|
IBM 2991
The IBM 2991 Blood Cell Processor was a blood cell washer developed by IBM Systems Development Division in Endicott, New York. It was first marketed by IBM Systems Supplies Division (SSD) in 1972. The processor washed fresh blood or frozen, thawed blood. In the case of frozen, thawed blood, the blood was washed to remove the cryogenic agent, typically, glycerol. History and development In 1964, IBM received a grant from the National Cancer Institute (National Cancer Institute, NCI) of the National Institutes of Health (NIH). This was a result of an IBM engineer, George T. Judson, requesting to work on a continuous-flow blood centrifuge. He had observed the need for such a machine when visiting NCI in 1962 after his son was diagnosed with leukemia. As a result of this work, IBM developed the IBM 2997, NCI-IBM Blood Cell Separator which was announced in 1965. At that announcement, Judson and his co-worker Alan Jones were approached by Dr. James R. Pert, Director of the American Red Cr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Blood Cell
A blood cell, also called a hematopoietic cell, hemocyte, or hematocyte, is a cell produced through hematopoiesis and found mainly in the blood. Major types of blood cells include red blood cells (erythrocytes), white blood cells (leukocytes), and platelets (thrombocytes). Together, these three kinds of blood cells add up to a total 45% of the blood tissue by volume, with the remaining 55% of the volume composed of plasma, the liquid component of blood. Red blood cells Red blood cells or ''erythrocytes'', primarily carry oxygen and collect carbon dioxide through the use of hemoglobin. Hemoglobin is an iron-containing protein that gives red blood cells their color and facilitates transportation of oxygen from the lungs to tissues and carbon dioxide from tissues to the lungs to be exhaled. Red blood cells are the most abundant cell in the blood, accounting for about 40-45% of its volume. Red blood cells are circular, biconcave, disk-shaped and deformable to allow them to squ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
National Cancer Institute
The National Cancer Institute (NCI) coordinates the United States National Cancer Program and is part of the National Institutes of Health (NIH), which is one of eleven agencies that are part of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services. The NCI conducts and supports research, training, health information dissemination, and other activities related to the causes, prevention, diagnosis, and treatment of cancer; the supportive care of cancer patients and their families; and cancer survivorship. NCI is the oldest and has the largest budget and research program of the 27 institutes and centers of the NIH ($6.9 billion in 2020). It fulfills the majority of its mission via an extramural program that provides grants for cancer research. Additionally, the National Cancer Institute has intramural research programs in Bethesda, Maryland, and at the Frederick National Laboratory for Cancer Research at Fort Detrick in Frederick, Maryland. The NCI receives more than in funding eac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
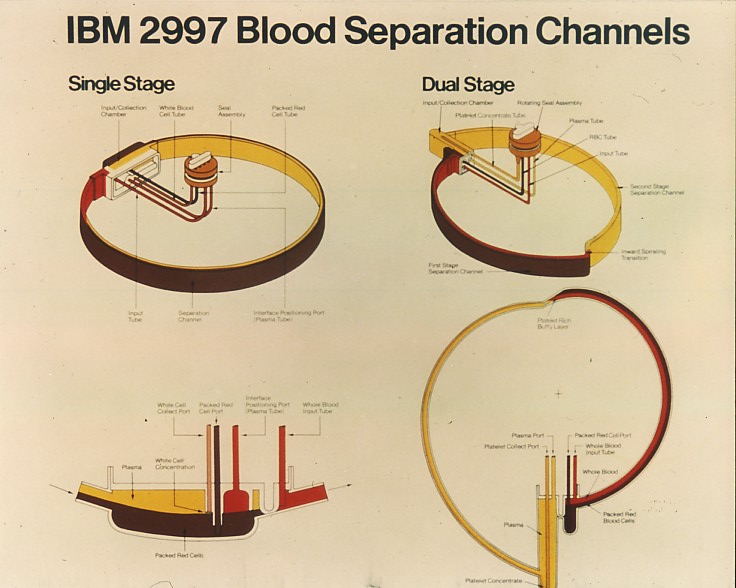
IBM 2997
The earliest roots of IBM's development of the IBM 2997 Blood cell Separator lay in the personal tragedy of one of IBM's development engineers, George Judson. In 1962, Judson's son, Tom, was diagnosed with leukemia. His physician was able to have Tom admitted to the Clinical Center of the National Cancer Institute (NCI) at the National Institutes of Health (NIH). On admission, they showed Judson a procedure to remove white blood cells from a patient. It was laborious. They would remove two units (450 ml) of blood, spin them in a bucket centrifuge, express the plasma into a satellite bag, and the white cells into another satellite bag. The packed red cells and the plasma would be recombined and administered to the patient. This would be repeated over and over. Judson, being an engineer, suggested that this could be done on a continuous-flow basis. He was sent to see Dr. Emil J. Freireich who expressed enthusiasm for the project. Judson returned to IBM and asked for a year's leave o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Punch Cards
A punched card (also punch card or punched-card) is a piece of stiff paper that holds digital data represented by the presence or absence of holes in predefined positions. Punched cards were once common in data processing applications or to directly control automated machinery. Punched cards were widely used through much of the 20th century in the data processing industry, where specialized and increasingly complex unit record machines, organized into semiautomatic data processing systems, used punched cards for data input, output, and storage. The IBM 12-row/80-column punched card format came to dominate the industry. Many early digital computers used punched cards as the primary medium for input of both computer programs and data. While punched cards are now obsolete as a storage medium, as of 2012, some voting machines still used punched cards to record votes. They also had a significant cultural impact. History The idea of control and data storage via punched holes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
IBM 5880
The IBM 5880, also known as the IBM 5880 Electrocardiograph System, is a computerized electrocardiograph and diagnostic tool. It was developed by IBM scientist Ray Bonner in the early 1970s and announced in 1978. The IBM 5880 was designed to analyze electrocardiograms, measurements of the electrical activity of the heart, and provide diagnostic advice to the same standards as a cardiologist. Similar programs already ran on mainframe computer A mainframe computer, informally called a mainframe or big iron, is a computer used primarily by large organizations for critical applications like bulk data processing for tasks such as censuses, industry and consumer statistics, enterpris ...s, but the 5880 was the first version that could be placed in a cart and taken into hospital conditions. When it first arrived in the hospitals doctors were afraid that they no longer would be paid to "read" and EKG. Going forward all EKGs done by the 5880 in the hospital still had to be "revi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Centrifuge
A centrifuge is a device that uses centrifugal force to separate various components of a fluid. This is achieved by spinning the fluid at high speed within a container, thereby separating fluids of different densities (e.g. cream from milk) or liquids from solids. It works by causing denser substances and particles to move outward in the radial direction. At the same time, objects that are less dense are displaced and moved to the centre. In a laboratory centrifuge that uses sample tubes, the radial acceleration causes denser particles to settle to the bottom of the tube, while low-density substances rise to the top. A centrifuge can be a very effective filter that separates contaminants from the main body of fluid. Industrial scale centrifuges are commonly used in manufacturing and waste processing to sediment suspended solids, or to separate immiscible liquids. An example is the cream separator found in dairies. Very high speed centrifuges and ultracentrifuges able to prov ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Saline Solution
Saline (also known as saline solution) is a mixture of sodium chloride (salt) and water. It has a number of uses in medicine including cleaning wounds, removal and storage of contact lenses, and help with dry eyes. By injection into a vein it is used to treat dehydration such as that from gastroenteritis and diabetic ketoacidosis. Large amounts may result in fluid overload, swelling, acidosis, and high blood sodium. In those with long-standing low blood sodium, excessive use may result in osmotic demyelination syndrome. Saline is in the crystalloid family of medications. It is most commonly used as a sterile 9 g of salt per litre (0.9%) solution, known as normal saline. Higher and lower concentrations may also occasionally be used. Saline is acidic, with a pH of 5.5 (due mainly to dissolved carbon dioxide). The medical use of saline began around 1831. It is on the World Health Organization's List of Essential Medicines. In 2020, sodium was the 274th most common ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Blood Plasma
Blood plasma is a light amber-colored liquid component of blood in which blood cells are absent, but contains proteins and other constituents of whole blood in suspension. It makes up about 55% of the body's total blood volume. It is the intravascular part of extracellular fluid (all body fluid outside cells). It is mostly water (up to 95% by volume), and contains important dissolved proteins (6–8%; e.g., serum albumins, globulins, and fibrinogen), glucose, clotting factors, electrolytes (, , , , , etc.), hormones, carbon dioxide (plasma being the main medium for excretory product transportation), and oxygen. It plays a vital role in an intravascular osmotic effect that keeps electrolyte concentration balanced and protects the body from infection and other blood-related disorders. Blood plasma is separated from the blood by spinning a vessel of fresh blood containing an anticoagulant in a centrifuge until the blood cells fall to the bottom of the tube. The bloo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glycerol
Glycerol (), also called glycerine in British English and glycerin in American English, is a simple triol compound. It is a colorless, odorless, viscous liquid that is sweet-tasting and non-toxic. The glycerol backbone is found in lipids known as glycerides. Because it has antimicrobial and antiviral properties, it is widely used in wound and burn treatments approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration. Conversely, it is also used as a bacterial culture medium. It can be used as an effective marker to measure liver disease. It is also widely used as a sweetener in the food industry and as a humectant in pharmaceutical formulations. Because of its three hydroxyl groups, glycerol is miscible with water and is hygroscopic in nature. Structure Although achiral, glycerol is prochiral with respect to reactions of one of the two primary alcohols. Thus, in substituted derivatives, the stereospecific numbering labels the molecule with a "sn-" prefix before the stem name ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plasma Protein
Blood-proteins, also termed plasma proteins, are proteins present in blood plasma. They serve many different functions, including transport of lipids, hormones, vitamins and minerals in activity and functioning of the immune system. Other blood proteins act as enzymes, complement components, protease inhibitors or kinin precursors. Contrary to popular belief, haemoglobin is not a blood protein, as it is carried within red blood cells, rather than in the blood serum. Serum albumin accounts for 55% of blood proteins, is a major contributor to maintaining the oncotic pressure of plasma and assists, as a carrier, in the transport of lipids and steroid hormones. Globulins make up 38% of blood proteins and transport ions, hormones, and lipids assisting in immune function. Fibrinogen comprises 7% of blood proteins; conversion of fibrinogen to insoluble fibrin is essential for blood clotting. The remainder of the plasma proteins (1%) are regulatory proteins, such as enzymes, proenzyme ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.jpg)


