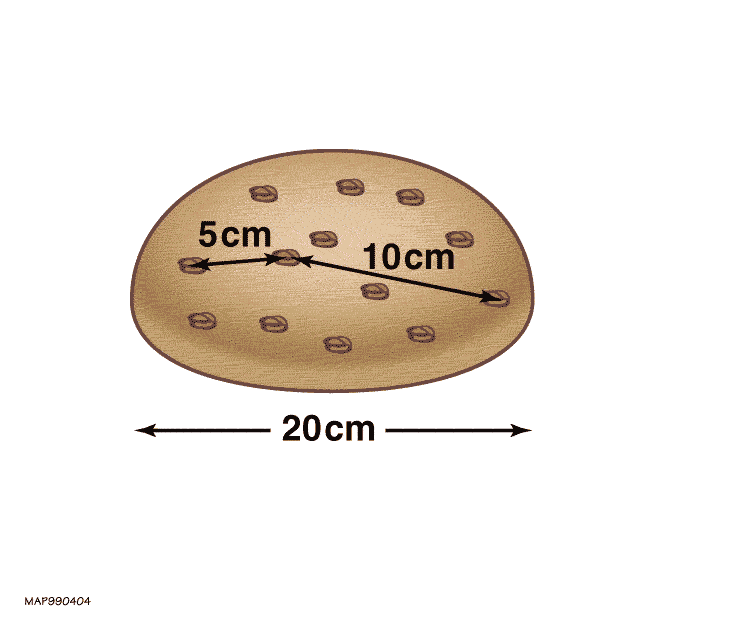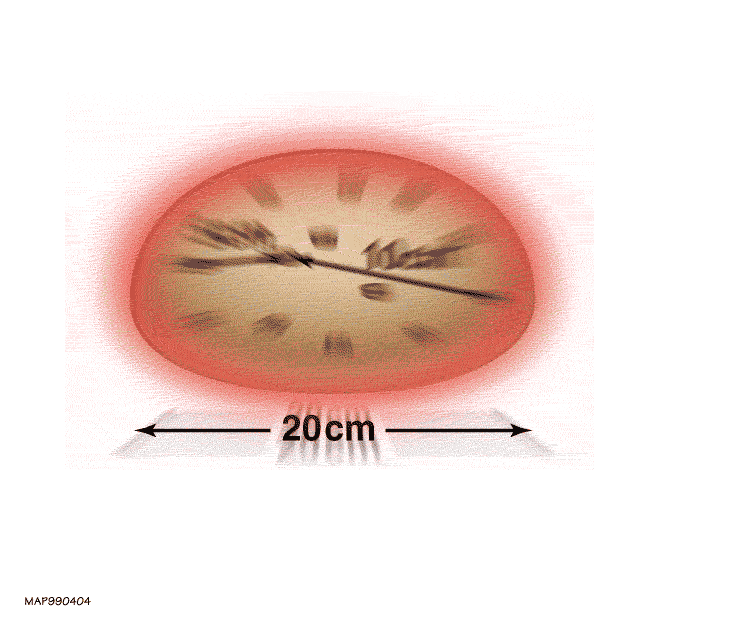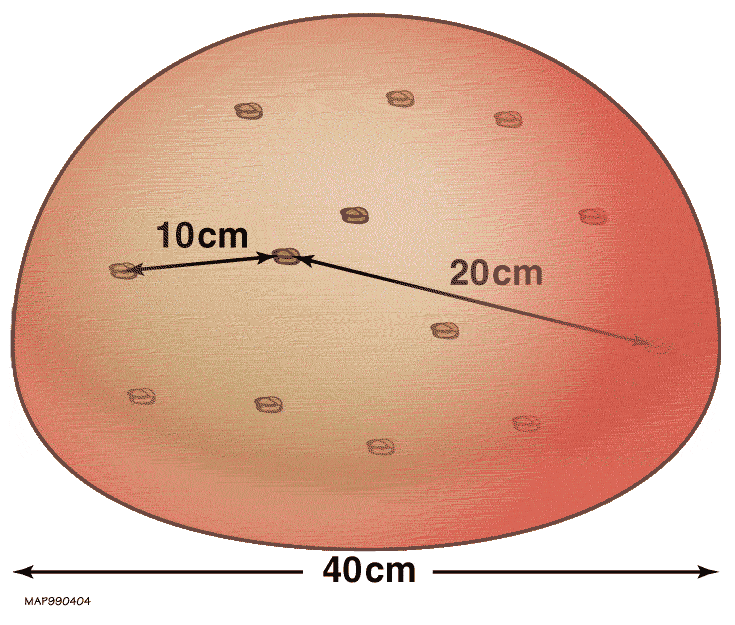
|
Hubble Constant
Hubble's law, also known as the Hubble–Lemaître law, is the observation in physical cosmology that galaxies are moving away from Earth at speeds proportional to their distance. In other words, the farther a galaxy is from the Earth, the faster it moves away. A galaxy's recessional velocity is typically determined by measuring its redshift, a shift in the frequency of light emitted by the galaxy. The discovery of Hubble's law is attributed to work published by Edwin Hubble in 1929, but the notion of the universe expanding at a calculable rate was first derived from general relativity equations in 1922 by Alexander Friedmann. The Friedmann equations showed the universe might be expanding, and presented the expansion speed if that were the case. Before Hubble, astronomer Carl Wilhelm Wirtz had, in 1922 and 1924, deduced with his own data that galaxies that appeared smaller and dimmer had larger redshifts and thus that more distant galaxies recede faster from the observer. In ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Raisinbread
Raisin bread or fruit bread (also known as fruit toast or raisin toast in New Zealand and Australia) is a type of bread made with raisins and flavored with cinnamon. It is "usually a white flour or egg dough bread". Aside from white flour, raisin bread is also made with other flours, such as all-purpose flour, oat flour, or whole wheat flour. Some recipes include honey, brown sugar, eggs, or butter. Variations of the recipe include the addition of walnuts, hazelnuts, pecans or, for a dessert, rum or whisky. Raisin bread is eaten in many different forms, including being served toasted for breakfast ("raisin toast") or made into sandwiches. Some restaurants serve raisin bread with their cheeseboards. History Its invention has been popularly incorrectly attributed to Henry David Thoreau in Concord, Massachusetts lore, as there have been published recipes for bread with raisins since 1671. Since the 15th century, breads made with raisins were made in Europe. In Germany stollen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Monthly Notices Of The Royal Astronomical Society
''Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society'' (MNRAS) is a peer-reviewed scientific journal in astronomy, astrophysics and related fields. It publishes original research in two formats: papers (of any length) and letters (limited to five pages). MNRAS publishes more articles per year than any other astronomy journal. The learned society journal has been in continuous existence since 1827 and became online only in 2020. It operates as a partnership between the Royal Astronomical Society (RAS), who select and peer-review the contents, and Oxford University Press (OUP), who publish and market the journal. Despite its name, MNRAS is no longer monthly, nor does it carry the notices of the RAS. In 2024 MNRAS became a purely gold open access journal. History The first issue of MNRAS was published on 9 February 1827 as ''Monthly Notices of the Astronomical Society of London'' and it has been in continuous publication ever since. It took its current name from the second vo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Derivative
In mathematics, the derivative is a fundamental tool that quantifies the sensitivity to change of a function's output with respect to its input. The derivative of a function of a single variable at a chosen input value, when it exists, is the slope of the tangent line to the graph of the function at that point. The tangent line is the best linear approximation of the function near that input value. For this reason, the derivative is often described as the instantaneous rate of change, the ratio of the instantaneous change in the dependent variable to that of the independent variable. The process of finding a derivative is called differentiation. There are multiple different notations for differentiation. '' Leibniz notation'', named after Gottfried Wilhelm Leibniz, is represented as the ratio of two differentials, whereas ''prime notation'' is written by adding a prime mark. Higher order notations represent repeated differentiation, and they are usually denoted in Leib ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Comoving And Proper Distances
In standard cosmology, comoving distance and proper distance (or physical distance) are two closely related distance measures used by cosmologists to define distances between objects. ''Comoving distance'' factors out the expansion of the universe, giving a distance that does not change in time except due to local factors, such as the motion of a galaxy within a cluster. ''Proper distance'' roughly corresponds to where a distant object would be at a specific moment of cosmological time, which can change over time due to the expansion of the universe. Comoving distance and proper distance are defined to be equal at the present time. At other times, the Universe's expansion results in the proper distance changing, while the comoving distance remains constant. Comoving coordinates Although general relativity allows the formulation of the laws of physics using arbitrary coordinates, some coordinate choices are easier to work with. Comoving coordinates are an example of such a coor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Swinburne University Of Technology
The Swinburne University of Technology (or simply Swinburne) is a public university, public research university in Melbourne, Australia. It is the modern descendant of the Eastern Suburbs Technical College established in 1908, renamed Swinburne Technical College in 1913 after its co-founders George Swinburne, George and Ethel Swinburne. It has three campuses in metropolitan Melbourne: Hawthorn, Victoria, Hawthorn, where its main campus is located; Wantirna, Victoria, Wantirna; and Croydon, Victoria, Croydon, as well the Swinburne University of Technology Sarawak Campus in the East Malaysian state of Sarawak. It also offers courses online and through its partnered institutions in Australia and overseas. The university offers study programs in Bachelor of Commerce, commerce, Health care, healthcare, teacher education, Jurisprudence, law, engineering, Flight training, aviation, architecture, the performing arts and various other fields including in the arts and sciences. It also of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Routledge
Routledge ( ) is a British multinational corporation, multinational publisher. It was founded in 1836 by George Routledge, and specialises in providing academic books, academic journals, journals and online resources in the fields of the humanities, behavioral science, behavioural science, education, law, and social science. The company publishes approximately 1,800 journals and 5,000 new books each year and their backlist encompasses over 140,000 titles. Routledge is claimed to be the largest global academic publisher within humanities and social sciences. In 1998, Routledge became a subdivision and Imprint (trade name), imprint of its former rival, Taylor & Francis, Taylor & Francis Group (T&F), as a result of a £90-million acquisition deal from Cinven, a venture capital group which had purchased it two years previously for £25 million. Following the merger of Informa and T&F in 2004, Routledge became a publishing unit and major imprint within the Informa "academic publishing ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
New York Times
''The New York Times'' (''NYT'') is an American daily newspaper based in New York City. ''The New York Times'' covers domestic, national, and international news, and publishes opinion pieces, investigative reports, and reviews. As one of the longest-running newspapers in the United States, the ''Times'' serves as one of the country's Newspaper of record, newspapers of record. , ''The New York Times'' had 9.13 million total and 8.83 million online subscribers, both by significant margins the List of newspapers in the United States, highest numbers for any newspaper in the United States; the total also included 296,330 print subscribers, making the ''Times'' the second-largest newspaper by print circulation in the United States, following ''The Wall Street Journal'', also based in New York City. ''The New York Times'' is published by the New York Times Company; since 1896, the company has been chaired by the Ochs-Sulzberger family, whose current chairman and the paper's publ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Big Bang
The Big Bang is a physical theory that describes how the universe expanded from an initial state of high density and temperature. Various cosmological models based on the Big Bang concept explain a broad range of phenomena, including the abundance of light elements, the cosmic microwave background (CMB) radiation, and large-scale structure. The uniformity of the universe, known as the horizon and flatness problems, is explained through cosmic inflation: a phase of accelerated expansion during the earliest stages. A wide range of empirical evidence strongly favors the Big Bang event, which is now essentially universally accepted.: "At the same time that observations tipped the balance definitely in favor of the relativistic big-bang theory, ..." Detailed measurements of the expansion rate of the universe place the Big Bang singularity at an estimated billion years ago, which is considered the age of the universe. Extrapolating this cosmic expansion backward in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Expansion Of The Universe
The expansion of the universe is the increase in proper length, distance between Gravitational binding energy, gravitationally unbound parts of the observable universe with time. It is an intrinsic and extrinsic properties (philosophy), intrinsic expansion, so it does not mean that the universe expands "into" anything or that space exists "outside" it. To any observer in the universe, it appears that all but Local Group, the nearest galaxies (which are bound to each other by gravity) move away at Hubble's law, speeds that are proportional to their distance from the observer, on average. While objects cannot move Faster-than-light, faster than light, this limitation applies only with respect to Principle of locality, local reference frames and does not limit the recession rates of cosmologically distant objects. Cosmic expansion is a key feature of Big Bang cosmology. It can be modeled mathematically with the Friedmann–Lemaître–Robertson–Walker metric (FLRW), where it corr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Henrietta Swan Leavitt
Henrietta Swan Leavitt (; July 4, 1868 – December 12, 1921) was an American astronomer. Her discovery of how to effectively measure vast distances to remote galaxies led to a shift in the understanding of the scale and nature of the universe. Nomination of Leavitt for the Nobel Prize had to be halted because of her death. A graduate of Radcliffe College, she worked at the Harvard College Observatory as a computer (occupation), human computer, tasked with measuring photographic plates to catalog the positions and brightness of stars. This work led her to discover the relation between the luminosity and the period of Cepheid variables. Leavitt's discovery provided astronomers with the first Cosmic distance ladder, standard candle with which to measure the distance to other galaxy, galaxies. Before Leavitt discovered the period-luminosity relationship for Cepheid variables (sometimes referred to as Leavitt's Law), the only techniques available to astronomers for measuring the di ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cambridge University Press
Cambridge University Press was the university press of the University of Cambridge. Granted a letters patent by King Henry VIII in 1534, it was the oldest university press in the world. Cambridge University Press merged with Cambridge Assessment to form Cambridge University Press and Assessment under Queen Elizabeth II's approval in August 2021. With a global sales presence, publishing hubs, and offices in more than 40 countries, it published over 50,000 titles by authors from over 100 countries. Its publications include more than 420 academic journals, monographs, reference works, school and university textbooks, and English language teaching and learning publications. It also published Bibles, runs a bookshop in Cambridge, sells through Amazon, and has a conference venues business in Cambridge at the Pitt Building and the Sir Geoffrey Cass Sports and Social Centre. It also served as the King's Printer. Cambridge University Press, as part of the University of Cambridge, was a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vesto Slipher
Vesto Melvin Slipher (; November 11, 1875 – November 8, 1969) was an American astronomer who performed the first measurements of radial velocities for galaxies. He was the first to discover that distant galaxies are redshifted, thus providing the first empirical basis for the expansion of the universe. He was also the first to relate these redshifts to velocity. Early life and education Vesto Melvin Slipher was born in Mulberry, Indiana, to Daniel Clark and Hannah App Slipher. He spent his early years working on his family farm in Mulberry. Vesto had a younger brother, Earl C. Slipher, who was also an astronomer at Lowell Observatory. Slipher went to high school in Frankfort, Indiana. He then attended Indiana University Bloomington and earned his Bachelor's Degree in Mechanics and Astronomy in June 1901. Two years later, Slipher earned his Master's Degree in the same program. At the age of 33, Vesto graduated with his Ph.D. in Mechanics and Astronomy from Indiana Universi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |