|
Hiri Trade Cycle
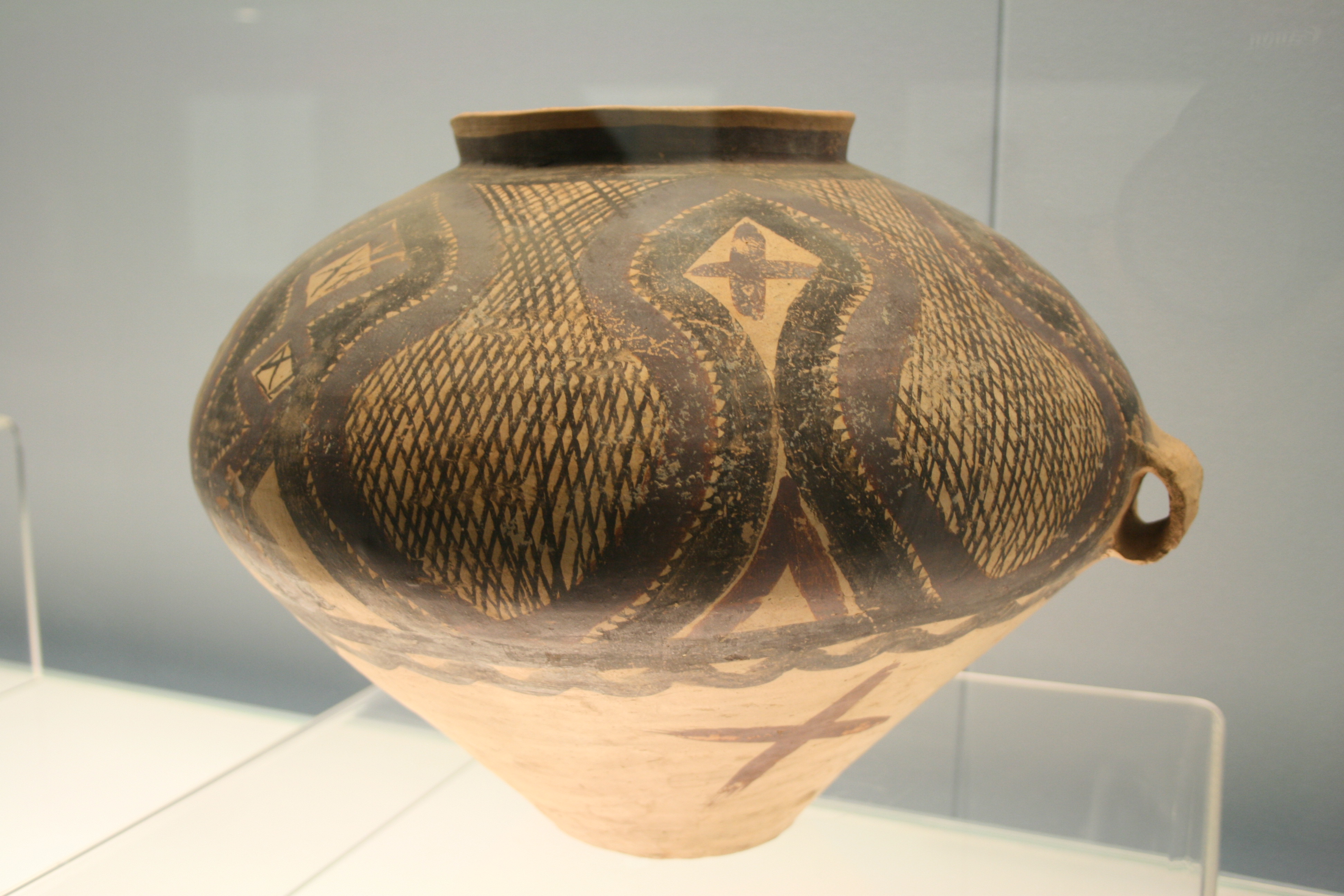
Hiri is the name for the traditional trade voyages that formed an important part of the culture of the Motu people of Papua New Guinea. Origins The Motu live in a comparative rain shadow – the dry season is unusually harsh, and there are not enough suitable areas for the growing of sago (''rabia''). On the other hand, the Motu, unlike most people of Papua New Guinea, were skilled in the art of making clay cooking pots (''uro''). The traditional Hiri voyages carried the much-prized Motu cooking pots to the people of the Gulf of Papua, and brought back plentiful supplies of sago for the Motu. Legend Edai Siabo, from the village of Boera, was returning from a fishing trip when a great eel appeared and dragged him under the water. The eel was really the spirit of the sea. He returned Edai to the surface of the sea, after instructing him to build a great lagatoi, to fill it with cooking pots, and to sail westward, following the south-east trade wind called the ''laurabada'' in t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trade
Trade involves the transfer of goods and services from one person or entity to another, often in exchange for money. Economists refer to a system or network that allows trade as a market. Traders generally negotiate through a medium of credit or exchange, such as money. Though some economists characterize barter (i.e. trading things without the use of money) as an early form of trade, money was invented before written history began. Consequently, any story of how money first developed is mostly based on conjecture and logical inference. Letters of credit, paper money, and non-physical money have greatly simplified and promoted trade as buying can be separated from selling, or earning. Trade between two traders is called bilateral trade, while trade involving more than two traders is called multilateral trade. In one modern view, trade exists due to specialization and the division of labor, a predominant form of economic activity in which individuals and groups ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Motuan People
The Motu are Indigenous peoples of Oceania, native inhabitants of Papua New Guinea, living along the southern coastal area of the country. Their indigenous language is also known as Motu language, Motu, and like several other languages of the region is an Austronesian languages, Austronesian language. They and the Koitabu people are the original inhabitants and owners of the land on which Port Moresby — the national capital city — stands. The largest Motu village is Hanuabada, northwest of Port Moresby. History Friedrich Ratzel in ''The History of Mankind'' in 1896 reported the tattooing in Melanesia. Among the relatively light-skinned Motu he found tattooing in patterns similar to those of Micronesia. He also reported, among the old women, blackening the body with a kind of earth which gives a lustre like black lead. This was said to be a sign of mourning. Charles Gabriel Seligman came into contact with the Motu, in 1904. He noted that, unlike many of their neighbors i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Papua New Guinea
Papua New Guinea, officially the Independent State of Papua New Guinea, is an island country in Oceania that comprises the eastern half of the island of New Guinea and offshore islands in Melanesia, a region of the southwestern Pacific Ocean north of Australia. It has Indonesia–Papua New Guinea border, a land border with Indonesia to the west and neighbours Australia to the south and the Solomon Islands to the east. Its capital, on its southern coast, is Port Moresby. The country is the world's third largest list of island countries, island country, with an area of . The nation was split in the 1880s between German New Guinea in the North and the Territory of Papua, British Territory of Papua in the South, the latter of which was ceded to Australia in 1902. All of present-day Papua New Guinea came under Australian control following World War I, with the legally distinct Territory of New Guinea being established out of the former German colony as a League of Nations mandate. T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hiri Moale Festival , a traditional trade-route in South East coastal New Guinea before European contact
{{disambig ...
The word Hiri has several meanings: * Hiri, a cross-platform desktop email-client * Mount Hiri, a volcanic island north of Ternate in the Maluku Islands of Indonesia * Hiri Motu, an official language of Papua New Guinea * Hiri Rural LLG, a local-level government area in Papua New Guinea * The Hiri trade cycle Hiri is the name for the traditional trade voyages that formed an important part of the culture of the Motu people of Papua New Guinea. Origins The Motu live in a comparative rain shadow – the dry season is unusually harsh, and there are not ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
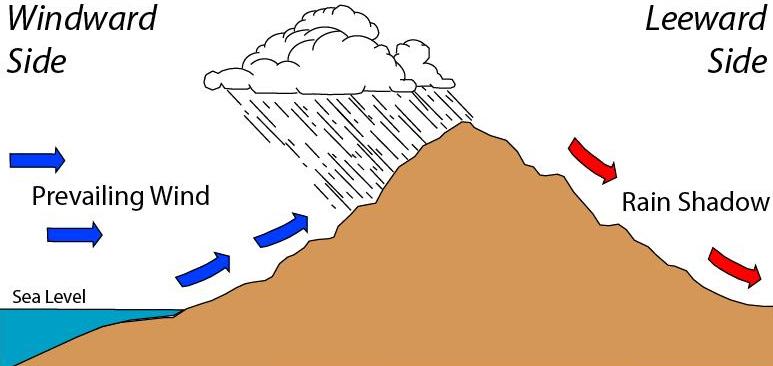
Rain Shadow
A rain shadow is an area of significantly reduced rainfall behind a mountainous region, on the side facing away from prevailing winds, known as its leeward side. Evaporated moisture from body of water, bodies of water (such as oceans and large lakes) is carried by the prevailing sea breeze, onshore breezes towards the drier and hotter inland areas. When encountering elevated landforms, the moist air is orographic lift, driven upslope towards the summit, peak, where it expands, cools, and its moisture condenses and starts to Precipitation, precipitate. If the landforms are tall and wide enough, most of the humidity will be lost to precipitation over the windward side (also known as the ''rainward'' side) before ever making it past the top. As the air descends the leeward side of the landforms, it is compressed and heated, producing Foehn winds that ''absorb'' moisture downslope and cast a broad "shadow" of arid, dry climate region behind the ridge, mountain crests. This climate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dry Season
The dry season is a yearly period of low rainfall, especially in the tropics. The weather in the tropics is dominated by the tropical rain belt, which moves from the northern to the southern tropics and back over the course of the year. The temperate counterpart to the tropical dry season is summer or winter. Rain belt The tropical rain belt lies in the southern hemisphere roughly from November to March; during that time the northern tropics have a dry season with sparser precipitation, and days are typically sunny throughout. From May to September, the rain belt lies in the northern hemisphere, and the southern tropics have their dry season. Under the Köppen climate classification, for tropical climates, a dry season month is defined as a month when average precipitation is below . The rain belt reaches roughly as far north as the Tropic of Cancer and as far south as the Tropic of Capricorn. Near these latitudes, there is one wet season and one dry season annually. At the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sago
Sago () is a starch extracted from the pith, or spongy core tissue, of various tropical palm stems, especially those of ''Metroxylon sagu''. It is a major staple food for the lowland peoples of New Guinea and the Maluku Islands, where it is called ''saksak'', ''rabia'' and ''sagu''. The largest supply of sago comes from Melanesia region, particularly Eastern Indonesia. Large quantities of sago are sent to Europe and North America for cooking purposes. It is traditionally cooked and eaten in various forms, such as rolled into balls, mixed with boiling water to form a glue-like paste (Papeda (food), papeda), or as a pancake. Sago is often produced commercially in the form of "pearls" (small rounded starch aggregates, partly Starch gelatinization, gelatinized by heating). Sago pearls can be boiled with water or milk and sugar to make a sweet sago pudding. Sago pearls are similar in appearance to the pearled starches of other origin, e.g. cassava starch (tapioca) and potato starch ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pottery
Pottery is the process and the products of forming vessels and other objects with clay and other raw materials, which are fired at high temperatures to give them a hard and durable form. The place where such wares are made by a ''potter'' is also called a ''pottery'' (plural ''potteries''). The definition of ''pottery'', used by the ASTM International, is "all fired ceramic wares that contain clay when formed, except technical, structural, and refractory products". End applications include tableware, ceramic art, decorative ware, toilet, sanitary ware, and in technology and industry such as Insulator (electricity), electrical insulators and laboratory ware. In art history and archaeology, especially of ancient and prehistoric periods, pottery often means only vessels, and sculpture, sculpted figurines of the same material are called terracottas. Pottery is one of the Timeline of historic inventions, oldest human inventions, originating before the Neolithic, Neolithic period, w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gulf Of Papua
The Gulf of Papua is located in the southern coast region of New Guinea. It has a total surface area of . Geography Some of New Guinea's largest rivers, such as the Fly River, Turama River, Kikori River, Purari River, and Wawoi River flow into the gulf, making it a large delta. While the western coast is characterized by swampy tidal waterways, land to the east ending at Cape Possession is flat and sandy. The Papuan Gulf's central and eastern interior slowly rises to meet the mountainous Southern Highlands and is covered in a variety of inland swamps and dense tropical hardwood forests. The western interior possesses a large region of limestone karst. The dry season begins in October and extends to February, after which the wet season starts. The southern border of the gulf is defined as a line from the southwestern corner of the Fly River Delta in the west, to Cape Suckling 355 km east of this, which is 70 km northwest of Port Moresby. This encloses a sea are ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
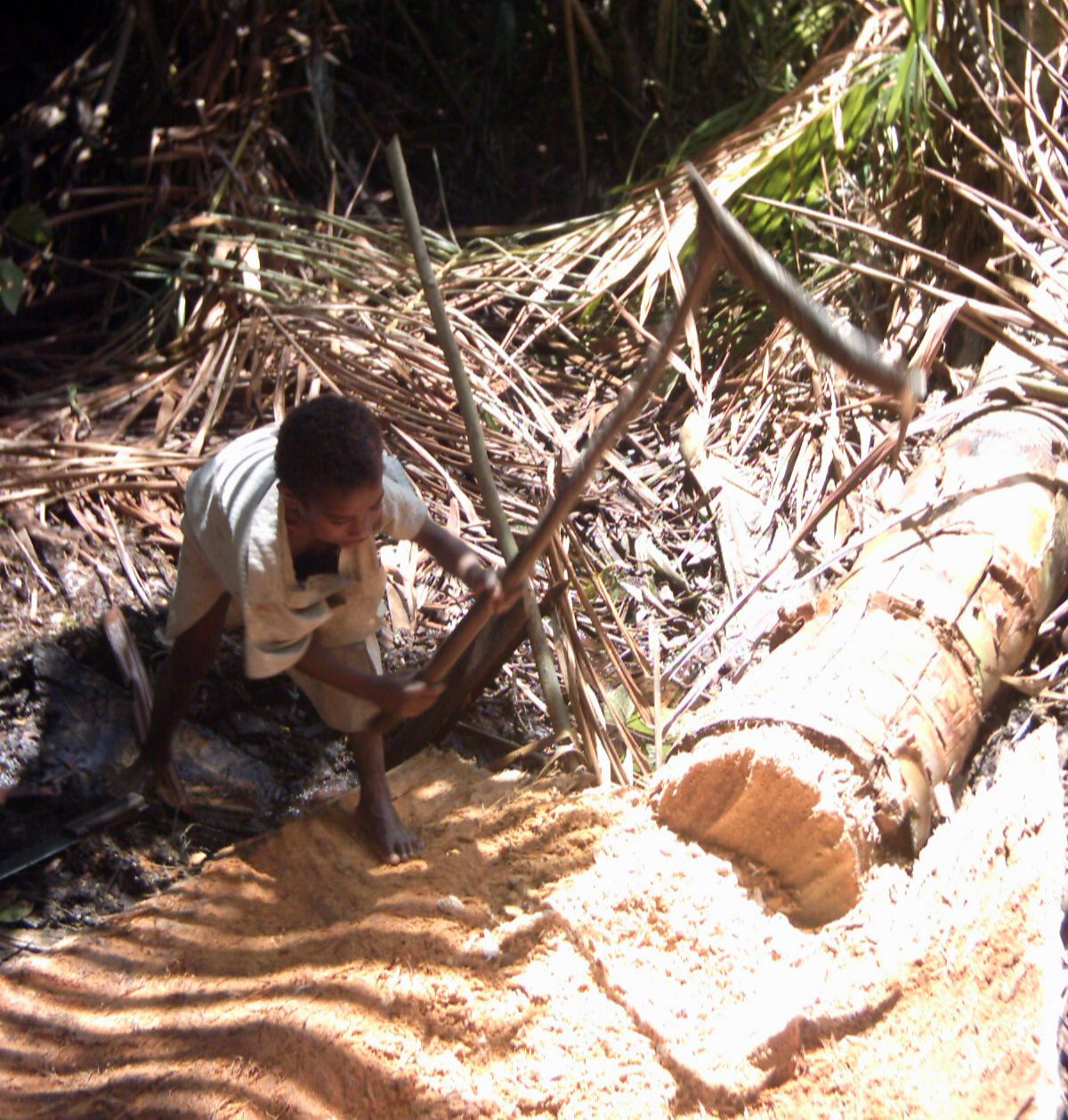
Lakatoi
Lakatoi (also Lagatoi) are multiple-hulled sailing watercraft of Papua New Guinea. They are named in the Motu language and traditionally used in the Hiri trade cycle. Lakatoi (whose literal meaning is ''three dugouts)'' are fashioned from two or more dugout logs fastened together to give stability and cargo-carrying capacity. The two or more dugouts are joined by booms, with a platform built on top. The sail is a crab-claw sail. Horridge (2008) discusses the rig and how the craft is manouvred. Gallery File:Picturesque New Guinea Plate V (a) - Loading Lakatoi, Port Moresby.jpg, Loading a ''lakatoi'' at Port Moresby, prior to 1885 File:Picturesque New Guinea Plate VII (a) - Lakatoi, Near Elevala Island.jpg, ''Lakatoi'' near Elevala Island, prior to 1885 File:PSM V52 D045 Papuan lake dwellings with a lakatoi under sail.jpg, Papuan lake dwellings with a ''lakatoi'' under sail, 1898 or before File:Papua Lakatoi 2s 6d stamp with POSTAGIE variety.jpg, 1901 stamp by the British Gov ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trade Wind
The trade winds or easterlies are permanent east-to-west prevailing winds that flow in the Earth's equatorial region. The trade winds blow mainly from the northeast in the Northern Hemisphere and from the southeast in the Southern Hemisphere, strengthening during the winter and when the Arctic oscillation is in its warm phase. Trade winds have been used by captains of sailing ships to cross the world's oceans for centuries. They enabled European colonization of the Americas, and trade routes to become established across the Atlantic Ocean and the Pacific Ocean. In meteorology, they act as the prevailing winds, steering flow for tropical storms that form over the Atlantic, Pacific, and southern Indian Ocean, Indian oceans and cause rainfall in North America, Southeast Asia, and Madagascar and East Africa. Shallow Trade wind cumulus cloud, cumulus clouds are seen within trade wind regimes and are capped from becoming taller by a trade wind Inversion (meteorology), inversion, whi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hiri Motu
Hiri Motu, also known as Police Motu, Pidgin Motu, or just Hiri, is a language of Papua New Guinea, which is spoken in surrounding areas of its capital city, Port Moresby. It is a simplified version of Motu, from the Austronesian language family. Although it is strictly neither a pidgin nor a creole, it possesses some features from both language types. Phonological and grammatical differences make Hiri Motu not mutually intelligible with Motu. The languages are lexically very similar, and retain a common, albeit simplified, Austronesian syntactical basis. It has also been influenced to some degree by Tok Pisin. Even in the areas where it was once well established as a ''lingua franca'', the use of Hiri Motu has been declining in favour of Tok Pisin and English for many years. The language has some statutory recognition. Origins The term '' hiri'' is the name for the traditional trade voyages that created a culture and style of living for the Motu people. Hiri Motu becam ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |