|
Human Genes
Lists of human genes are as follows: By chromosome Human chromosomes, each of which contains an incomplete list of genes located on that chromosome, are as follows: * Chromosome 1 * Chromosome 2 * Chromosome 3 * Chromosome 4 * Chromosome 5 * Chromosome 6 * Chromosome 7 * Chromosome 8 * Chromosome 9 * Chromosome 10 * Chromosome 11 * Chromosome 12 * Chromosome 13 * Chromosome 14 * Chromosome 15 * Chromosome 16 * Chromosome 17 * Chromosome 18 * Chromosome 19 * Chromosome 20 * Chromosome 21 * Chromosome 22 * X Chromosome * Y Chromosome Protein-coding genes The lists below constitute a complete list of all known human protein-coding genes: Transcription factors 1639 genes which encode proteins that are known or expected to function as human transcription factors: * List of human transcription factors See also * List of enzymes * List of proteins Proteins are a class of macromolecular organic compounds that are essential to life. They consist of a long polypeptide chain that us ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Human Chromosome
A chromosome is a package of DNA containing part or all of the genetic material of an organism. In most chromosomes, the very long thin DNA fibers are coated with nucleosome-forming packaging proteins; in eukaryotic cells, the most important of these proteins are the histones. Aided by chaperone proteins, the histones bind to and condense the DNA molecule to maintain its integrity. These eukaryotic chromosomes display a complex three-dimensional structure that has a significant role in transcriptional regulation. Normally, chromosomes are visible under a light microscope only during the metaphase of cell division, where all chromosomes are aligned in the center of the cell in their condensed form. Before this stage occurs, each chromosome is duplicated (S phase), and the two copies are joined by a centromere—resulting in either an X-shaped structure if the centromere is located equatorially, or a two-armed structure if the centromere is located distally; the joined co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chromosome 17
Chromosome 17 is one of the 23 pairs of chromosomes in humans. People normally have two copies of this chromosome. Chromosome 17 spans more than 84 million base pairs (the building material of DNA) and represents between 2.5 and 3% of the total DNA in cells. Chromosome 17 contains the Homeobox B gene cluster. Genes Number of genes The following are some of the gene count estimates of human chromosome 17. Because researchers use different approaches to genome annotation their predictions of the number of genes on each chromosome varies (for technical details, see gene prediction). The most conservative estimate, from CCDS, represents a lower bound on the total number of human protein-coding genes. Gene list The following is a partial list of genes on human chromosome 17. For complete list, see the link in the infobox on the right. The following are some of the genes and their corresponding Cytogenetic location on chromosome 17: p-arm q-arm Diseases and disord ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Disabled Human Pseudogenes
This is a list of human pseudogenes that are known to be disabled genes. * NCF1C pseudogene, associated with a type of white blood cell. It is related to NCF1. It may disable NCF1 by recombination, leading to chronic granulomatous disease. * GULO pseudogene, associated with the production of Vitamin C * hHaA pseudogene, associated with fur-like body hair: see hypertrichosis * DEFT1P pseudogene, associated with the immune system * HTR5BP pseudogene, associated with a variant of the 5-HT5 receptor. * Urate oxidase pseudogene, associated with the processing of uric acid * Photolyase pseudogene, associated with repairing DNA damaged by UV radiation. ** Photolyase is no longer encoded for despite obvious advantages. Instead, this gene is mutated to encode for cryptochromes. * TLR12P pseudogene, encodes a toll-like receptor. In mice, this gene recognizes profilin. It has also been duplicated in mice into TLR11 (recognizes profilin, bacterial flagellin). TLR13 (recognizes bacterial r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Proteins
Proteins are a class of macromolecular organic compounds that are essential to life. They consist of a long polypeptide chain that usually adopts a single stable Protein folding, three-dimensional structure. They fulfill a wide variety of Protein#Cellular functions, functions including providing Protein#Structural proteins, structural stability to cells, catalyzing chemical reactions that produce or store energy or synthesize other biomolecules including nucleic acids and proteins, transporting essential nutrients, or serving other roles such as signal transduction. They are selectively Protein targeting, transported to various compartments of the cell or in some cases, secretory protein, secreted from the cell. This list aims to organize information on how proteins are most often classified: by structure, by function, or by location. Structure Proteins may be classified as to their three-dimensional Protein structure#Structural classifications of proteins, structure (also kno ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Enzymes
Enzymes are listed here by their classification in the International Union of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology's Enzyme Commission (EC) numbering system: :Oxidoreductases (EC 1) ( Oxidoreductase) * Dehydrogenase * Luciferase * DMSO reductase :EC 1.1 (act on the CH-OH group of donors) * :EC 1.1.1 (with NAD+ or NADP+ as acceptor) ** Alcohol dehydrogenase (NAD) ** Alcohol dehydrogenase (NADP) ** Homoserine dehydrogenase ** Aminopropanol oxidoreductase ** Diacetyl reductase ** Glycerol dehydrogenase ** Propanediol-phosphate dehydrogenase ** glycerol-3-phoshitiendopene dehydrogenase (NAD+) ** D-xylulose reductase ** L-xylulose reductase ** Lactate dehydrogenase ** Malate dehydrogenase ** Isocitrate dehydrogenase ** HMG-CoA reductase * :EC 1.1.2 (with a cytochrome as acceptor) * :EC 1.1.3 (with oxygen as acceptor) ** Glucose oxidase ** L-gulonolactone oxidase ** Thiamine oxidase ** Xanthine oxidase * EC 1.1.4 (with a disulfide as accep ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Human Transcription Factors
This list of manually curated human transcription factor In molecular biology, a transcription factor (TF) (or sequence-specific DNA-binding factor) is a protein that controls the rate of transcription (genetics), transcription of genetics, genetic information from DNA to messenger RNA, by binding t ...s is taken from Lambert, Jolma, Campitelli et al. It was assembled by manual curation. More detailed information is found in the manuscript and the web site accompanying the paperHuman Transcription Factors List of human transcription factors (1639) References {{DEFAULTSORT:Human transcription factors Transcription factors Biology-related lists ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Transcription Factor
In molecular biology, a transcription factor (TF) (or sequence-specific DNA-binding factor) is a protein that controls the rate of transcription (genetics), transcription of genetics, genetic information from DNA to messenger RNA, by binding to a specific DNA sequence. The function of TFs is to regulate—turn on and off—genes in order to make sure that they are Gene expression, expressed in the desired Cell (biology), cells at the right time and in the right amount throughout the life of the cell and the organism. Groups of TFs function in a coordinated fashion to direct cell division, cell growth, and cell death throughout life; cell migration and organization (body plan) during embryonic development; and intermittently in response to signals from outside the cell, such as a hormone. There are approximately 1600 TFs in the human genome. Transcription factors are members of the proteome as well as regulome. TFs work alone or with other proteins in a complex, by promoting (a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Protein-coding Genes
The human genome is a complete set of nucleic acid sequences for humans, encoded as the DNA within each of the 23 distinct chromosomes in the cell nucleus. A small DNA molecule is found within individual mitochondria. These are usually treated separately as the nuclear genome and the mitochondrial genome. Human genomes include both protein-coding DNA sequences and various types of DNA that does not encode proteins. The latter is a diverse category that includes DNA coding for non-translated RNA, such as that for ribosomal RNA, transfer RNA, ribozymes, small nuclear RNAs, and several types of regulatory RNAs. It also includes promoters and their associated gene-regulatory elements, DNA playing structural and replicatory roles, such as scaffolding regions, telomeres, centromeres, and origins of replication, plus large numbers of transposable elements, inserted viral DNA, non-functional pseudogenes and simple, highly repetitive sequences. Introns make up a large percentage ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Y Chromosome
The Y chromosome is one of two sex chromosomes in therian mammals and other organisms. Along with the X chromosome, it is part of the XY sex-determination system, in which the Y is the sex-determining chromosome because the presence of the Y chromosome causes offspring produced in sexual reproduction to be of male sex. In mammals, the Y chromosome contains the SRY gene, which triggers development of male gonads. The Y chromosome is passed only from male parents to male offspring. Overview Discovery The Y chromosome was identified as a sex-determining chromosome by Nettie Stevens at Bryn Mawr College in 1905 during a study of the mealworm ''Tenebrio molitor''. Edmund Beecher Wilson independently discovered the same mechanisms the same year, working with Hemiptera. Stevens proposed that chromosomes always existed in pairs and that the smaller chromosome (now labelled "Y") was the pair of the X chromosome discovered in 1890 by Hermann Henking. She realized that th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
X Chromosome
The X chromosome is one of the two sex chromosomes in many organisms, including mammals, and is found in both males and females. It is a part of the XY sex-determination system and XO sex-determination system. The X chromosome was named for its unique properties by early researchers, which resulted in the naming of its counterpart Y chromosome, for the next letter in the alphabet, following its subsequent discovery. Discovery It was first noted that the X chromosome was special in 1890 by Hermann Henking in Leipzig. Henking was studying the testicles of '' Pyrrhocoris'' and noticed that one chromosome did not take part in meiosis. Chromosomes are so named because of their ability to take up staining (''chroma'' in Greek means ''color''). Although the X chromosome could be stained just as well as the others, Henking was unsure whether it was a different class of the object and consequently named it ''X element'', which later became X chromosome after it was established that it w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
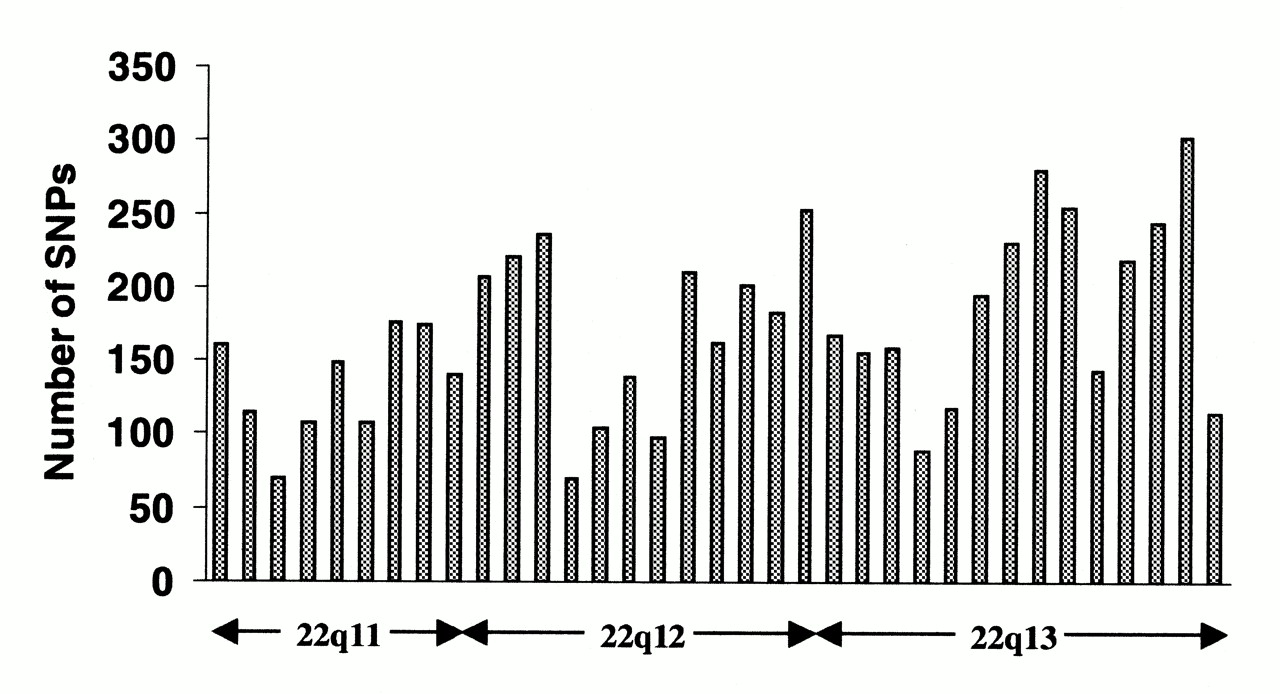
Chromosome 22
Chromosome 22 is one of the 23 pairs of chromosomes in human cells. Humans normally have two copies of chromosome 22 in each cell. Chromosome 22 is the second smallest human chromosome, spanning about 51 million DNA base pairs and representing between 1.5 and 2% of the total DNA in cells. In 1999, researchers working on the Human Genome Project announced they had determined the sequence of base pairs that make up this chromosome. Chromosome 22 was the first human chromosome to be fully sequenced. Human chromosomes are numbered by their apparent size in the karyotype, with chromosome 1 being the largest and chromosome 22 having originally been identified as the smallest. However, genome sequencing has revealed that chromosome 21 is actually smaller than chromosome 22. Genes Number of genes The following are some of the gene count estimates of human chromosome 22. Because researchers use different approaches to genome annotation, their predictions of the number of genes on e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chromosome 21
Chromosome 21 is one of the 23 pairs of chromosomes in humans. Chromosome 21 is both the smallest human autosome and chromosome, with 46.7 million base pairs (the building material of DNA) representing about 1.5 percent of the total DNA in cells. Most people have two copies of chromosome 21, while those with three copies of chromosome 21 (trisomy 21) have Down syndrome. Researchers working on the Human Genome Project announced in May 2000 that they had determined the sequence of base pairs that make up this chromosome. Chromosome 21 was the second human chromosome to be fully sequenced, after chromosome 22. Genes Number of genes The following are some of the gene count estimates of human chromosome 21. Because researchers use different approaches to genome annotation, their predictions of the number of genes on each chromosome varies (for technical details, see gene prediction). Among various projects, the collaborative consensus coding sequence project ( CCDS) takes an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |