|
Human Microbiota
Human microbiota are microorganisms (bacteria, viruses, fungi and archaea) found in a specific environment. They can be found in the stomach, intestines, skin, genitals and other parts of the body. Various body parts have diverse microorganisms. Some microbes are specific to certain body parts and others are associated with many microbiomes. This article lists some of the species recognized as belonging to the human microbiome and focuses on the oral, vaginal, ovarian follicle, uterus and the male reproductive tract microbiota. Categories of bacteria The "reference" 70 kg human body is estimated to have around 39 trillion bacteria with a mass of about 0.2 kg. These can be separated into about 10,000 microbial species, about 180 of the most studied is listed below here. However, these can broadly be put into three categories: Spheres or ball-shaped (cocci bacteria) Cocci are usually round or spherical in shape. They can form clusters and are non-motile. Examples incl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Human Microbiome
The human microbiome is the aggregate of all microbiota that reside on or within human tissues and biofluids along with the corresponding List of human anatomical features, anatomical sites in which they reside, including the human gastrointestinal tract, gastrointestinal tract, Human skin, skin, mammary glands, seminal fluid, uterus, ovarian follicles, lung, saliva, oral mucosa, conjunctiva, and the biliary tract. Types of List of human microbiota, human microbiota include Bacterium, bacteria, archaea, Fungus, fungi, protists, and viruses. Though micro-animals can also live on the human body, they are typically excluded from this definition. In the context of genomics, the term ''human microbiome'' is sometimes used to refer to the collective genomes of resident microorganisms; however, the term ''metagenome, human metagenome'' has the same meaning. The human body hosts many microorganisms, with approximately the same order of magnitude of non-human cells as human cells. Some ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cutibacterium Acnes
''Cutibacterium acnes'' (''Propionibacterium acnes'') is the relatively slow-growing, typically aerotolerant anaerobic, gram-positive bacterium (rod) linked to the skin condition of acne; it can also cause chronic blepharitis and endophthalmitis, the latter particularly following intraocular surgery. Its genome has been sequenced and a study has shown several genes can generate enzymes for degrading skin and proteins that may be immunogenic (activating the immune system). The species is largely commensal and part of the skin flora present on most healthy adult humans' skin. It is usually just barely detectable on the skin of healthy preadolescents. It lives, among other things, primarily on fatty acids in sebum secreted by sebaceous glands in the follicles. It may also be found throughout the gastrointestinal tract. Originally identified as ''Bacillus acnes'', it was later named ''Propionibacterium acnes'' for its ability to generate propionic acid. In 2016, ''P. acnes'' was ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Staphylococcus Epidermidis
''Staphylococcus epidermidis'' is a Gram-positive bacterium, and one of over 40 species belonging to the genus ''Staphylococcus''. It is part of the human flora, normal human microbiota, typically the skin flora, skin microbiota, and less commonly the mucosal microbiota and also found in marine sponges. It is a facultative anaerobic bacteria. Although ''S. epidermidis'' is not usually Pathogenic bacteria, pathogenic, patients with compromised immune systems are at risk of developing infection. These infections are generally Hospital-acquired infection, hospital-acquired. ''S. epidermidis'' is a particular concern for people with catheters or other surgical implants because it is known to form biofilms that grow on these devices. Being part of the normal skin microbiota, ''S. epidermidis'' is a frequent contaminant of specimens sent to the diagnostic laboratory. Some strains of ''S. epidermidis'' are highly salt tolerant and commonly found in marine environments. S.I. Paul et al ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Staphylococcus Aureus
''Staphylococcus aureus'' is a Gram-positive spherically shaped bacterium, a member of the Bacillota, and is a usual member of the microbiota of the body, frequently found in the upper respiratory tract and on the skin. It is often positive for catalase and nitrate reduction and is a facultative anaerobe, meaning that it can grow without oxygen. Although ''S. aureus'' usually acts as a commensal of the human microbiota, it can also become an opportunistic pathogen, being a common cause of skin infections including abscesses, respiratory infections such as sinusitis, and food poisoning. Pathogenic strains often promote infections by producing virulence factors such as potent protein toxins, and the expression of a cell-surface protein that binds and inactivates antibodies. ''S. aureus'' is one of the leading pathogens for deaths associated with antimicrobial resistance and the emergence of antibiotic-resistant strains, such as methicillin-resistant ''S. aur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
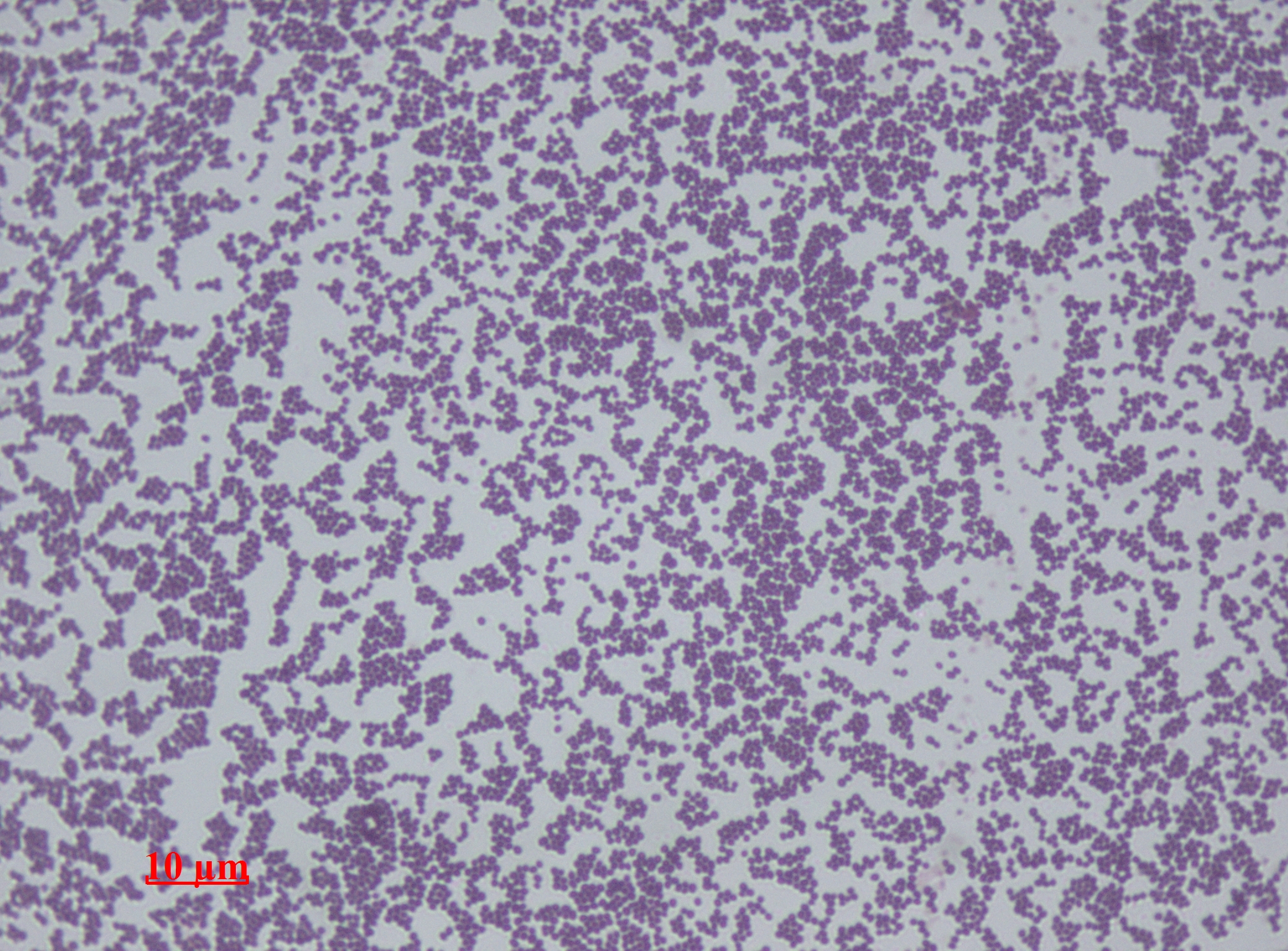
Sarcina (genus)
''Sarcina'' is a genus of gram-positive cocci bacteria in the family Clostridiaceae. A synthesizer of microbial cellulose, various members of the genus are human flora and may be found in the skin and large intestine. The genus takes its name from the Latin word "sarcina," meaning pack or bundle, after the cuboidal (2x2x2) cellular associations they form during division along three planes. The genus's type species is '' Sarcina ventriculi'', a variety found on the surface of cereal seeds, in soil, mud, and in the stomachs of humans, rabbits, and guinea pigs. Phylogeny The currently accepted taxonomy is based on the List of Prokaryotic names with Standing in Nomenclature (LPSN) and National Center for Biotechnology Information (NCBI) Species * '' Sarcina aurantiaca'' * '' Sarcina lutea'' has been reclassified to '' Micrococcus luteus'' * '' Sarcina troglodytae'' is a chimpanzee pathogen See also * List of bacterial orders * List of bacteria genera This article lists the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
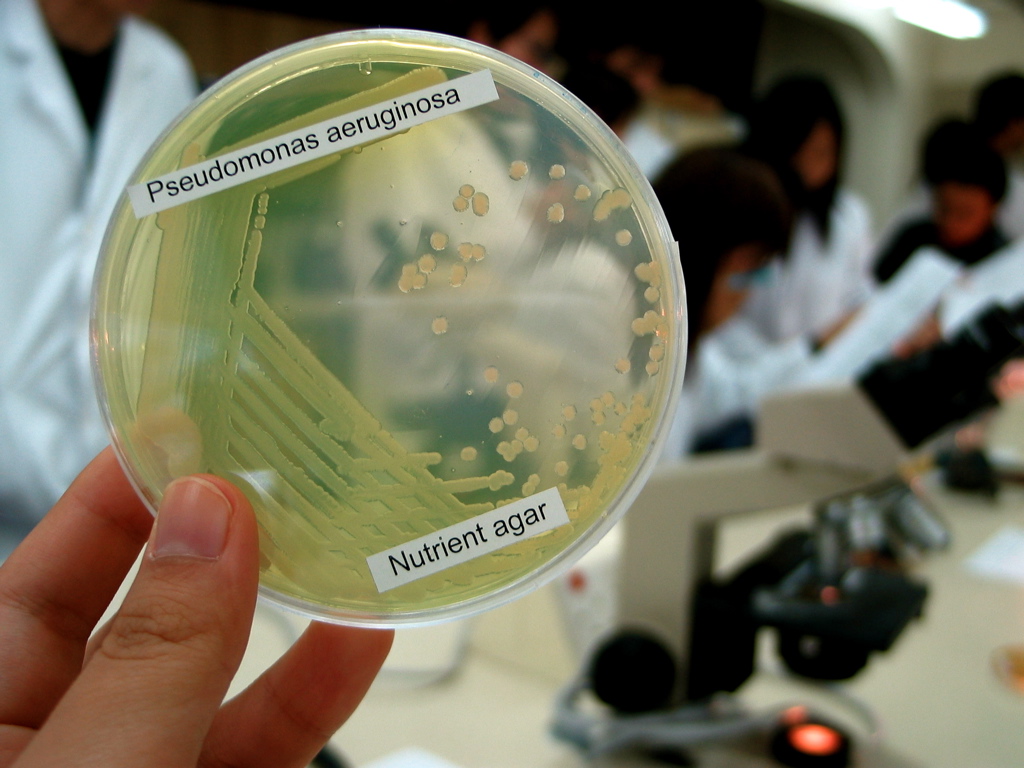
Pseudomonas Aeruginosa
''Pseudomonas aeruginosa'' is a common Bacterial capsule, encapsulated, Gram-negative bacteria, Gram-negative, Aerobic organism, aerobic–facultative anaerobe, facultatively anaerobic, Bacillus (shape), rod-shaped bacteria, bacterium that can cause disease in plants and animals, including humans. A species of considerable medical importance, ''P. aeruginosa'' is a multiple drug resistance, multidrug resistant pathogen recognized for its ubiquity, its Intrinsic and extrinsic properties, intrinsically advanced antibiotic resistance mechanisms, and its association with serious illnesses – hospital-acquired infections such as ventilator-associated pneumonia and various sepsis syndromes. ''P. aeruginosa'' is able to selectively inhibit various antibiotics from penetrating its outer membrane'' ''– and has high resistance to several antibiotics. According to the World Health Organization ''P. aeruginosa'' poses one of the greatest threats to humans in terms of an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Propionibacterium
''Propionibacterium'' is a gram-positive, anaerobic, rod-shaped genus of bacteria named for their unique metabolism: They are able to synthesize propionic acid by using unusual transcarboxylase enzymes. Its members are primarily facultative parasites and commensals of humans and other animals, living in and around the sweat glands, sebaceous glands, and other areas of the skin. They are virtually ubiquitous and do not cause problems for most people, but propionibacteria have been implicated in acne and other skin conditions. One study found the ''Propionibacterium'' was the most prevalent human skin-associated genus of microorganisms. In ruminants, propionibacteria reduce nitrate to nontoxic nitrogen compounds. Members of the genus ''Propionibacterium'' are widely used in the production of vitamin B12, tetrapyrrole compounds, and propionic acid, as well as in the probiotics and cheese industries. The strain ''Propionibacterium freudenreichii'' subsp. ''shermanii'' is used ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
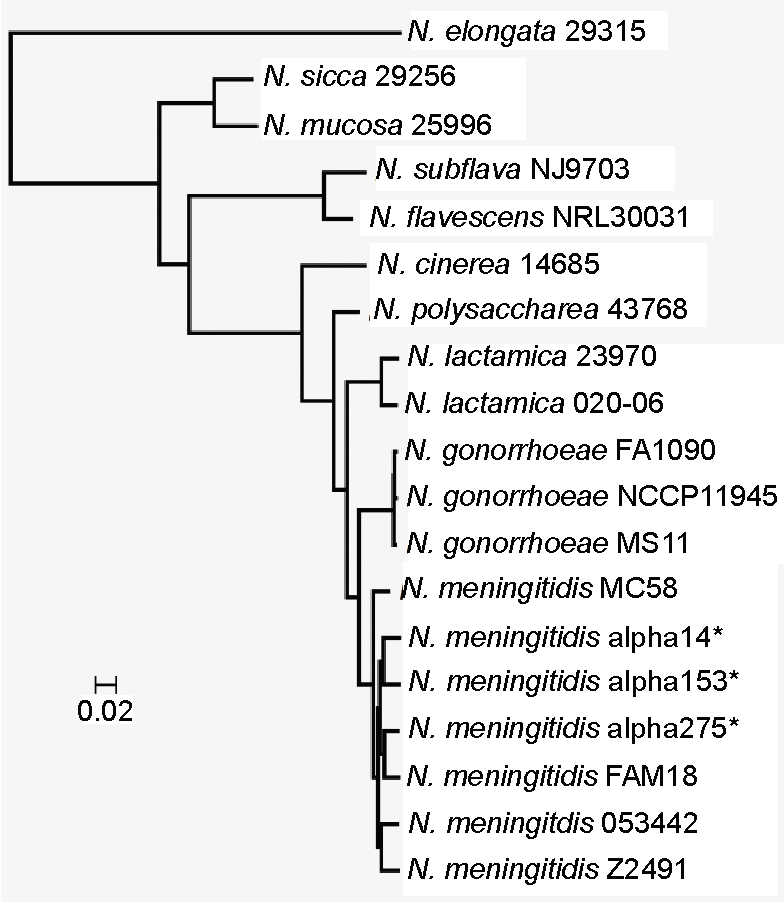
Neisseria
''Neisseria'' is a large genus of bacteria that colonize the mucous membranes of many animals. Of the 11 species that colonize humans, only two are pathogens: '' N. meningitidis'' and '' N. gonorrhoeae''. ''Neisseria'' species are Gram-negative bacteria included among the Pseudomonadota, a large group of Gram-negative forms. ''Neisseria'' diplococci resemble coffee beans when viewed microscopically. Pathogenesis and classification Pathogens Species of this genus (family Neisseriaceae) of parasitic bacteria grow in pairs and occasionally fours, and thrive best at 98.6 °F (37 °C) in the animal body or serum media. The genus includes: * '' N. gonorrhoeae'' (also called the gonococcus) causes gonorrhea. * '' N. meningitidis'' (also called the meningococcus) is one of the most common causes of bacterial meningitis and the causative agent of meningococcal septicaemia. The immune system's neutrophils are restricted in function due to the ability of ''Neisseria'' to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mycobacterium
''Mycobacterium'' is a genus of over 190 species in the phylum Actinomycetota, assigned its own family, Mycobacteriaceae. This genus includes pathogens known to cause serious diseases in mammals, including tuberculosis (''Mycobacterium tuberculosis, M. tuberculosis'') and leprosy (''Mycobacterium leprae, M. leprae'') in humans. The Greek language, Greek prefix ''myco-'' means 'fungus', alluding to this genus' Mold (fungus), mold-like colony surfaces. Since this genus has cell walls with a waxy lipid-rich outer layer containing high concentrations of mycolic acid, acid-fast staining is used to emphasize their resistance to acids, compared to other cell types. Mycobacterial species are generally aerobic, non-motile, and capable of growing with minimal nutrition. The genus is divided based on each species' pigment production and growth rate. While most ''Mycobacterium'' species are non-pathogenic, the genus' characteristic complex cell wall contributes to evasion from host defenses. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Micrococcus
''Micrococcus'', from Ancient Greek μικρός (''mikrós''), meaning "small", and κόκκος (''kókkos''), meaning "sphere", is a genus of bacteria in the Micrococcaceae family (biology), family. ''Micrococcus'' occurs in a wide range of environments, including water, dust, and soil. Micrococci have Gram-positive spherical cells ranging from about 0.5 to 3 micrometers in diameter and typically appear in tetrads. They are catalase positive, oxidase positive, indole negative and citrate test, citrate negative. ''Micrococcus'' has a substantial cell wall, which may comprise as much as 50% of the cell mass. The genome of ''Micrococcus'' is rich in guanine and cytosine (GC), typically exhibiting 65 to 75% GC-content. Micrococci often carry plasmids (ranging from 1 to 100 MDa in size) that provide the organism with useful traits. Some species of ''Micrococcus'', such as ''M. luteus'' (yellow) and ''M. roseus'' (red) produce yellow or pink colonies when grown on mannitol salt agar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Micrococcus Luteus
''Micrococcus luteus'' is a Gram-positive to Gram-variable, nonmotile, tetrad-arranging, pigmented, saprotrophic coccus bacterium in the family Micrococcaceae. It is urease and catalase positive. An obligate aerobe, ''M. luteus'' is found in soil, dust, water and air, and as part of the normal microbiota of the mammalian skin. The bacterium also colonizes the human mouth, mucosae, oropharynx and upper respiratory tract. ''Micrococcus luteus'' is generally harmless but can become an opportunistic pathogen in immunocompromised people or those with indwelling catheters. It resists antibiotic treatment by slowing of major metabolic processes and induction of unique genes. Its genome has a high G + C content. ''Micrococcus luteus'' is coagulase negative, bacitracin susceptible, and forms bright yellow colonies on nutrient agar (hence its scientific species name ''luteus'' which means "yellow" in Latin). ''Micrococcus luteus'' has been shown to survive in oligotrophic environment ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Malassezia
''Malassezia'' is a genus of fungi (specifically, a yeast belonging to the division Basidiomycota). Some species of ''Malassezia'' are found on the skin of animals, including humans. Because malassezia requires fat to grow, it is most common in areas with many sebaceous glandson the scalp, face, and upper part of the body. Role in human diseases ''Malassezia'' infections of human skin can cause or aggravate a variety of conditions, including dandruff, seborrheic dermatitis, and acne. Dermatitis and dandruff When ''Malassezia'' grows too rapidly, the natural renewal of cells is disturbed, and dandruff can appear with itching (a similar process may also occur with other fungi or bacteria). Identification of ''Malassezia'' on skin has been aided by the application of molecular or DNA-based techniques. These investigations show that ''M. globosa'' is the species that causes most skin disease in humans, and that it is the most common cause of dandruff and seborrhoeic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |