|
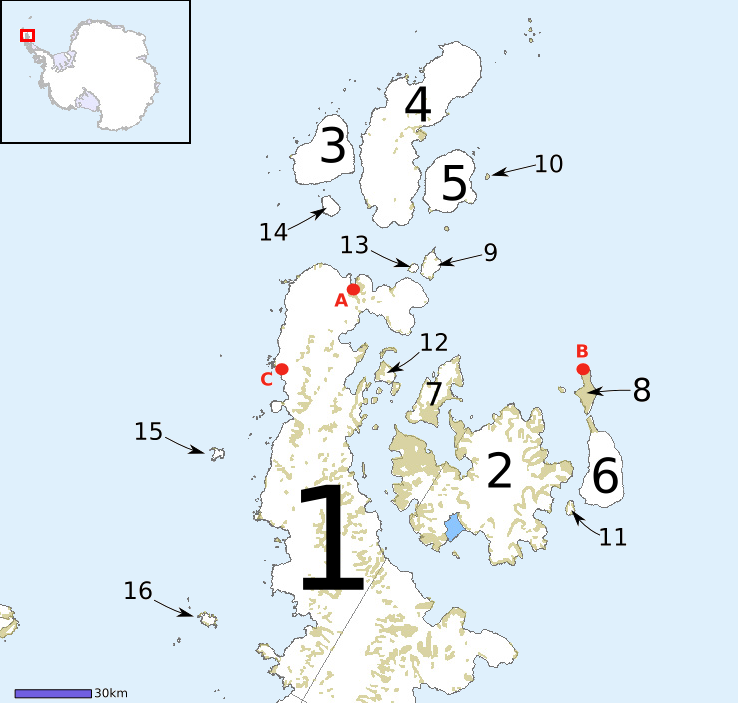
Hurst Bay
The Naze () is a peninsula in north James Ross Island, marking the southeast entrance to Herbert Sound and extending about northeast from Terrapin Hill toward the south-central shore of Vega Island. Location The Naze is to the east of Croft Bay extending north into Herbert Sound towards Vega Island. It is east of Ulu Peninsula, which forms the west side of Croft Bay, and north of Mount Haddington. Discovery and name The Naze was discovered and named "Nasudden" by the Swedish Antarctic Expedition (SwedAE), 1901-04, under Otto Nordenskjöld. The recommended form is the English version used by Nordenskjold. Features Terrapin Hill . Rounded, reddish-colored hill, high high, standing at the south end of The Naze. This area was first explored by the SwedAE, 1901-04, under Otto Nordenskjöld. Terrapin Hill was first charted by the FIDS, 1945, who in 1948 applied this name which is descriptive of its shape. Fortress Hill . A hill, high, which stands north of Terrapin Hi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
James Ross Island
James Ross Island () is a large island off the southeast side and near the northeastern extremity of the Antarctic Peninsula, from which it is separated by Prince Gustav Channel. Rising to , it is irregularly shaped and extends in a north–south direction. Location James Ross Island is separated from Trinity Peninsula, at the tip of the Antarctic Peninsula to the northwest, by the Prince Gustav Channel. Vega Island is to the north of the island, separated from James Ross Island by the Herbert Sound. Erebus and Terror Gulf is to the northeast. Seymour Island and Snow Hill Island are to the southeast. It is in the James Ross Island group. The island was connected to the Antarctic mainland by an ice shelf until 1995, when the ice shelf collapsed, making the Prince Gustav Channel passable for the first time. Mendel Polar Station, the first Czech Antarctic Base, is located on the island. Exploration and name James Ross Island was charted in October 1903 by the Swedish Antarct ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Herbert Sound
The James Ross Island group () is a group of islands located close to the northeastern tip of the Antarctic Peninsula. The largest islands in the group are James Ross Island, Snow Hill Island, Vega Island, and Seymour Island. The islands lie to the south of the Joinville Island group. The groups contains several scientific bases, notably Marambio Base, and numerous important palaeontological sites. Location The James Ross Island group lies in Graham Land to the east of the tip of Trinity Peninsula, which is itself the tip of the Antarctic Peninsula. It is separated from the mainland by Prince Gustav Channel, to the west. Eagle Island is to the north of this channel. The Erebus and Terror Gulf is to the northeast. The Weddell Sea is to the south and east. The main islands are James Ross Island, separated from Vega Island to the north by Herbert Sound, Seymour Island, Snow Hill Island and Lockyer Island. Features Herbert Sound . A sound extending from Cape Lachman ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vega Island
Vega Island () is an island in Antarctica, long and wide, which is the northernmost of the James Ross Island group and lies in the west part of Erebus and Terror Gulf. It is separated from James Ross Island by Herbert Sound and from Trinity Peninsula by Prince Gustav Channel. Location Vega Island is in Graham Land, to the southeast of the Trinity Peninsula, which is the tip of the Antarctic Peninsula. Erebus and Terror Gulf is to the east. James Ross Island is to the south, and the Ulu Peninsula of James Ross Island is to the west, separated from Vega Island by the Herbert Sound. The Prince Gustav Channel separates it from Corry Island and Eagle Island to the north. Cape Gordon is at the east end of the island. Sailing directions The US Defense Mapping Agency's ''Sailing Directions for Antarctica'' (1976) describes Vega Island as follows: Name Vega Island was named by Dr. Otto Nordenskjöld, leader of the Swedish Antarctic Expedition (SwedAE; 1901–04), apparen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trinity Peninsula
Trinity Peninsula is the northernmost part of the Antarctic Peninsula. It extends northeastward for about 130 km (80 mi) to Cape Dubouzet from an imaginary line connecting Cape Kater on the north-west coast and Cape Longing on the south-east coast. Prime Head is the northernmost point of this peninsula. Some 20 kilometers southeast of Prime Head is Hope Bay, Antarctica, Hope Bay with the year-round Argentinian Esperanza Base. History It was first sighted on 30 January 1820 by Edward Bransfield, Master, Royal Navy, immediately after his charting of the newly discovered South Shetland Islands nearby. In the century following the peninsula's discovery, chartmakers used various names (Trinity Land, Palmer Land, and Land of Louis Philippe) for this portion of it, each name having some historical merit. The recommended name derives from "Trinity Land", given by Bransfield during 1820 in likely recognition of the Corporation of Trinity House, Britain's historical maritime pil ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Croft Bay
Croft Bay () is a bay which indents the north-central side of James Ross Island and forms the southern part of Herbert Sound, south of the northeastern end of the Antarctic Peninsula. Location Croft Bay deeply indents the north shore of James Ross Island, which lies to the southwest of Trinity Peninsula, at the tip of the Antarctic Peninsula in Graham Land. The bay opens into Herbert Sound, to the north, which separates in from Vega Island. The Ulu Peninsula defines its west margin. Exploration and name Croft Bay was discovered in 1903 by the Swedish Antarctic Expedition under Otto Nordenskiöld. It was charted in 1945 by the Falkland Islands Dependencies Survey (FIDS), who named it for William Noble Croft, a FIDS geologist at Hope Bay in 1946. Features Blancmange Hill . An outstanding ice-free coastal landmark located northeast of Stark Point on the east side of Croft Bay. Named bythe UK Antarctic Place-Names Committee (UK-APC) following FIDS surveys taken 1958–1961 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ulu Peninsula
Ulu Peninsula () is that portion of James Ross Island northwest of the narrow neck of land between Rohss Bay and Croft Bay, extending from Cape Obelisk to Cape Lachman, in Antarctica. Location Ulu Peninsula forms the northwest of James Ross Island. It is separated from Trinity Peninsula, at the tip of the Antarctic Peninsula to the west, by the Prince Gustav Channel. Vega Island is to the east of the peninsula. Name Ulu Peninsula was named descriptively by the United Kingdom Antarctic Place-Names Committee (UK-APC) in 1987. In plan view the cove is shaped like an ulu, a type of knife traditionally used by Inuit women. Southwest features Features to the southwest of Holluschickie Bay include, from south to north, Crisscross Crags . An irregularly shaped system of crags with arms extending in four directions, rising to high east of Rum Cove. Named descriptively by the UK-APC in 1987. Rum Cove . A cove indenting the northwest coast of James Ross Island between Tumble ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mount Haddington
Mount Haddington is a massive high shield volcano comprising much of James Ross Island in Graham Land, Antarctica. It is wide and has had numerous subglacial eruptions throughout its history, forming many tuyas. Some of its single eruptions were bigger in volume than a whole normal-sized volcano. Old eruption shorelines are widespread on the volcano's deeply eroded flanks. Haddington formed along the Larsen Rift dominantly during the Miocene and Pliocene epochs but more recent eruptions have produced tuff cones on its slopes. The youngest tuff cones and pyroclastic cones on the eastern slope are situated below the summit icecap and may have formed in the last few thousand years. Effusive eruptions have created large deltas composed of hyaloclastite breccia and lava flows. Mount Haddington was discovered on December 31, 1842 by the Ross expedition, a voyage of scientific exploration of the Antarctic from 1839 to 1843 led by James Clark Ross. Ross named the mountain after the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Swedish Antarctic Expedition
The Swedish Antarctic Expedition of 1901–1903 was a scientific expedition led by Otto Nordenskjöld and Carl Anton Larsen. It was the first Swedish endeavour to Antarctica in the Heroic Age of Antarctic Exploration. Background Otto Nordenskjöld, a Swedish geologist and geographer, organized and led a scientific expedition of the Antarctic Peninsula. The expedition's overall command was placed under the Norwegian Carl Anton Larsen, an experienced Antarctic explorer who served as captain of , and who had previously commanded a whaling reconnaissance mission in 1892–1893. Seven other scientists, including archaeologist Johan Gunnar Andersson, botanist Carl Skottsberg, and zoologist Axel Ohlin, along with 16 officers and men joined them on the voyage. On 16 October 1901, the ''Antarctic'' left the Port of Gothenburg. Events Despite its end and the great hardships endured, the expedition would be considered a scientific success, with the parties having explored mu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Otto Nordenskjöld
Nils Otto Gustaf Nordenskjöld (6 December 1869 – 2 June 1928) was a Swedish geologist, geographer, and polar explorer. Early life Nordenskjöld was born in Hässleby in Småland in eastern Sweden, in a family that included his maternal uncle, the polar explorer Adolf Erik Nordenskiöld, and cousin Gustaf Nordenskiöld. His father and mother were cousins, but his father's family name was "Nordenskjöld", while his mother's family name was spelled "Nordenskiöld". He studied at Uppsala University, obtaining a doctorate in geology in 1894, and later became a lecturer and then associate professor in the university's geology department. Career Otto Nordenskjöld led mineralogical expeditions to Patagonia in the 1890s, and to Alaska and the Klondike area in 1898. Antarctic Expedition Nordenskjöld led the 1901–1904 Swedish Antarctic Expedition. Their ship ''Antarctic'', commanded by the seasoned Antarctic sailor Carl Anton Larsen, visited Buenos Aires and the Falkla ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Falkland Islands Dependencies Survey
The Falkland Islands and Dependencies Aerial Survey Expedition (FIDASE) was an aerial survey of the Falkland Islands Dependencies The Falkland Islands Dependencies was the constitutional arrangement from 1843 until 1985 for administering the various British territories in List of Antarctic and sub-Antarctic islands, Sub-Antarctica and Antarctica which were governed from t ... and the Antarctic Peninsula which took place in the 1955–56 and 1956–57 southern summers. Funded by the Colonial Office and organized by Peter Mott, the survey was carried out by Hunting Aerosurveys Ltd. The expedition was based at Deception Island and utilized the ''Oluf Sven'', two Canso flying-boats, and several helicopters. The photographic collection, held by the British Antarctic Survey as the United Kingdom Antarctic Mapping Centre, comprises about 12,800 frames taken on 26,700 kilometers of ground track. References {{reflist British Antarctic Territory Surveying of the United Kingdom ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
UK Antarctic Place-Names Committee
The UK Antarctic Place-Names Committee (or UK-APC) is a United Kingdom government committee, part of the Foreign and Commonwealth Office, responsible for recommending names of geographical locations within the British Antarctic Territory (BAT) and the South Georgia and the South Sandwich Islands (SGSSI). Such names are formally approved by the Commissioners of the BAT and SGSSI respectively and published in the BAT Gazetteer and the SGSSI Gazetteer maintained by the Committee. The BAT names are also published in the international Composite Gazetteer of Antarctica maintained by SCAR. The Committee may also consider proposals for new place names for geographical features in areas of Antarctica outside BAT and SGSSI, which are referred to other Antarctic place-naming authorities or decided by the Committee itself if situated in the unclaimed sector of Antarctica. Names attributed by the committee * Anvil Crag, named for descriptive features * Anckorn Nunataks, named after J. F ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |