|
Human Genetic Variability
Human genetic variation is the genetic differences in and among populations. There may be multiple variants of any given gene in the human population (alleles), a situation called polymorphism. No two humans are genetically identical. Even monozygotic twins (who develop from one zygote) have infrequent genetic differences due to mutations occurring during development and gene copy-number variation. Differences between individuals, even closely related individuals, are the key to techniques such as genetic fingerprinting. The human genome has a total length of approximately 3.2 billion base pairs (bp) in 46 chromosomes of DNA as well as slightly under 17,000 bp DNA in cellular mitochondria. In 2015, the typical difference between an individual's genome and the reference genome was estimated at 20 million base pairs (or 0.6% of the total). As of 2017, there were a total of 324 million known variants from sequenced human genomes. Comparatively speaking, humans are a genetically ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
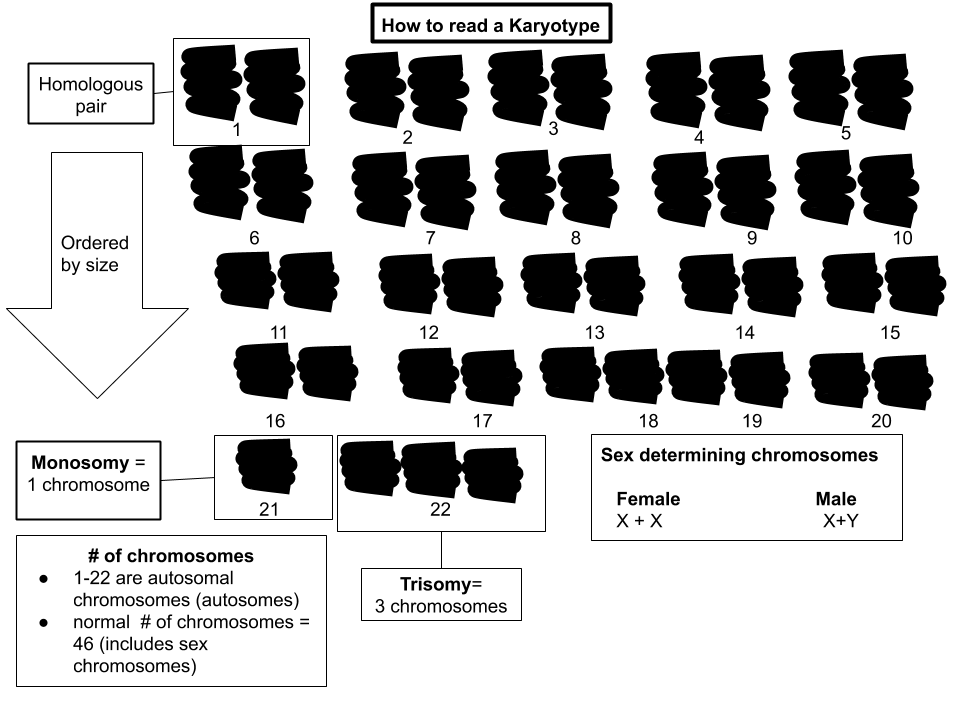
Human Karyotype
A karyotype is the general appearance of the complete set of chromosomes in the cells of a species or in an individual organism, mainly including their sizes, numbers, and shapes. Karyotyping is the process by which a karyotype is discerned by determining the chromosome complement of an individual, including the number of chromosomes and any abnormalities. A karyogram or idiogram is a graphical depiction of a karyotype, wherein chromosomes are generally organized in pairs, ordered by size and position of centromere for chromosomes of the same size. Karyotyping generally combines light microscopy and photography in the metaphase of the cell cycle, and results in a photomicrographic (or simply micrographic) karyogram. In contrast, a schematic karyogram is a designed graphic representation of a karyotype. In schematic karyograms, just one of the sister chromatids of each chromosome is generally shown for brevity, and in reality they are generally so close together that they look as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Science Daily
''ScienceDaily'' is an American website launched in 1995 that aggregates press releases and publishes lightly edited press releases (a practice called churnalism) about science, similar to Phys.org and EurekAlert!. History The site was founded by married couple Dan and Michele Hogan in 1995; Dan Hogan formerly worked in the public affairs department of Jackson Laboratory writing press releases. The site makes money from selling advertisements. the site said that it had grown "from a two-person operation to a full-fledged news business with worldwide contributors". At the time, it was run out of the Hogans' home, had no reporters, and only reprinted press releases. In 2012, Quantcast ranked it at 614 with 2.6 million U.S. visitors. Sections As of August 2023, ''ScienceDaily'' mainly has five sections, Health, Tech, Enviro, Society, and Quirky, the last of which includes the top news. References External links * Alexa - ScienceDaily��{{Webarchive, url=https://web.a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Miscarriage
Miscarriage, also known in medical terms as a spontaneous abortion, is an end to pregnancy resulting in the loss and expulsion of an embryo or fetus from the womb before it can fetal viability, survive independently. Miscarriage before 6 weeks of gestation is defined as biochemical loss by European Society of Human Reproduction and Embryology, ESHRE. Once ultrasound or histological evidence shows that a pregnancy has existed, the term used is clinical miscarriage, which can be "early" (before 12 weeks) or "late" (between 12 and 21 weeks). Spontaneous fetal termination after 20 weeks of gestation is known as a stillbirth. The term ''miscarriage'' is sometimes used to refer to all forms of pregnancy loss and pregnancy with abortive outcomes before 20 weeks of gestation. The most common symptom of a miscarriage is vaginal bleeding, with or without pain. Tissue (biology), Tissue and clot-like material may leave the uterus and pass through and out of the vagina. Risk factors for misc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sex Chromosome Disorders (other)
Sex chromosome anomalies belong to a group of genetic conditions that are caused or affected by the loss, damage or addition of one or both sex chromosomes (also called ''gonosomes''). In humans this may refer to: * 45, X, also known as Turner syndrome * 45,X/46,XY mosaicism, also known as X0/XY mosaicism and mixed gonadal dysgenesis * 46, XX/XY * 47, XXX, also known as trisomy X or triple X syndrome * 47, XXY, also known as Klinefelter syndrome * 47, XYY, also known as Jacobs syndrome * 48, XXXX, also known as tetrasomy X * 48, XXXY * 48, XXYY * 48, XYYY * 49, XXXXY * 49, XYYYY * 49, XXXXX, also known as pentasomy X * 46, XX gonadal dysgenesis * 46, XY gonadal dysgenesis, also known as Swyer syndrome * 46, XX male syndrome, also known as de la Chapelle syndrome In this list, the karyotype is summarized by the number of chromosomes, followed by the sex chromosomes present in each cell. (In the second and third cases the karyotype varies from cell to cell, while in th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chromosome Abnormalities
A chromosomal abnormality, chromosomal anomaly, chromosomal aberration, chromosomal mutation, or chromosomal disorder is a missing, extra, or irregular portion of chromosomal DNA. These can occur in the form of numerical abnormalities, where there is an atypical number of chromosomes, or as structural abnormalities, where one or more individual chromosomes are altered. Chromosome mutation was formerly used in a strict sense to mean a change in a chromosomal segment, involving more than one gene. Chromosome anomalies usually occur when there is an error in cell division following meiosis or mitosis. Chromosome abnormalities may be detected or confirmed by comparing an individual's karyotype, or full set of chromosomes, to a typical karyotype for the species via genetic testing. Sometimes chromosomal abnormalities arise in the early stages of an embryo, sperm, or infant. They can be caused by various environmental factors. The implications of chromosomal abnormalities depend on the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nucleotide
Nucleotides are Organic compound, organic molecules composed of a nitrogenous base, a pentose sugar and a phosphate. They serve as monomeric units of the nucleic acid polymers – deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) and ribonucleic acid (RNA), both of which are essential biomolecules within all Life, life-forms on Earth. Nucleotides are obtained in the diet and are also synthesized from common Nutrient, nutrients by the liver. Nucleotides are composed of three subunit molecules: a nucleobase, a pentose, five-carbon sugar (ribose or deoxyribose), and a phosphate group consisting of one to three phosphates. The four nucleobases in DNA are guanine, adenine, cytosine, and thymine; in RNA, uracil is used in place of thymine. Nucleotides also play a central role in metabolism at a fundamental, cellular level. They provide chemical energy—in the form of the nucleoside triphosphates, adenosine triphosphate (ATP), guanosine triphosphate (GTP), cytidine triphosphate (CTP), and uridine triph ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Karyotype
A karyotype is the general appearance of the complete set of chromosomes in the cells of a species or in an individual organism, mainly including their sizes, numbers, and shapes. Karyotyping is the process by which a karyotype is discerned by determining the chromosome complement of an individual, including the number of chromosomes and any abnormalities. A karyogram or idiogram is a graphical depiction of a karyotype, wherein chromosomes are generally organized in pairs, ordered by size and position of centromere for chromosomes of the same size. Karyotyping generally combines light microscopy and photography in the metaphase of the cell cycle, and results in a photomicrographic (or simply micrographic) karyogram. In contrast, a schematic karyogram is a designed graphic representation of a karyotype. In schematic karyograms, just one of the sister chromatids of each chromosome is generally shown for brevity, and in reality they are generally so close together that they look as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Founder Effect
In population genetics, the founder effect is the loss of genetic variation that occurs when a new population is established by a very small number of individuals from a larger population. It was first fully outlined by Ernst Mayr in 1942, using existing theoretical work by those such as Sewall Wright. As a result of the loss of genetic variation, the new population may be distinctively different, both genotypically and phenotypically, from the parent population from which it is derived. In extreme cases, the founder effect is thought to lead to the speciation and subsequent evolution of new species. In the figure shown, the original population has nearly equal numbers of blue and red individuals. The three smaller founder populations show that one or the other color may predominate (founder effect), due to random sampling of the original population. A population bottleneck may also cause a founder effect, though it is not strictly a new population. The founder effect o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neutral Theory Of Molecular Evolution
The neutral theory of molecular evolution holds that most evolutionary changes occur at the molecular level, and most of the variation within and between species are due to random genetic drift of mutant alleles that are selectively neutral. The theory applies only for evolution at the molecular level, and is compatible with phenotypic evolution being shaped by natural selection as postulated by Charles Darwin. The neutral theory allows for the possibility that most mutations are deleterious, but holds that because these are rapidly removed by natural selection, they do not make significant contributions to variation within and between species at the molecular level. A neutral mutation is one that does not affect an organism's ability to survive and reproduce. The neutral theory assumes that most mutations that are not deleterious are neutral rather than beneficial. Because only a fraction of gametes are sampled in each generation of a species, the neutral theory suggests that ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Genetic Drift
Genetic drift, also known as random genetic drift, allelic drift or the Wright effect, is the change in the Allele frequency, frequency of an existing gene variant (allele) in a population due to random chance. Genetic drift may cause gene variants to disappear completely and thereby reduce genetic variation. It can also cause initially rare alleles to become much more frequent and even fixed. When few copies of an allele exist, the effect of genetic drift is more notable, and when many copies exist, the effect is less notable (due to the law of large numbers). In the middle of the 20th century, vigorous debates occurred over the relative importance of natural selection versus neutral processes, including genetic drift. Ronald Fisher, who explained natural selection using Mendelian inheritance, Mendelian genetics, held the view that genetic drift plays at most a minor role in evolution, and this remained the dominant view for several decades. In 1968, population geneticist Mot ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Selection (biology)
Natural selection is the differential survival and reproduction of individuals due to differences in phenotype. It is a key mechanism of evolution, the change in the Heredity, heritable traits characteristic of a population over generations. Charles Darwin popularised the term "natural selection", contrasting it with selective breeding, artificial selection, which is intentional, whereas natural selection is not. Genetic diversity, Variation of traits, both Genotype, genotypic and phenotypic, exists within all populations of organisms. However, some traits are more likely to facilitate survival and reproductive success. Thus, these traits are passed the next generation. These traits can also become more Allele frequency, common within a population if the environment that favours these traits remains fixed. If new traits become more favoured due to changes in a specific Ecological niche, niche, microevolution occurs. If new traits become more favoured due to changes in the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mutation
In biology, a mutation is an alteration in the nucleic acid sequence of the genome of an organism, virus, or extrachromosomal DNA. Viral genomes contain either DNA or RNA. Mutations result from errors during DNA or viral replication, mitosis, or meiosis or other types of damage to DNA (such as pyrimidine dimers caused by exposure to ultraviolet radiation), which then may undergo error-prone repair (especially microhomology-mediated end joining), cause an error during other forms of repair, or cause an error during replication ( translesion synthesis). Mutations may also result from substitution, insertion or deletion of segments of DNA due to mobile genetic elements. Mutations may or may not produce detectable changes in the observable characteristics ( phenotype) of an organism. Mutations play a part in both normal and abnormal biological processes including: evolution, cancer, and the development of the immune system, including junctional diversity. Mutati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |