|
Hunzahúa Well
The Hunzahúa Well (Spanish: ''Pozo de Hunzahúa'') is an archeological site of the Muisca located in the city of Tunja, Boyacá, which in the time of the Muisca Confederation was called Hunza. The well is named after the first ''zaque'' of Hunza, Hunzahúa. The well was called ''Pozo de Donato'' for a while, after 17th century Jerónimo Donato de Rojas.Hunzahúa Well - Pueblos Originarios The well is located on the campus of the Pedagogical and Technological University of Colombia in Tunja. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hunzahúa
Hunzahúa was the first ''zaque''; ruler of the northern Muisca with capital Hunza, named after him. His contemporary ''zipa'' of the southern Muisca was Meicuchuca. Biography Hunzahúa, heir of Idacansás, was a ''cacique'' in the sacred valley of the ''iraca'' and was chosen by the other ''caciques'' of the region to make peace between the battling parties. He became the first ''zaque'' of the northern Muisca region based in Hunza, present-day Tunja, and one of his policies was the ban on the use of weapons. According to Muisca scholar Javier Ocampo López, who wrote extensively about the religion and mythology of the Muisca, his mother was named Faravita and his sister Noncetá. Legend tells that Hunzahúa fell in love with his older sister and made her his wife when he left Hunza for Chipatá. Faravita, the mother of the ''zaque'', disagreed with the marriage of her two children and attacked the couple, spilling a bowl of chicha. This created the Hunzahúa Well. When Hun ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tundama
Tundama or Saymoso (15th century - Duitama, late December 1539) was a ''cacique'' of the Muisca Confederation, a loose confederation of different rulers of the Muisca who inhabited the central highlands (Altiplano Cundiboyacense) of the Colombian Andes. The city of Tundama, currently known as Duitama and part of the Tundama Province, Boyacá, were named after the ''cacique''. Tundama ruled over the northernmost territories of the Muisca, submitted last by the Spanish conquistadores. Tundama was killed late December 1539 with a large hammer by Spanish conquistador Baltasar Maldonado. His successor, ''Don Juan'' was killed shortly after, ending the reign of the Muisca in the New Kingdom of Granada, the name for present-day Colombia and a part of Venezuela in the Spanish Empire. Knowledge about Tundama has been compiled by scholar Lucas Fernández de Piedrahita. Background In the time before the Spanish conquest of central Colombia, there were several main rulers and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cojines Del Zaque
The ''Cojines del Zaque'' (English: "Cushions of the ''Zaque''") is an archeological site of the Muisca located in the city of Tunja, Boyacá, which in the time of the Muisca Confederation was called Hunza. The ''cojines'' are two round stones used in the religion of the Muisca to worship Sun god Sué and his wife; Moon goddess Chía. When the Spanish conquistadores arrived, they called them ''Cojines del Diablo''. Background During the time before the Spanish conquest of the Muisca, the central highlands of the Colombian Andes (Altiplano Cundiboyacense) were populated by the Muisca. This advanced civilization had its own religion and rituals, centered around the most important deities Sué and Chía. The northern territories were ruled by the ''iraca'' of Sugamuxi, the ''tundama'' of Tundama and the ''zaque'' based in Hunza. Description The Cojines are two circular stones made of sandstone located at the base of the San Lázaro hill in Tunja. The northernmost ''Cojín'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Muisca Religion
Muisca religion describes the religion of the Muisca who inhabited the central highlands of the Colombian Andes before the Spanish conquest of the Muisca. The Muisca formed a confederation of holy rulers and had a variety of deities, temples and rituals incorporated in their culture. Supreme being of the Muisca was Chiminigagua who created light and the Earth. He was not directly honoured, yet that was done through Chía, goddess of the Moon, and her husband Sué, god of the Sun. The representation of the two main celestial bodies as husband and wife showed the complementary character of man and woman and the sacred status of marriage.Muisca religion - Pueblos Originarios - accessed 04-05-2016 The Muisca worshipped their gods at sacred sites, both natural, such as |
Conquistador
Conquistadors (, ) or conquistadores (, ; meaning 'conquerors') were the explorer-soldiers of the Spanish Empire, Spanish and Portuguese Empires of the 15th and 16th centuries. During the Age of Discovery, conquistadors sailed beyond Europe to the Americas, Oceania, Africa, and Asia, Colonization, colonizing and opening trade routes. They brought much of the Americas under the dominion of Spain and Portugal. After arrival in the West Indies in 1492, the Spanish, usually led by Hidalgo (nobility), hidalgos from the west and south of Spain, began building an American empire in the Caribbean using islands such as Captaincy General of Santo Domingo, Hispaniola, Captaincy General of Cuba, Cuba, and Captaincy General of Puerto Rico, Puerto Rico as bases. From 1519 to 1521, Hernán Cortés waged a Spanish conquest of the Aztec Empire, campaign against the Aztec Empire, ruled by Moctezuma II. From the territories of the Aztec Empire, conquistadors expanded Spanish rule to northern Cent ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
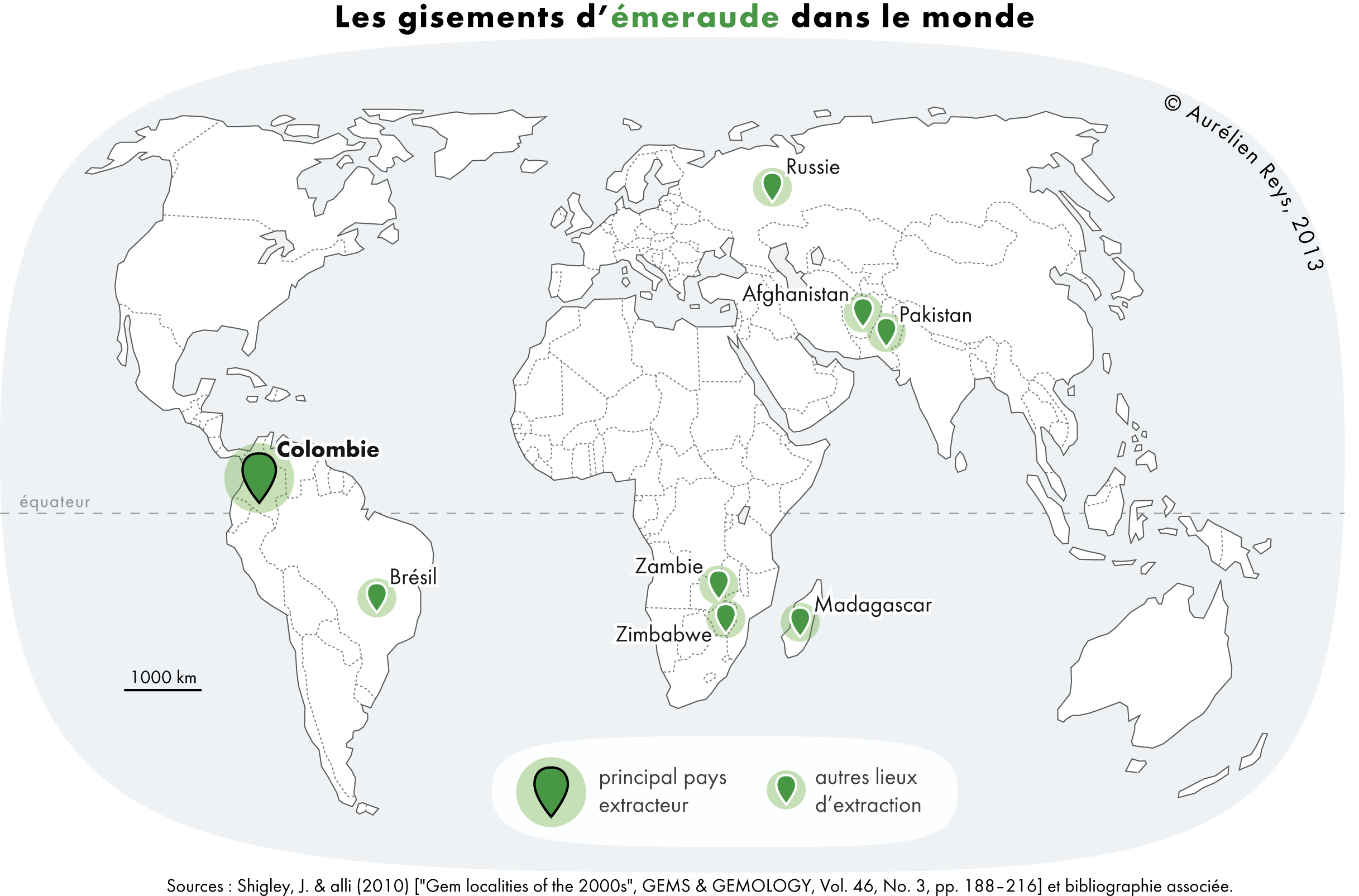
Emerald
Emerald is a gemstone and a variety of the mineral beryl (Be3Al2(SiO3)6) colored green by trace amounts of chromium or sometimes vanadium.Hurlbut, Cornelius S. Jr. and Kammerling, Robert C. (1991) ''Gemology'', John Wiley & Sons, New York, p. 203, . Beryl has a hardness of 7.5–8 on the Mohs scale. Most emeralds are highly included, so their toughness (resistance to breakage) is classified as generally poor. Emerald is a cyclosilicate. Etymology The word "emerald" is derived (via fro, esmeraude and enm, emeraude), from Vulgar Latin: ''esmaralda''/''esmaraldus'', a variant of Latin ''smaragdus'', which was a via grc, σμάραγδος (smáragdos; "green gem") from a Semitic language. According to Webster's Dictionary the term emerald was first used in the 14th century. Properties determining value Emeralds, like all colored gemstones, are graded using four basic parameters–the four ''C''s of connoisseurship: ''color'', ''clarity,'' ''cut'' and ''carat weight''. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gold
Gold is a chemical element with the symbol Au (from la, aurum) and atomic number 79. This makes it one of the higher atomic number elements that occur naturally. It is a bright, slightly orange-yellow, dense, soft, malleable, and ductile metal in a pure form. Chemically, gold is a transition metal and a group 11 element. It is one of the least reactive chemical elements and is solid under standard conditions. Gold often occurs in free elemental (native state), as nuggets or grains, in rocks, veins, and alluvial deposits. It occurs in a solid solution series with the native element silver (as electrum), naturally alloyed with other metals like copper and palladium, and mineral inclusions such as within pyrite. Less commonly, it occurs in minerals as gold compounds, often with tellurium ( gold tellurides). Gold is resistant to most acids, though it does dissolve in aqua regia (a mixture of nitric acid and hydrochloric acid), forming a soluble tetrachloroau ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quemuenchatocha
Quemuenchatocha or Quimuinchateca (named in the earliest sources Eucaneme) ( Hunza, 1472– Ramiriquí, 1538) was the second-last '' hoa'' of Hunza, currently known as Tunja, as of 1490. He was the ruler of the northern Muisca when the Spanish conquistadores arrived in the Muisca highlands. His contemporary enemy '' psihipquas'' of the southern Muisca were successively Nemequene and Bogotá. Biography Eucaneme was eighteen years old when he accessed the throne, succeeding his predecessor Michuá as ruler of the northern Muisca. His reign was cruel and under his tyranny the Muisca feared him. His rule was so brutal that when the Spanish conquerors entered the outskirts of the capital Hunza and found a hill with poles where bodies were dangling, they named it ''Cerro de la Horca'' ("Gallows Hill").Biography of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tequendama Falls
The Tequendama Falls () is a high waterfall of the Bogotá River, located southwest of Bogotá in the municipality of Soacha. Established in approximately 10,000 BCE, El Abra and Tequendama were the first permanent settlements in Colombia. One of the country's tourist attractions, the falls are located in a forested area west of Bogotá. The river surges through a rocky gorge that narrows to about at the brink of the high falls. During the month of December the falls become completely dry. The falls, once a common site for suicides, may be reached by road from Bogotá. Muisca origin The name ''Tequendama'' means in Chibcha: "he who precipitated downward". According to the Muisca religion, the waterfall was created by the legendary hero Bochica, who used his staff to break the rock and release the water that covered the Bogotá savanna. According to another legend, during the Spanish conquest and evangelization of the Americas, in order to escape the new colonial order ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Susa, Cundinamarca
Susa is a town and municipality in the Ubaté Province, part of the Cundinamarca Department, Colombia. The town centre is located at an altitude of on the Altiplano Cundiboyacense at from the capital Bogotá. Susa borders Simijaca, Fúquene, San Miguel de Sema and Lake Fúquene. Etymology In the Chibcha language of the Muisca, ''susa'' means "white reed" or "soft reed". History The area of Susa before the Spanish conquest was part of the Muisca Confederation. Initially loyal to the ''zaque'' of Hunza, Susa changed rule around 1490 when it was submitted by ''zipa'' Saguamanchica. In pre-Columbian times, the territory of the current municipality of Susa was inhabited by the Muiscas. Around 1537, the passage of Gonzalo Jiménez de Quesada through the territory of Susa to the south was recorded.14 On August 2, 1600, the Oidor Luis Enríquez issued from Cucunubá the order of founding of the new Indian towns of Susa, Simijaca, Fúquene and Nemoquá. On the same August 2, L ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chicha
''Chicha'' is a fermented (alcoholic) or non-fermented beverage of Latin America, emerging from the Andes and Amazonia regions. In both the pre- and post- Spanish conquest periods, corn beer ('' chicha de jora'') made from a variety of maize landraces has been the most common form of ''chicha''. However, ''chicha'' is also made from a variety of other cultigens and wild plants, including, among others, quinoa (''Chenopodium quinia''), kañiwa (''Chenopodium pallidicaule''), peanut, manioc (also called yuca or cassava), palm fruit, rice, potato, oca (''Oxalis tuberosa''), and chañar (''Geoffroea decorticans''). There are many regional variations of ''chicha''. In the Inca Empire, ''chicha'' had ceremonial and ritual uses. Etymology and related phrases The exact origin of the word ''chicha'' is debated. One belief is that the word ''chicha'' is of Taino origin and became a generic term used by the Spanish to define any and all fermented beverages brewed by indigenous pe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chipatá, Santander
Chipatá is a town and municipality in the Vélez Province, part of the Santander Department in northeastern Colombia. The urban centre is situated at an altitude of at a distance of from the department capital Bucaramanga and at from the national capital Bogotá. The municipality borders Vélez in the south and west, La Paz in the north, San Benito, Güepsa and Barbosa in the east. Etymology Chipatá is named after ''cacique Chipatá'' and means in Chibcha: ''chi'' = "our", ''pa'' = "father", ''tá'' = "farmland"; "farmland of our father". History The area of Chipatá was one of the northernmost territories of the Muisca, bordered by Guane territories to the north and east. It was ruled by a ''cacique'', who was independent within the loose Muisca Confederation. Modern Chipatá was the first settlement founded by conquistador Gonzalo Jiménez de Quesada and his brother, on March 8, 1537, during his expedition of conquest. After the local elections of October 20 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |