|
Hyaladherin
Hyaladherins, also known as hyaluronan-binding proteins, are proteins capable of binding to hyaluronic acid. Most hyaladherins belong to the Link module superfamily, including its main receptor CD44, hyalectans and TSG-6. In addition there is a diverse group of hyaladherins lacking a Link module; these include the receptor RHAMM, C1QBP (HABP1) and HABP2. The primary roles of hyaladherins are cell adhesion, structural support of the extracellular matrix (ECM) and cell signalling. Due to the role of aberrant hyaluronic acid synthesis and degradation in various cancers, hyaladherins, as well as hyaluronic acid, are considered a promising target for cancer therapy. See also * Hyaluronan synthase *Hyaluronidase Hyaluronidases are a family of enzymes that catalyse the degradation of hyaluronic acid. Karl Meyer classified these enzymes in 1971, into three distinct groups, a scheme based on the enzyme reaction products. The three main types of hyaluroni ... References {{refl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Link Module
A Link domain or Link module, also known as Xlink domain (X for extracellular), is a protein domain that binds to hyaluronic acid. It is important in blood cell migration and apoptosis. The link domain is found in some extracellular proteins in vertebrates such as the hyalectans. It appears to be involved in extracellular matrix assembly and stability, cell adhesion, and migration. Structure The structure has been shown to consist of two alpha helices and two antiparallel beta sheets arranged around a large hydrophobic core similar to that of C-type lectin. This domain contains four conserved cysteines involved in two disulphide bonds. The link domain has also been termed HABM (hyaluronic acid binding module) and PTR (proteoglycan tandem repeat). Link domain proteins Proteins which contain the link domain include: * the hyalectans (a family of proteoglycans): aggrecan, brevican, neurocan and versican, which are expressed in the CNS; * the cartilage link protein (LP), a p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hyalectan
Lecticans, also known as hyalectans, are a family of large chondroitin sulfate proteoglycans found in the extracellular matrix. There are four members of the lectican family: aggrecan, brevican, neurocan, and versican. Lecticans interact with hyaluronic acid and tenascin-R to form a ternary complex. Tissue distribution Aggregan and versican are widely distributed throughout all tissues. Where aggrecan is a major extracellular matrix constituent in cartilage, versican is widely expressed in a number of connective tissues, including those in vascular smooth muscle, skin, and the cells of central and peripheral nervous systems. Brevican and neurocan are primarily restricted to the central nervous system (CNS) and are particularly abundant in perineuronal nets. Structure All four lecticans contain an N-terminal globular domain (G1 domain) that in turn contains an immunoglobulin V-set domain and a Link domain that binds hyaluronic acid; a long extended central domain (CS) that is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hyaluronic Acid
Hyaluronic acid (; abbreviated HA; conjugate base hyaluronate), also called hyaluronan, is an anionic, nonsulfated glycosaminoglycan distributed widely throughout connective, epithelial, and neural tissues. It is unique among glycosaminoglycans as it is non-sulfated, forms in the plasma membrane instead of the Golgi apparatus, and can be very large: human synovial HA averages about per molecule, or about 20,000 disaccharide monomers, while other sources mention . Medically, hyaluronic acid is used to treat osteoarthritis of the knee and dry eye, for wound repair, and as a cosmetic filler. The average 70 kg (150 lb) person has roughly 15 grams of hyaluronan in the body, one third of which is turned over (i.e., degraded and synthesized) per day. As one of the chief components of the extracellular matrix, it contributes significantly to cell proliferation and migration, and is involved in the progression of many malignant tumors. Hyaluronic acid is also a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
CD44
The CD44 antigen is a cell-surface glycoprotein involved in cell–cell interactions, cell adhesion and migration. In humans, the CD44 antigen is encoded by the ''CD44'' gene on chromosome 11. CD44 has been referred to as HCAM (homing cell adhesion molecule), Pgp-1 (phagocytic glycoprotein-1), Hermes antigen, lymphocyte homing receptor, ECM-III, and HUTCH-1. Tissue distribution and isoforms CD44 is expressed in a large number of mammalian cell types. The standard isoform, designated CD44s, comprising exons 1–5 and 16–20 is expressed in most cell types. CD44 splice variants containing variable exons are designated CD44v. Some epithelial cells also express a larger isoform (CD44E), which includes exons v8–10. Function CD44 participates in a wide variety of cellular functions including lymphocyte activation, recirculation and homing, hematopoiesis, and tumor metastasis. CD44 is a receptor for hyaluronic acid and internalizes metals bound to hyaluronic acid and can a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
TSG-6
Tumor necrosis factor-inducible gene 6 protein also known as TNF-stimulated gene 6 protein or TSG-6 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''TNFAIP6'' (tumor necrosis factor, alpha-induced protein 6) gene. Structure and function TSG-6 is a 30 kDa secreted protein that contains a hyaluronan-binding LINK domain a and thus is a member of the hyaluronan-binding protein family, also called hyaladherins. The hyaluronan-binding domain is known to be involved in extracellular matrix stability and cell migration. This protein has been shown to form a stable, covalent complex with inter-alpha-inhibitor ( IαI), and thus enhance the serine protease inhibitory activity of IαI, which is important in the protease network associated with inflammation. The expression of this gene can be induced by a number of signalling molecules, principally tumor necrosis factor α (TNF-α) and interleukin-1 ( IL-1). The expression can also be induced by mechanical stimuli in vascular smooth muscle ce ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
RHAMM
Hyaluronan-mediated motility receptor (HMMR), also known as RHAMM (Receptor for Hyaluronan Mediated Motility) is a protein which in humans is encoded by the ''HMMR'' gene. RHAMM recently has been also designated CD168 (cluster of differentiation 168). Function RHAMM was originally discovered as a soluble protein that altered migratory cell behavior and bound to hyaluronan. RHAMM is less well studied than the main hyaluronan (HA) receptor, CD44. In contrast to CD44 and other cell-surface receptors which contain the classical membrane spanning domain and signal sequence for secretion from the endoplasmic reticulum / Golgi complex, RHAMM does not contain a membrane spanning domain nor does the mRNA transcript contain a signal sequence. RHAMM is localized inside the cell and is unconventionally exported to the cell surface in response to certain defined stimuli such as wounding and cytokines including TGF-β. The precise unconventional export mechanism for transporting RHAMM to th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
C1QBP
Complement component 1 Q subcomponent-binding protein, mitochondrial is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''C1QBP'' gene. The human complement subcomponent C1q associates with C1r and C1s in order to yield the first component of the serum complement system. The protein encoded by this gene is known to bind to the globular heads of C1q molecules and inhibit C1 activation. This protein has also been identified as the p32 subunit of pre-mRNA splicing factor SF2, as well as a hyaluronic acid-binding protein. Protein subunit C1QBP is 282 amino acid in length and has three homologous subunit with its N-terminal 73 amino acid residues cleaved off to produce mature C1QBP. C1QBP appears as a monomer around 33 kDa on SDS-PAGE gel under both reducing and nonreducing condition but migrates as a trimer on size-exclusion chromatography (gel filtration). Protein structure The crystal structure of C1QBP at 2.25 Å resolution shows a homotrimeric ring displaying symmetry. The individua ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
HABP2
Hyaluronan-binding protein 2 also known as factor VII activating protease (FSAP) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''HABP2'' gene. The protein encoded by this gene is an extracellular serine protease which binds hyaluronic acid. It is involved in cell adhesion. The protein is synthesized as a single chain, but then undergoes an autoproteolytic event to form the functional heterodimer. Further autoproteolysis leads to smaller, inactive peptides. Two transcript variants utilizing alternative polyA Polyadenylation is the addition of a poly(A) tail to an RNA transcript, typically a messenger RNA (mRNA). The poly(A) tail consists of multiple adenosine monophosphates; in other words, it is a stretch of RNA that has only adenine bases. In euka ... sites exist for this gene. References Further reading * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * {{gene-10-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
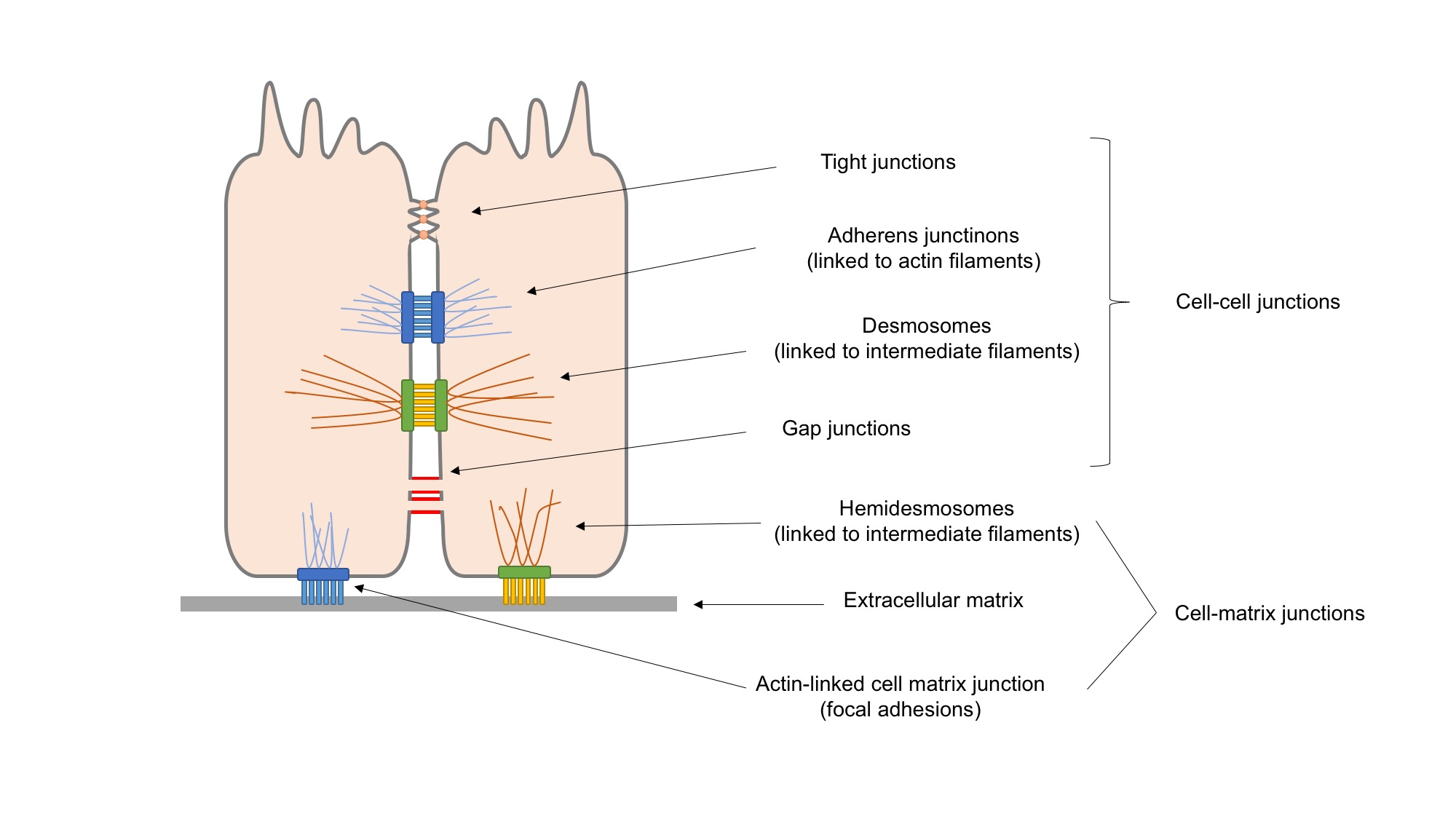
Cell Adhesion
Cell adhesion is the process by which cells interact and attach to neighbouring cells through specialised molecules of the cell surface. This process can occur either through direct contact between cell surfaces such as Cell_junction, cell junctions or indirect interaction, where cells attach to surrounding extracellular matrix (ECM), a gel-like structure containing molecules released by cells into spaces between them. Cells adhesion occurs from the interactions between cell adhesion molecules, cell-adhesion molecules (CAMs), transmembrane proteins located on the cell surface. Cell adhesion links cells in different ways and can be involved in signal transduction for cells to detect and respond to changes in the surroundings. Other cellular processes regulated by cell adhesion include cell migration and tissue development in multicellular organisms. Alterations in cell adhesion can disrupt important cellular processes and lead to a variety of diseases, including cancer and arthrit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Extracellular Matrix
In biology, the extracellular matrix (ECM), also called intercellular matrix (ICM), is a network consisting of extracellular macromolecules and minerals, such as collagen, enzymes, glycoproteins and hydroxyapatite that provide structural and biochemical support to surrounding cells. Because multicellularity evolved independently in different multicellular lineages, the composition of ECM varies between multicellular structures; however, cell adhesion, cell-to-cell communication and differentiation are common functions of the ECM. The animal extracellular matrix includes the interstitial matrix and the basement membrane. Interstitial matrix is present between various animal cells (i.e., in the intercellular spaces). Gels of polysaccharides and fibrous proteins fill the interstitial space and act as a compression buffer against the stress placed on the ECM. Basement membranes are sheet-like depositions of ECM on which various epithelial cells rest. Each type of connective tissue ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cell Signalling
In biology, cell signaling (cell signalling in British English) is the process by which a cell interacts with itself, other cells, and the environment. Cell signaling is a fundamental property of all cellular life in both prokaryotes and eukaryotes. Typically, the signaling process involves three components: the signal, the receptor, and the effector. In biology, signals are mostly chemical in nature, but can also be physical cues such as pressure, voltage, temperature, or light. Chemical signals are molecules with the ability to bind and activate a specific receptor. These molecules, also referred to as ligands, are chemically diverse, including ions (e.g. Na+, K+, Ca2+, etc.), lipids (e.g. steroid, prostaglandin), peptides (e.g. insulin, ACTH), carbohydrates, glycosylated proteins (proteoglycans), nucleic acids, etc. Peptide and lipid ligands are particularly important, as most hormones belong to these classes of chemicals. Peptides are usually polar, hydrophilic molecules ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cancer
Cancer is a group of diseases involving Cell growth#Disorders, abnormal cell growth with the potential to Invasion (cancer), invade or Metastasis, spread to other parts of the body. These contrast with benign tumors, which do not spread. Possible Signs and symptoms of cancer, signs and symptoms include a lump, abnormal bleeding, prolonged cough, unexplained weight loss, and a change in defecation, bowel movements. While these symptoms may indicate cancer, they can also have other causes. List of cancer types, Over 100 types of cancers affect humans. Tobacco use is the cause of about 22% of cancer deaths. Another 10% are due to obesity, poor Diet (nutrition), diet, sedentary lifestyle, lack of physical activity or Alcohol abuse, excessive alcohol consumption. Other factors include certain infections, exposure to ionizing radiation, and environmental pollutants. infectious causes of cancer, Infection with specific viruses, bacteria and parasites is an environmental factor cau ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |