|
Hope Mars Mission
The Emirates Mars Mission () is a United Arab Emirates Space Agency uncrewed space exploration mission to Mars. The ''Hope'' probe (, ''Misbar Al-Amal'') was launched on 20 July 2020, and went into orbit around Mars on 9 February 2021. The project was headed by Omran Sharaf. 200 Emirati scientists and engineers from the UAE and partner institutes were involved in the project. The mission design, development, and operations are led by the Mohammed bin Rashid Space Centre (MBRSC). The spacecraft was assembled in the United States at the University of Colorado Boulder's Laboratory for Atmospheric and Space Physics (LASP) by the Emirati engineers, assisted by their American counterparts, with support from Arizona State University (ASU) and the University of California, Berkeley. The project was led by MBRSC at every stage. The space probe will study daily and seasonal weather cycles, weather events in the lower atmosphere such as dust storms, and how the weather varies in di ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mohammed Bin Rashid Space Centre
The Mohammed Bin Rashid Space Centre (MBRSC, ) is a Government of Dubai, Dubai Government organization working on the UAE space program, which includes various Satellite, space satellites projects, such as the Emirates Mars Mission, the Emirates Lunar Mission, and the UAE astronaut program. The center actively works to promote Outline of space science, space science and research in the region and encompasses the Emirates Institution for Advanced Science and Technology (EIAST). Overview Mohammed bin Rashid Al Maktoum, vice president and prime minister of the United Arab Emirates and ruler of Dubai, established the Emirates Institution for Advanced Science and Technology (EIAST) on 6 February 2006. On 17th April 2015, Mohammed bin Rashid Space Center was created, incorporating EIAST into it. MBRSC contributes towards the development of various sectors within the United Arab Emirates and across the globe, using data from UAE satellites, and various applications related to space s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Space Exploration
Space exploration is the process of utilizing astronomy and space technology to investigate outer space. While the exploration of space is currently carried out mainly by astronomers with telescopes, its physical exploration is conducted both by robotic spacecraft, uncrewed robotic space probes and human spaceflight. Space exploration, like its classical form astronomy, is one of the main sources for space science. While the observation of objects in space, known as astronomy, predates reliable recorded history, it was the development of large and relatively efficient rockets during the mid-twentieth century that allowed physical space exploration to become a reality. Common rationales for exploring space include advancing scientific research, national prestige, uniting different nations, ensuring the future survival of humanity, and developing military and strategic advantages against other countries. The early era of space exploration was driven by a "Space Race" between ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Perseverance (rover)
''Perseverance'' is a car-sized Mars rover designed to explore the Jezero (crater), Jezero crater on Mars as part of NASA's Mars 2020 mission. It was manufactured by the Jet Propulsion Laboratory and launched on July 30, 2020, at 11:50 Coordinated Universal Time, UTC. Confirmation that the rover successfully landed on Mars was received on February 18, 2021, at 20:55 UTC. As of , ''Perseverance'' has been active on Mars for Sol (day on Mars), sols ( days, Earth days, or ) since its landing. Following the rover's arrival, NASA named the landing site Octavia E. Butler Landing. ''Perseverance'' has a similar design to its predecessor rover, ''Curiosity (rover), Curiosity'', although it was moderately upgraded. It carries seven primary payload instruments, nineteen cameras, and two microphones. The rover also carried the mini-helicopter ''Ingenuity (helicopter), Ingenuity'' to Mars, an experimental technology testbed that made the first powered aircraft flight on another plane ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mars 2020
Mars 2020 is a NASA mission that includes the rover ''Perseverance (rover), Perseverance'', the now-retired small robotic helicopter ''Ingenuity (helicopter), Ingenuity'', and associated delivery systems, as part of the Mars Exploration Program. Mars 2020 was launched on an Atlas V rocket at 11:50:01 Coordinated Universal Time, UTC on July 30, 2020, and landed in the Martian crater Jezero (crater), Jezero on February 18, 2021, with confirmation received at 20:55 UTC. On March 5, 2021, NASA named the landing site Octavia E. Butler Landing. As of , ''Perseverance'' has been on Mars for Sol (day on Mars), sols ( days, total days; ). ''Ingenuity'' operated on Mars for Sol (day on Mars), sols ( days, total days; ) before sustaining serious damage to its rotor blades, possibly all four, causing NASA to retire the craft on January 25, 2024. ''Perseverance'' is investigating an Astrobiology, astrobiologically relevant ancient environment on Mars for its Geology of Mars, surface ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
NASA
The National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA ) is an independent agencies of the United States government, independent agency of the federal government of the United States, US federal government responsible for the United States's civil list of government space agencies, space program, aeronautics research and outer space, space research. National Aeronautics and Space Act, Established in 1958, it succeeded the National Advisory Committee for Aeronautics (NACA) to give the American space development effort a distinct civilian orientation, emphasizing peaceful applications in space science. It has since led most of America's space exploration programs, including Project Mercury, Project Gemini, the 1968–1972 Apollo program missions, the Skylab space station, and the Space Shuttle. Currently, NASA supports the International Space Station (ISS) along with the Commercial Crew Program and oversees the development of the Orion (spacecraft), Orion spacecraft and the Sp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zhurong (rover)
( zh, c=祝融, p=Zhùróng, l=) is a Chinese rover on Mars, the country's first to land on another planet after it previously landed two rovers on the Moon. The rover is part of the '' Tianwen-1'' mission to Mars conducted by the China National Space Administration (CNSA). The spacecraft was launched on 23 July 2020 and inserted into Martian orbit on 10 February 2021. The lander, carrying the rover, performed a soft landing on Mars on 14 May 2021, making China the third country to successfully soft-land a spacecraft on Mars and the second one to deploy a rover on Mars, after the United States. ''Zhurong'' was deployed on 22 May 2021, 02:40 UTC. Designed for a lifespan of 90 sols (93 Earth days), ''Zhurong'' was active for more than 347 sols (358 days) after its deployment on Mars's surface. The rover became inactive on 20 May 2022 due to approaching sandstorms and Martian winter. With appropriate temperature and sunlight conditions, ''Zhurong'' was expected to wake up i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
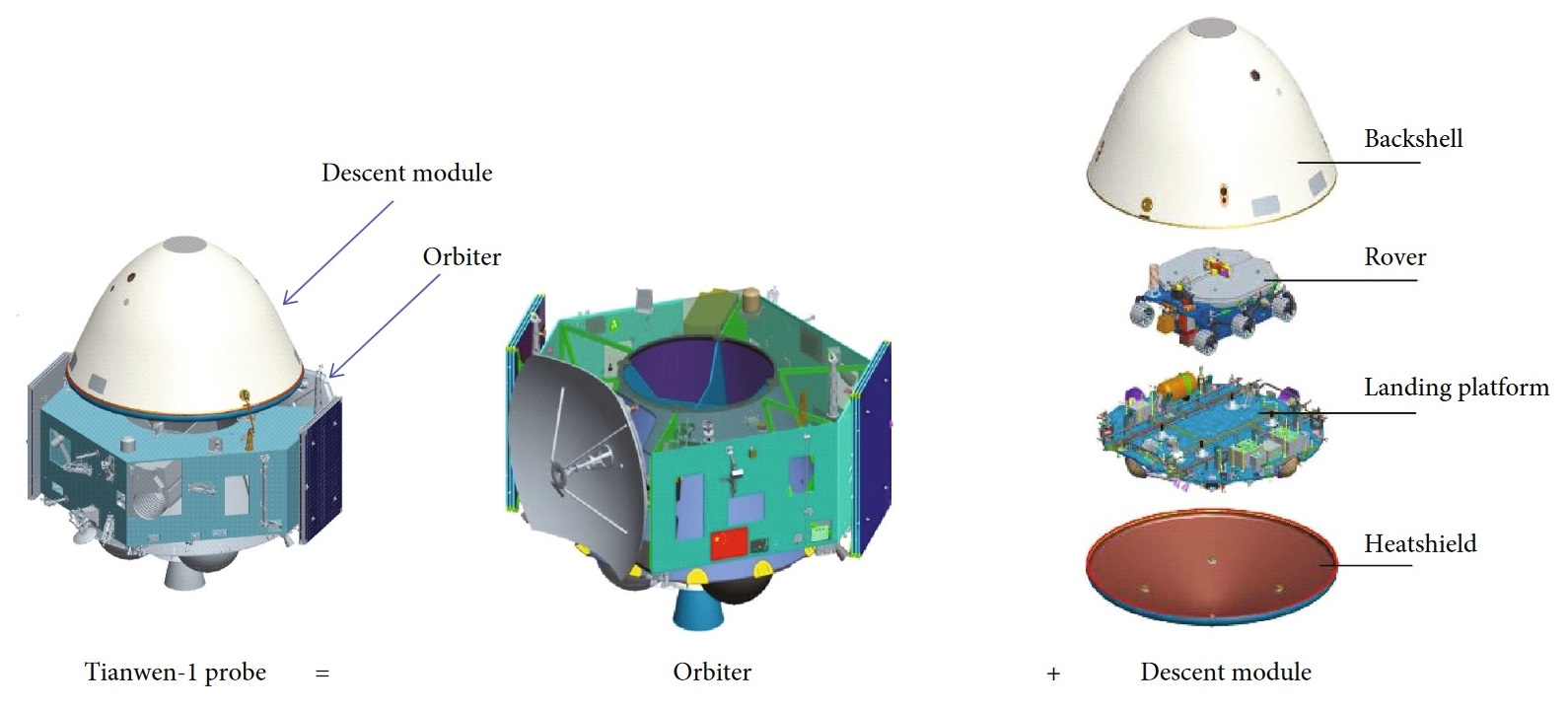
Tianwen-1
-1 ( zh , s = 天问一号) (also referred to as TW-1) is an interplanetary mission by the China National Space Administration (CNSA) which sent a robotic spacecraft to Mars, consisting of 6 spacecraft: an orbiter, two deployable cameras, lander, remote camera, and the ' rover. The spacecraft, with a total mass of nearly five tons, is one of the heaviest probes launched to Mars and carries 14 scientific instruments. It is the first in a series of planned missions undertaken by CNSA as part of its Planetary Exploration of China program. The mission's scientific objectives include: investigation of Martian surface geology and internal structure, search for indications of current and past presence of water, and characterization of the space environment and the atmosphere of Mars. The mission was launched from the Wenchang Spacecraft Launch Site on 23 July 2020 on a Long March 5 heavy-lift launch vehicle. After seven months of transit through the inner Solar System, the spac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
China National Space Administration
The China National Space Administration (CNSA) is a government agency of the People's Republic of China headquartered in Haidian District, Haidian, Beijing, responsible for civil space administration and international space cooperation. These responsibilities include organizing or leading foreign exchanges and cooperation in the aerospace field. The CNSA is an administrative agency under the State Administration of Science, Technology and Industry for National Defense. Founded in 1993, CNSA has pioneered a number of achievements in space for China despite its relatively short history, including becoming the first space agency to land on the far side of the Moon with Chang'e 4, bringing material back from the Moon with Chang'e 5 and Chang'e 6, 6, and being the second agency who successfully landed a rover on Mars with Tianwen-1. Tianwen-2 is enroute to explore the co-orbital near-Earth asteroid 469219 Kamoʻoalewa and the active asteroid 311P/PanSTARRS and collecting samples of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mars Launch Window
The planet Mars has been explored remotely by spacecraft. Probes sent from Earth, beginning in the late 20th century, have yielded a large increase in knowledge about the Martian system, focused primarily on understanding its geology and habitability potential. Engineering interplanetary journeys is complicated and the exploration of Mars has experienced a high failure rate, especially the early attempts. Roughly sixty percent of all spacecraft destined for Mars failed before completing their missions, with some failing before their observations could begin. Some missions have been met with unexpected success, such as the twin Mars Exploration Rovers, '' Spirit'' and ''Opportunity'', which operated for years beyond their specification. Current status There are two functional rovers on the surface of Mars, the ''Curiosity'' and ''Perseverance'' rovers, both operated by the American space agency NASA. ''Perseverance'' was accompanied by the '' Ingenuity'' helicopter, which s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Knowledge-based Economy
The knowledge economy, or knowledge-based economy, is an economic system in which the production of goods and services is based principally on Knowledge intensive services, knowledge-intensive activities that contribute to advancement in Technology, technical and scientific innovation. The key element of value is the greater dependence on human capital and intellectual property as the source of innovative Idea, ideas, information, and Practice (learning method), practices. Organisations are required to Capitalism, capitalise on this "knowledge" in their production to stimulate and deepen the business development process. There is less reliance on Factors of production, physical input and natural resources. A knowledge-based economy relies on the crucial role of intangible assets within the organisations' settings in facilitating modern economic growth. Overview Description A knowledge economy features a highly Skilled worker, skilled workforce within the Microeconomics, microeco ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Atmosphere Of Mars
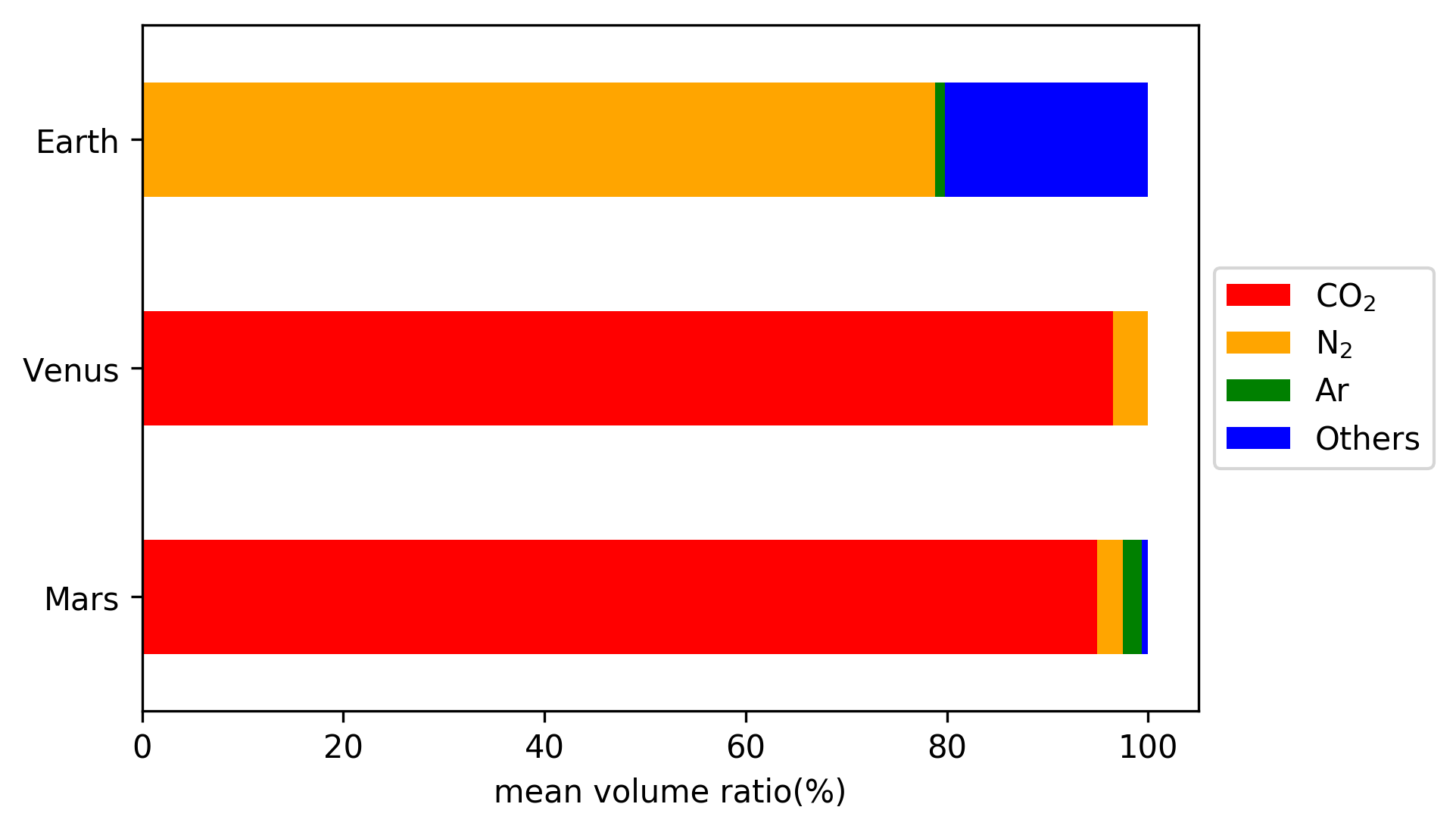
The atmosphere of Mars is the layer of gases surrounding Mars. It is primarily composed of carbon dioxide (95%), molecular nitrogen (2.85%), and argon (2%). It also contains trace levels of water vapor, oxygen, carbon monoxide, hydrogen, and noble gases. The atmosphere of Mars is much thinner and colder than Atmosphere of Earth, Earth's having a max density 20 g/m3 (about 2% of Earth’s value) with a temperature generally below zero down to –60 °C. The average Atmospheric pressure, surface pressure is about which is 0.6% of the Earth's value. The currently thin Martian atmosphere prohibits the existence of liquid water on the surface of Mars, but many studies suggest that the Martian atmosphere was much thicker in the past. The higher density during spring and fall is reduced by 25% during the winter when carbon dioxide partly freezes at the pole caps. The highest atmospheric density on Mars is equal to the density found above the Earth's surface and is ≈0.020 kg/m3 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Climate Of Mars
The climate of Mars has been a topic of scientific curiosity for centuries, in part because it is the only terrestrial planet whose surface can be easily directly observed in detail from Earth with help from a telescope. Although Mars is smaller than Earth with only one tenth of Earth's mass, and 50% farther from the Sun than Earth, its climate has important similarities, such as the presence of polar ice caps, seasonal changes and observable weather patterns. It has attracted sustained study from planetologists and climatologists. While Mars's climate has similarities to Earth's, including periodic ice ages, there are also important differences, such as much lower thermal inertia. Mars's atmosphere has a scale height of approximately , 60% greater than that on Earth. The climate is of considerable relevance to the question of whether life is or ever has been present on the planet. Mars has been studied by Earth-based instruments since the 17th century, but it is only since ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |