|
Jingzhou (ancient China)
Jingzhou or Jing Province was one of the Nine Provinces of ancient China referenced in early Chinese texts such as the '' Tribute of Yu'', '' Erya'', and '' Rites of Zhou''. Jingzhou became an administrative division during the reign of Emperor Wu (r. 141–87 BCE) in the Western Han dynasty (206 BCE–9 CE). It usually corresponded with the modern-day provinces of Hubei and Hunan until the Sui dynasty, after which it referred to the city of Jingzhou. History Pre-Qin era In the Warring States period, the Chu state covered most of present-day Hubei and Hunan, the areas that would form Jingzhou in a later era. The Qin state dropped the name "Chu" (楚) (literally " chaste tree") and used its synonym "Jing" (荊) instead to avoid a naming taboo, since the personal name of Qin's King Zhuangxiang (281–247 BCE) was "Zichu" (子楚; lit. "son of Chu") because his adoptive mother, Lady Huayang, was from Chu. Chu was conquered by Qin in 223 BCE in the final stages of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nine Provinces
The term Nine Provinces or Nine Regions (), is used in ancient Chinese histories to refer to territorial divisions or islands during the Xia dynasty, Xia and Shang dynasty, Shang dynasties and has now come to symbolically represent China. "Province" is the word used to translate ''Zhou (country subdivision), zhou'' (州) – since before the Tang dynasty (618–907 CE), it was the largest Chinese territorial division. Although the current definition of the Nine Provinces can be dated to the Spring and Autumn period, Spring and Autumn and Warring States period, Warring States periods, it was not until the Eastern Han dynasty that the Nine Provinces were treated as actual History of the administrative divisions of China before 1912, administrative regions. Different interpretations of the Nine Provinces The ''Rongcheng Shi'' bamboo slips from the Chu (state), Chu state has the earliest interpretation of the Nine Provinces, but these early descriptions differ widely from th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Han Provinces
Han may refer to: Arts, entertainment, and media * "Han", a The West Wing (season 5), fifth season episode of ''The West Wing'' * Han (musician), born Han Ji-sung, a South Korean singer-songwriter, rapper, and record producer, member of Stray Kids * Han Lue, a character in the ''Fast & Furious'' franchise * Han Solo, a character in the ''Star Wars'' franchise Education * Han school, Japan, Edo period * HAN University of Applied Sciences, in the Netherlands People Ethnic groups * Han Chinese, or Han people (): the name for the largest ethnic group in China, which also constitutes the world's largest ethnic group ** Han Taiwanese (): the name for the ethnic group of the Taiwanese people who are fully or partially of Han Chinese descent * Han Minjok, or Han people (): the Korean native name referring to Koreans * Hän: one of the First Nations peoples of Canada Names * Han (name), a given name and surname ** Han (Chinese surname), also Haan, Hahn or Hann, the Romanized spelling of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
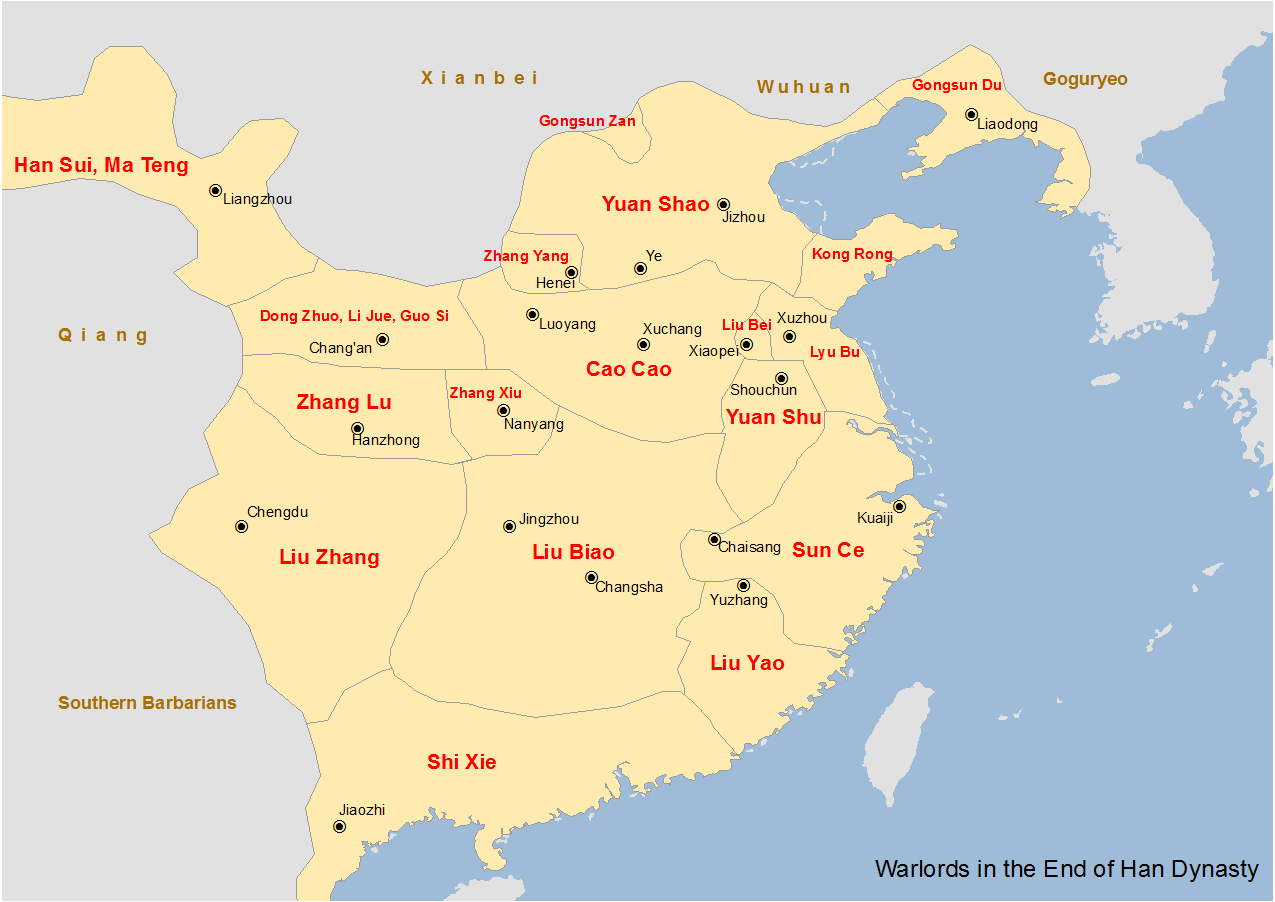
Liu Cong (Han Dynasty)
Liu Cong () ( 207–208) was a Chinese politician who lived during the late Eastern Han dynasty of China. He was the younger son of Liu Biao, the Governor of Jing Province. Life Liu Cong's ancestral home was in Gaoping, Shanyang (present-day Zoucheng, Shandong). He was the second son of Liu Biao, the Governor of Jing Province (荊州; covering present-day Hubei and Hunan). He was a descendant of Liu Yu, Prince Gong of Lu. He had an elder brother, Liu Qi, who was also born to Liu Biao's first wife Lady Chen. Their mother died early. Liu Biao initially favoured his elder son Liu Qi because the latter resembled him in appearance. Liu Cong later married the niece of Liu Biao's second wife, Lady Cai. Due to this, the Cai family was naturally inclined to support Liu Cong, and they often spoke ill of Liu Qi in front of Liu Biao. Liu Qi fell out of his father's favour and heeded Zhuge Liang's suggestion to leave Jing Province's capital Xiangyang and travel to Jiangxia Commandery. O ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Xiangyang
Xiangyang is the second-largest prefecture-level city by population in northwestern Hubei province, China. It was known as Xiangfan from 1950 to 2010. The Han River (Hanshui), Han River runs through Xiangyang's centre and divides the city north–south. The city itself is an agglomeration of two once separate cities: Fancheng and Xiangyang (or Xiangcheng District, Xiangyang, Xiangcheng), and was known as Xiangfan before 2010. What remains of old Xiangyang is located south of the Han River (Hanshui), Han River and contains one of the oldest still-intact city walls in China, while Fancheng is located to the north of the Han River. Both cities served prominent historical roles in both ancient and pre-modern Chinese history. Today, the city has been a target of government and private investment as the country seeks to urbanize and develop the interior provinces. Its built-up area made up of 3 urban districts had 2,319,640 inhabitants at the 2020 census while the whole municipalit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yellow Turban Rebellion
The Yellow Turban Rebellion, alternatively translated as the Yellow Scarves Rebellion, was a peasant revolt during the late Eastern Han dynasty of ancient China. The uprising broke out in 184 CE, during the reign of Emperor Ling. Although the main rebellion was suppressed by 185 CE, it took 21 years for full suppression of resistant areas and emerging rebellions by 205 CE. The weakening of the imperial court and the rising political influence of ultra-autonomous regional military-governors, who helped suppress the rebellion, eventually led to rampant warlord dominance and the resultant Three Kingdoms period. The rebellion, which got its name from the color of the rebels' headwear ( ''jīn'', defined as more of a scarf than the turban of South Asia) marked an important point in the history of Taoism due to the rebel leaders' association with the then secret Taoist societies. The revolt was also used as the opening event in the 14th-century historical novel '' Romance of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Changde
Changde (; Traditional Chinese characters, traditional Chinese: 常德區 ) is a prefecture-level city in the northwest of Hunan province, People's Republic of China. Changde, known as "Wuling" in ancient times, is located on the west side of Dongting Lake in the south of the Yangtze, Yangtze River, at the foot of Wuling Mountains, Wuling Mountain. It is historically known as "the throat of Sichuan and Guizhou, and the gateway to Yunnan and Guizhou". In addition to the urban districts, Changde also administers the county-level city of Jinshi City, Jinshi and six counties. Changde is adjacent to Dongting Lake to the east, the city of Yiyang to the south, Wuling Mountains, Wuling and Xuefeng Mountains to the west, and Hubei province to the north. The area has been inhabited by humans since around 8,000 years ago. In that time, the city has changed names several times, but it has been known as Changde since the 12th century. The city is well known for the Battle of Changde during th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hanshou County
Hanshou County () is a county in Hunan Province, China, it is under the administration of Changde prefecture-city. The County is located on the north in Hunan Province and the southeast in Changde City, it borders to the north and the west by Dingcheng District, to the south by Ziyang District of Yiyang City and Taojiang County, and to the east by Yuanjiang and Nan County. It has an area of with registered population of 821,266 (as of 2015). It is divided into four subdistricts, 16 towns and three townships under its jurisdiction. The county seat is Longyang Subdistrict (). History Abundant source of waters and rivers make Hanshou County a productive fish and rice area. Dongting Lake was once the largest lake in China. This changed in the 1950s when the national Chinese government encouraged plantation of rice and built many dams in the lake. The area of Dongting Lake shrank dramatically. Owing to the river network in this district, a land transportation system was underdevel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Emperor Xian Of Han
Emperor Xian of Han (2 April 181 – 21 April 234), personal name Liu Xie (劉協), courtesy name Bohe, was the 14th and last Emperor of China, emperor of the Han dynasty#Eastern Han (25–220 AD), Eastern Han dynasty of China. He reigned from 28 September 189 until his abdication and subsequent End of the Han dynasty, end of the dynasty on 11 December 220. Liu Xie was a son of Emperor Ling of Han, Liu Hong (Emperor Ling) and was a younger half-brother of his predecessor, Liu Bian (Emperor Shao). In 189, at the age of eight, he became emperor after the warlord Dong Zhuo, who had seized control of the Han central government, deposed Emperor Shao and replaced him with Liu Xie. The newly enthroned Liu Xie, historically known as Emperor Xian, was in fact a puppet ruler under Dong Zhuo's control. In 190, when a coalition of regional warlords launched a punitive campaign against Dong Zhuo in the name of freeing Emperor Xian, Dong Zhuo ordered the destruction of the imperial capital, L ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Liu Biao
Liu Biao () () ( 151 – September 208), courtesy name Jingsheng, was a Chinese military general, politician, and warlord who lived in the late Eastern Han dynasty of China. He is best known for serving as the governor of Jing Province (covering present-day Hubei and Hunan) from 192 until his death in 208. He was also a member of the extended family of the Han emperors through his ancestor Liu Yu, the fifth son of Emperor Jing. Liu Biao was described as a handsome man and was over eight '' chi'' tall (1.86 metres). Life In 166 to 167, when Liu Biao was 17 (by East Asian reckoning), he became a student of Wang Chang (grandfather of Wang Can). At the time, Wang Chang was Administrator of Nanyang (南阳太守). Liu Biao gained control of Jing Province (covering present-day Hubei and Hunan) in 190 CE, when Dong Zhuo appointed him to the position after the death of its previous governor (or inspector), Wang Rui. Liu Biao later started a war against the warlord Yuan Shu and his ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Commandery (China)
A commandery ( zh, s=郡, p=jùn) was a historical administrative division of China that was in use from the Eastern Zhou (c. 7th century BCE) until the early Tang dynasty (c. 7th century CE). Several neighboring countries adopted Chinese commanderies as the basis for their own administrative divisions. History and development China Eastern Zhou During the Eastern Zhou's Spring and Autumn period from the 8th to 5th centuries BCE, the larger and more powerful of the Zhou dynasty, Zhou's Chinese feudalism, vassal states—including Qin (state), Qin, Jin (Chinese state), Jin and Wei (state), Wei—began annexing their smaller rivals. These new lands were not part of their original fiefs and were instead organized into Counties of the People's Republic of China#History, counties (''xiàn''). Eventually, commanderies were developed as marchlands between the Warring States period, major realms. Despite having smaller populations and ranking lower on t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Book Of Han
The ''Book of Han'' is a history of China finished in 111 CE, covering the Western, or Former Han dynasty from the first emperor in 206 BCE to the fall of Wang Mang in 23 CE. The work was composed by Ban Gu (32–92 CE), an Eastern Han court official, with the help of his sister Ban Zhao, continuing the work of their father, Ban Biao. They modelled their work on the ''Records of the Grand Historian'' (), a cross-dynastic general history, but theirs was the first in this annals-biography form to cover a single dynasty. It is the best source, sometimes the only one, for many topics such as literature in this period. The ''Book of Han'' is also called the ''Book of the Former Han'' () to distinguish it from the '' Book of the Later Han'' () which covers the Eastern Han period (25–220 CE), and was composed in the fifth century by Fan Ye (398–445 CE). Contents This history developed from a continuation of Sima Qian's ''Records of the Grand Hi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eastern Han Dynasty
The Han dynasty was an Dynasties of China, imperial dynasty of China (202 BC9 AD, 25–220 AD) established by Liu Bang and ruled by the House of Liu. The dynasty was preceded by the short-lived Qin dynasty (221–206 BC) and a warring interregnum known as the Chu–Han Contention (206–202 BC), and it was succeeded by the Three Kingdoms period (220–280 AD). The dynasty was briefly interrupted by the Xin dynasty (9–23 AD) established by the usurping regent Wang Mang, and is thus separated into two periods—the #Western Han (202 BC – 9 AD), Western Han (202 BC9 AD) and the #Eastern Han (25–220 AD), Eastern Han (25–220 AD). Spanning over four centuries, the Han dynasty is considered a Golden ages of China, golden age in Chinese history, and had a permanent impact on Chinese identity in later periods. The majority ethnic group of modern China refer to themselves as the "Han people" or "Han Chinese". The spoken Chinese ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |