As of 2018, the region had a population of over 100 million people. The Maghreb is usually defined as encompassing much of the northern part of Africa, including a large portion of the Sahara Desert, but excluding Egypt and the Sudan, which are considered to be located in the Mashriq — the eastern part of the Arab world. The traditional definition of the Maghreb — which restricted its scope to the Atlas Mountains and the coastal plains of Morocco, Algeria, Tunisia and Libya — was expanded in modern times to include Mauritania and the disputed territory of Western Sahara. During the era of al-Andalus on the Iberian Peninsula (711–1492), the Maghreb's inhabita ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oxford
Oxford () is a City status in the United Kingdom, cathedral city and non-metropolitan district in Oxfordshire, England, of which it is the county town. The city is home to the University of Oxford, the List of oldest universities in continuous operation, oldest university in the English-speaking world; it has buildings in every style of Architecture of England, English architecture since late History of Anglo-Saxon England, Anglo-Saxon. Oxford's industries include motor manufacturing, education, publishing, science, and information technologies. Founded in the 8th century, it was granted city status in 1542. The city is located at the confluence of the rivers Thames (locally known as the Isis) and River Cherwell, Cherwell. It had a population of in . It is north-west of London, south-east of Birmingham and north-east of Bristol. History The history of Oxford in England dates back to its original settlement in the History of Anglo-Saxon England, Saxon period. The name � ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bodleian Library
The Bodleian Library () is the main research library of the University of Oxford. Founded in 1602 by Sir Thomas Bodley, it is one of the oldest libraries in Europe. With over 13 million printed items, it is the second-largest library in Britain after the British Library. Under the Legal Deposit Libraries Act 2003, it is one of six legal deposit libraries for works published in the United Kingdom, and under Irish law it is entitled to request a copy of each book published in the Republic of Ireland. Known to Oxford scholars as "Bodley" or "the Bod", it operates principally as a reference library and, in general, documents may not be removed from the reading rooms. In 2000, a number of libraries within the University of Oxford were brought together for administrative purposes under the aegis of what was initially known as Oxford University Library Services (OULS), and since 2010 as the Bodleian Libraries, of which the Bodleian Library is the largest component. All coll ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Manuscript
A manuscript (abbreviated MS for singular and MSS for plural) was, traditionally, any document written by hand or typewritten, as opposed to mechanically printed or reproduced in some indirect or automated way. More recently, the term has come to be understood to further include ''any'' written, typed, or word-processed copy of an author's work, as distinguished from the rendition as a printed version of the same. Before the arrival of prints, all documents and books were manuscripts. Manuscripts are not defined by their contents, which may combine writing with mathematical calculations, maps, music notation, explanatory figures, or illustrations. Terminology The word "manuscript" derives from the (from , hand and from , to write), and is first recorded in English in 1597. An earlier term in English that shares the meaning of a handwritten document is "hand-writ" (or "handwrit"), which is first attested around 1175 and is now rarely used. The study of the writing ( ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ptolemy
Claudius Ptolemy (; , ; ; – 160s/170s AD) was a Greco-Roman mathematician, astronomer, astrologer, geographer, and music theorist who wrote about a dozen scientific treatises, three of which were important to later Byzantine science, Byzantine, Islamic science, Islamic, and Science in the Renaissance, Western European science. The first was his astronomical treatise now known as the ''Almagest'', originally entitled ' (, ', ). The second is the ''Geography (Ptolemy), Geography'', which is a thorough discussion on maps and the geographic knowledge of the Greco-Roman world. The third is the astrological treatise in which he attempted to adapt horoscopic astrology to the Aristotelian physics, Aristotelian natural philosophy of his day. This is sometimes known as the ' (, 'On the Effects') but more commonly known as the ' (from the Koine Greek meaning 'four books'; ). The Catholic Church promoted his work, which included the only mathematically sound geocentric model of the Sola ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Apsis
An apsis (; ) is the farthest or nearest point in the orbit of a planetary body about its primary body. The line of apsides (also called apse line, or major axis of the orbit) is the line connecting the two extreme values. Apsides pertaining to orbits around different bodies have distinct names to differentiate themselves from other apsides. Apsides pertaining to geocentric orbits, orbits around the Earth, are at the farthest point called the ''apogee'', and at the nearest point the ''perigee'', like with orbits of satellites and the Moon around Earth. Apsides pertaining to orbits around the Sun are named ''aphelion'' for the farthest and ''perihelion'' for the nearest point in a heliocentric orbit. Earth's two apsides are the farthest point, ''aphelion'', and the nearest point, ''perihelion'', of its orbit around the host Sun. The terms ''aphelion'' and ''perihelion'' apply in the same way to the orbits of Jupiter and the other planets, the comets, and the asteroids of t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Longitude
Longitude (, ) is a geographic coordinate that specifies the east- west position of a point on the surface of the Earth, or another celestial body. It is an angular measurement, usually expressed in degrees and denoted by the Greek letter lambda (λ). Meridians are imaginary semicircular lines running from pole to pole that connect points with the same longitude. The prime meridian defines 0° longitude; by convention the International Reference Meridian for the Earth passes near the Royal Observatory in Greenwich, south-east London on the island of Great Britain. Positive longitudes are east of the prime meridian, and negative ones are west. Because of the Earth's rotation, there is a close connection between longitude and time measurement. Scientifically precise local time varies with longitude: a difference of 15° longitude corresponds to a one-hour difference in local time, due to the differing position in relation to the Sun. Comparing local time to an absol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
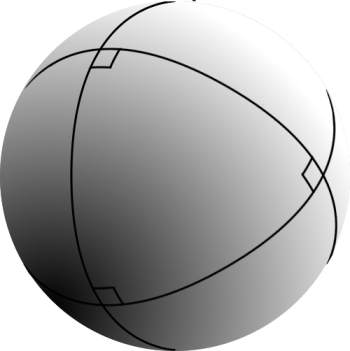
Spherical Trigonometrical
Spherical trigonometry is the branch of spherical geometry that deals with the metrical relationships between the sides and angles of spherical triangles, traditionally expressed using trigonometric functions. On the sphere, geodesics are great circles. Spherical trigonometry is of great importance for calculations in astronomy, geodesy, and navigation. The origins of spherical trigonometry in Greek mathematics and the major developments in Islamic mathematics are discussed fully in History of trigonometry and Mathematics in medieval Islam. The subject came to fruition in Early Modern times with important developments by John Napier, Delambre and others, and attained an essentially complete form by the end of the nineteenth century with the publication of Todhunter's textbook ''Spherical trigonometry for the use of colleges and Schools''. Since then, significant developments have been the application of vector methods, quaternion methods, and the use of numerical methods. Pr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
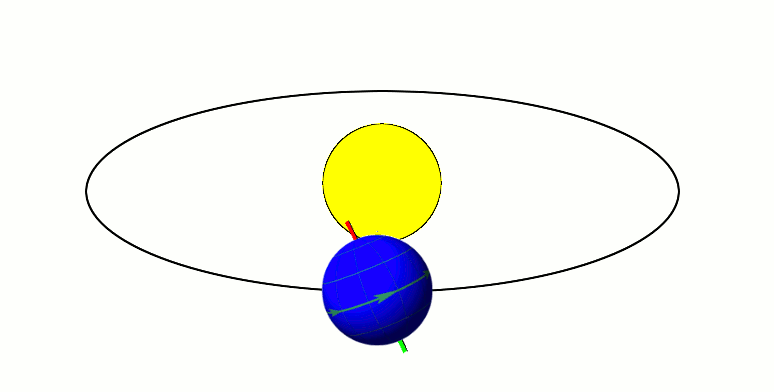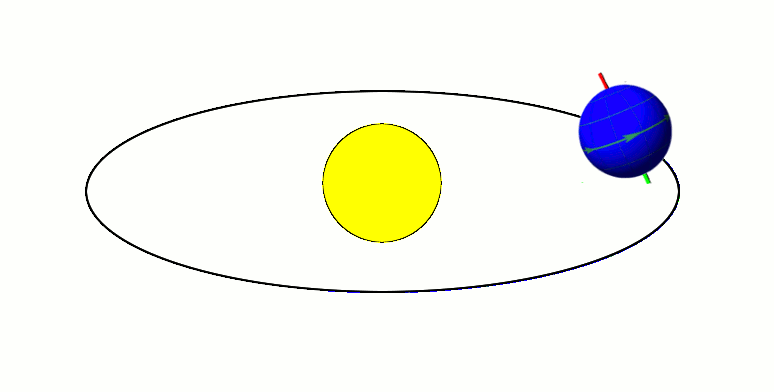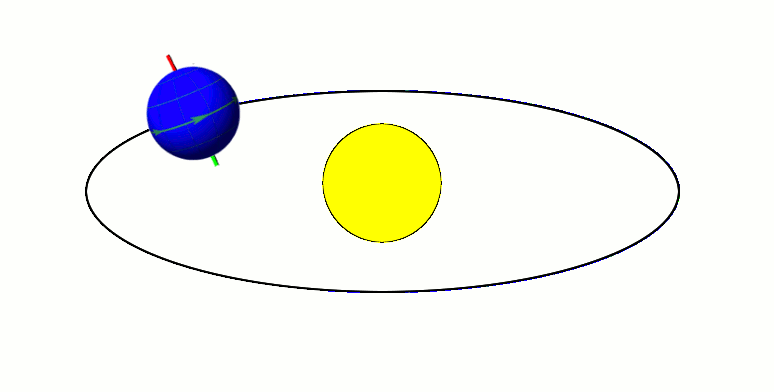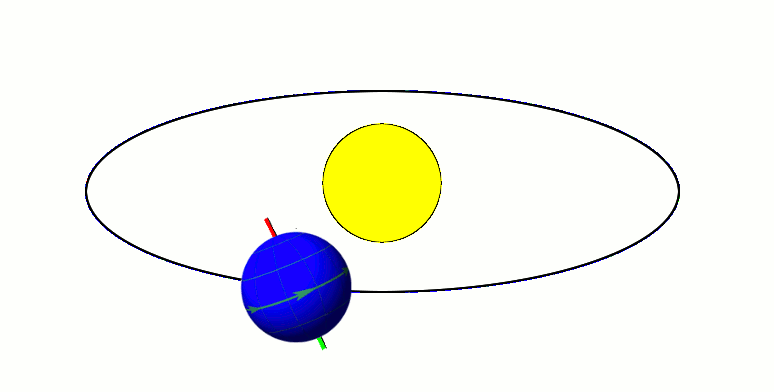
Axial Tilt
In astronomy, axial tilt, also known as obliquity, is the angle between an object's rotational axis and its orbital axis, which is the line perpendicular to its orbital plane; equivalently, it is the angle between its equatorial plane and orbital plane. It differs from orbital inclination. At an obliquity of 0 degrees, the two axes point in the same direction; that is, the rotational axis is perpendicular to the orbital plane. The rotational axis of Earth, for example, is the imaginary line that passes through both the North Pole and South Pole, whereas the Earth's orbital axis is the line perpendicular to the imaginary plane through which the Earth moves as it revolves around the Sun; the Earth's obliquity or axial tilt is the angle between these two lines. Over the course of an orbital period, the obliquity usually does not change considerably, and the orientation of the axis remains the same relative to the background of stars. This causes one pole to be pointed mo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oscillation
Oscillation is the repetitive or periodic variation, typically in time, of some measure about a central value (often a point of equilibrium) or between two or more different states. Familiar examples of oscillation include a swinging pendulum and alternating current. Oscillations can be used in physics to approximate complex interactions, such as those between atoms. Oscillations occur not only in mechanical systems but also in dynamic systems in virtually every area of science: for example the beating of the human heart (for circulation), business cycles in economics, predator–prey population cycles in ecology, geothermal geysers in geology, vibration of strings in guitar and other string instruments, periodic firing of nerve cells in the brain, and the periodic swelling of Cepheid variable stars in astronomy. The term ''vibration'' is precisely used to describe a mechanical oscillation. Oscillation, especially rapid oscillation, may be an undesirable phenomenon in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Said Al-Andalusi
Ṣāʿid al-Andalusī (), in full Abū al-Qāsim Ṣāʿid ibn Abū al-Walīd Aḥmad ibn Abd al-Raḥmān ibn Muḥammad ibn Ṣāʿid ibn ʿUthmān al-Taghlibi al-Qūrtūbi () (1029July 6, 1070 AD; 4206 Shawwal, 462 AH), was an Arab qadi of Toledo in al-Andalus, who wrote on the history of science, philosophy and thought. He was a mathematician and scientist with a special interest in astronomy and compiled a famous biographic encyclopedia of science that quickly became popular in the empire and the Islamic East. Life Ṣāʿid al-Andalusī was born in Almería in al-Andalus during the Dhulnunid dynasty and died in Toledo. His Arab origins came from the tribe of Taghlib and his family had fled Cordova to take refuge in Almería during the civil war. His grandfather had been qadi (judge) of Sidonia and his father was qadi of Toledo until he died in 1057 when Ṣāʿid succeeded him. The early biographers ibn Bashkuwal, Abu Ja'far Ahmad ibn Yahya al-Dabbi, al-Safadi a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |