|
Huguang
Huguang was a province of China during the Yuan and Ming dynasties. It was founded by the Yuan dynasty in 1274. During the Yuan dynasty it included the areas of modern Hubei south of the Yangtze river, Hunan, Guizhou, and Guangxi. During the Ming dynasty it came to include just the modern provinces of Hubei and Hunan, in the process adding areas north of the Yangtze. It was partitioned in 1644 by the newly established Qing dynasty, becoming the provinces of Hubei and Hunan, which were administered by the viceroy of Lianghu ("The Two Lake Provinces"). Governors Li Hongzhang was the viceroy of Huguang from 1867 to 1870. Zhang Zhidong became the viceroy of Huguang in 1896, following the First Sino-Japanese War. He was notable for employing foreigners to train and equip the local military to the standards of a contemporary European army. The most elite of Zhang's forces were known as the "Wuchang Division".Bonavia, David. ''China's Warlords''. New York: Oxford University Press. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Viceroy Of Huguang
The Viceroy of Huguang, fully in Chinese as the Governor-General of Hubei, Hunan and Other Local Areas, in Charge of Military Affairs, Food and Wages and Governor Affairs, was one of eight regional Viceroys in China#Qing dynasty, Viceroys during the Qing dynasty. The Viceroy of Huguang had jurisdiction of military, civil, and political affairs over then Hubei Province and then Hunan Province (approx. nowadays Hubei and Hunan). History The office was created in 1644 as the "Viceroy of Huguang" during the reign of the Shunzhi Emperor. Its headquarters were in Wuchang (present-day Wuchang District, Wuhan, Hubei). It was abolished in 1668 during the reign of the Kangxi Emperor but was restored in 1670 as the "Viceroy of Chuan-Hu" (川湖總督; "Viceroy of Sichuan, (Si)chuan and Hu(guang)"), with its headquarters in Chongqing. In 1674, the office of Viceroy of Chuan-Hu was split into the Viceroy of Sichuan and Viceroy of Huguang, and had remained as such until 1904. In 1904, during ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zhang Zhidong
Zhang Zhidong ( zh, t=張之洞) (2 September 18374 October 1909) was a Chinese politician who lived during the late Qing dynasty. Along with Zeng Guofan, Li Hongzhang and Zuo Zongtang, Zhang Zhidong was one of the four most famous officials of the late Qing dynasty. Known for advocating controlled reform and modernization of Chinese troops, he served as the governor of Shanxi Province and viceroy of Huguang, Liangguang and Liangjiang, and also as a member of the Grand Council. He took a leading role in the abolition of the Imperial examination system in 1905. The Red Guards destroyed his tomb in 1966 during the Cultural Revolution. His remains were rediscovered in 2007 and reburied. Other names Zhang Zhidong was also known by other names. An older Wade–Giles form was Chang Chih-tung. His courtesy name was Xiaoda ( zh, first=t, t=孝達, s=孝达, p=Xiàodá, labels=no) or Xiangtao ( zh, first=t, t=香濤, s=香涛, p=Xiāngtāo, labels=no). His pseudonyms were Xi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Li Hongzhang
Li Hongzhang, Marquess Suyi ( zh, t=李鴻章; also Li Hung-chang; February 15, 1823 – November 7, 1901) was a Chinese statesman, general and diplomat of the late Qing dynasty. He quelled several major rebellions and served in important positions in the Qing imperial court, including the Viceroy of Zhili, Viceroy of Huguang, Huguang and Viceroy of Liangguang, Liangguang. Although he was best known in the West for his generally pro-modern stance and importance as a negotiator, Li antagonised the British with his support of Russia as a foil against Japanese expansionism in Manchuria and fell from favour with the Chinese after their defeat in the First Sino-Japanese War. His image in China remains controversial, with criticism on one hand for political and military defeats and praise on the other for his success against the Taiping Rebellion, his diplomatic skills defending Chinese interests in the era of unequal treaties, and his role pioneering China's Kaiping Tramway, i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
History Of Hubei
Hubei is a province of China, province in Central China. It has the List of Chinese provincial-level divisions by GDP, seventh-largest economy among Chinese provinces, the second-largest within Central China, and the third-largest among inland provinces. Its provincial capital at Wuhan serves as a major political, cultural, and economic hub for the region. Hubei is associated with the historical state of E that existed during the Western Zhou dynasty (771 BCE). Its name means 'north of the lake', referring to Dongting Lake. It borders Henan to the north, Anhui and Jiangxi to the east, Hunan to the south, and Chongqing and Shaanxi to the west. The high-profile Three Gorges Dam is located at Yichang in the west of the province. History The Hubei region was home to sophisticated Neolithic cultures. By the Spring and Autumn period (770–476 BC), the territory of today's Hubei formed part of the powerful Chu (state), State of Chu. Chu, nominally a tributary state of the Zh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
History Of Hunan
Hunan is an inland province in Central China. Located in the middle reaches of the Yangtze watershed, it borders the province-level divisions of Hubei to the north, Jiangxi to the east, Guangdong and Guangxi to the south, and Guizhou and Chongqing to the northwest. Its capital and largest city is Changsha, which abuts the Xiang River. Hengyang, Zhuzhou, and Yueyang are among its most populous urban cities. With a population of just over 66 million residing in an area of approximately , it is China's 7th-most populous province, the third-most populous among landlocked provinces (after Henan and Sichuan), the third-most populous in South Central China (after Guangdong and Henan), and the second-most populous province in Central China. It is the largest province in South Central China and the fourth-largest landlocked province. Hunan's nominal GDP was US$747 billion (CN¥5.32 trillion) as of 2024, appearing in the world's top 20 largest sub-national economies, with its GDP ( ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hunan
Hunan is an inland Provinces of China, province in Central China. Located in the middle reaches of the Yangtze watershed, it borders the Administrative divisions of China, province-level divisions of Hubei to the north, Jiangxi to the east, Guangdong and Guangxi to the south, and Guizhou and Chongqing to the northwest. Its capital and largest city is Changsha, which abuts the Xiang River. Hengyang, Zhuzhou, and Yueyang are among its most populous urban cities. With a population of just over 66 million residing in an area of approximately , it is China's List of Chinese administrative divisions by population, 7th-most populous province, the third-most populous among landlocked provinces (after Henan and Sichuan), the third-most populous in South Central China (after Guangdong and Henan), and the second-most populous province in Central China. It is the largest province in South Central China and the fourth-largest landlocked province. Hunan's Gross domestic product#Nominal GDP ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Qing Dynasty
The Qing dynasty ( ), officially the Great Qing, was a Manchu-led Dynasties of China, imperial dynasty of China and an early modern empire in East Asia. The last imperial dynasty in Chinese history, the Qing dynasty was preceded by the Ming dynasty and succeeded by the Republic of China (1912–1949), Republic of China. At its height of power, the empire stretched from the Sea of Japan in the east to the Pamir Mountains in the west, and from the Mongolian Plateau in the north to the South China Sea in the south. Originally emerging from the Later Jin (1616–1636), Later Jin dynasty founded in 1616 and proclaimed in Shenyang in 1636, the dynasty seized control of the Ming capital Beijing and North China in 1644, traditionally considered the start of the dynasty's rule. The dynasty lasted until the Xinhai Revolution of October 1911 led to the abdication of the last emperor in February 1912. The multi-ethnic Qing dynasty Legacy of the Qing dynasty, assembled the territoria ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Romanization Of Chinese
Romanization of Chinese is the use of the Latin alphabet to transliterate Varieties of Chinese, Chinese. Chinese uses a logographic script and its Chinese characters, characters do not represent phonemes directly. There have been many systems using Romanization, Roman characters to represent Chinese throughout history. Linguist Daniel Kane (linguist), Daniel Kane wrote, "It used to be said that sinologists had to be like musicians, who might compose in one key and readily transcribe into other keys." The dominant international standard for Standard Chinese, Standard Mandarin since about 1982 has been Pinyin, Hanyu Pinyin, invented by a group of Chinese linguists, including Zhou Youguang, in the 1950s. Other well-known systems include Wade–Giles (Beijing Mandarin) and Yale romanization (Yale romanization of Mandarin, Beijing Mandarin and Yale romanization of Cantonese, Cantonese). There are many uses for Chinese romanization. Most broadly, it is used to provide a useful way for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
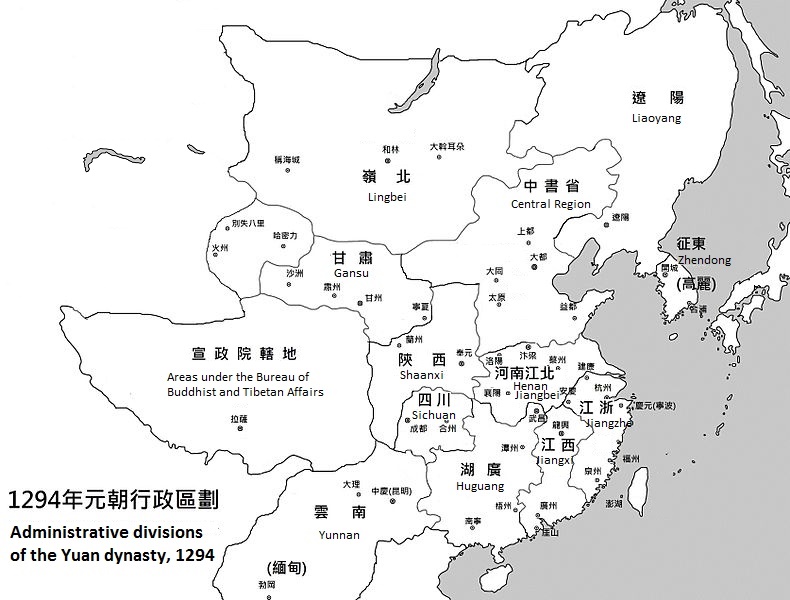
Administrative Divisions Of The Yuan Dynasty
The Yuan dynasty was a Mongols, Mongol-led Dynasties in Chinese history, imperial Chinese dynasty. During its existence, its territory was divided into the Central Region (腹裏) governed by the Zhongshu Sheng, Central Secretariat (Zhongshu Sheng) and places under control of various provinces (行省) or Branch Secretariats (行中書省), as well as the region under the Bureau of Buddhist and Tibetan Affairs (Xuanzheng Yuan). In addition, the List of emperors of the Yuan dynasty, Yuan emperors held nominal suzerainty over the western Mongol khanates, but in reality none of them were governed by the Yuan dynasty due to the division of the Mongol Empire. Overview The most important part of the Yuan Empire was the Central Region, which covered the region of the Yuan capital Khanbaliq (Dadu, modern Beijing). The Central Region consisted of present-day Hebei, Shandong, Shanxi, the south-eastern part of present-day Inner Mongolia and the Henan areas to the north of the Yellow River. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jingzhou (ancient China)
Jingzhou or Jing Province was one of the Nine Provinces of ancient China referenced in early Chinese texts such as the '' Tribute of Yu'', '' Erya'', and '' Rites of Zhou''. Jingzhou became an administrative division during the reign of Emperor Wu (r. 141–87 BCE) in the Western Han dynasty (206 BCE–9 CE). It usually corresponded with the modern-day provinces of Hubei and Hunan until the Sui dynasty, after which it referred to the city of Jingzhou. History Pre-Qin era In the Warring States period, the Chu state covered most of present-day Hubei and Hunan, the areas that would form Jingzhou in a later era. The Qin state dropped the name "Chu" (楚) (literally " chaste tree") and used its synonym "Jing" (荊) instead to avoid a naming taboo, since the personal name of Qin's King Zhuangxiang (281–247 BCE) was "Zichu" (子楚; lit. "son of Chu") because his adoptive mother, Lady Huayang, was from Chu. Chu was conquered by Qin in 223 BCE in the final stages of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |