|
High Endothelial Venules
High endothelial venules (HEV) are specialized post-capillary venules characterized by plump endothelial cells as opposed to the usual flatter endothelial cells found in regular venules. HEVs enable lymphocytes circulating in the blood to directly enter a lymph node (by crossing through the HEV). Table 14-1 In humans, HEVs are found in all secondary lymphoid organs (with the exception of spleen, where blood exits through open arterioles and enters the red pulp), including hundreds of lymph nodes dispersed in the body, tonsils and adenoids in the pharynx, Peyer's patches (PIs) in the small intestine, appendix, and small aggregates of gut-associated lymphoid tissue, lymphoid tissue in the stomach and large intestine. In contrast to the endothelial cells from other vessels, the high endothelial cells of HEVs have a distinctive appearance, consisting of a cuboidal morphology (biology), morphology and with various receptors to interact with leukocytes (express specialized ligands for lym ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
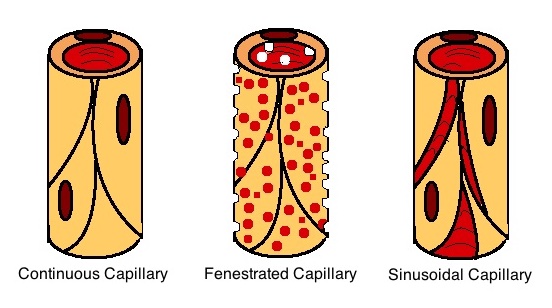
Capillary
A capillary is a small blood vessel, from 5 to 10 micrometres in diameter, and is part of the microcirculation system. Capillaries are microvessels and the smallest blood vessels in the body. They are composed of only the tunica intima (the innermost layer of an artery or vein), consisting of a thin wall of simple squamous endothelial cells. They are the site of the exchange of many substances from the surrounding interstitial fluid, and they convey blood from the smallest branches of the arteries (arterioles) to those of the veins (venules). Other substances which cross capillaries include water, oxygen, carbon dioxide, urea, glucose, uric acid, lactic acid and creatinine. Lymph capillaries connect with larger lymph vessels to drain lymphatic fluid collected in microcirculation. Etymology ''Capillary'' comes from the Latin word , meaning "of or resembling hair", with use in English beginning in the mid-17th century. The meaning stems from the tiny, hairlike diameter of a capi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
L-selectin
L-selectin, also known as CD62L, is a cell adhesion molecule found on the cell surface of leukocytes, and the blastocyst. It is coded for in the human by the ''SELL'' gene. L-selectin belongs to the selectin family of proteins, which recognize sialylated carbohydrate groups containing a Sialyl LewisX (sLeX) determinant. L-selectin plays an important role in both the innate and adaptive immune responses by facilitating leukocyte-endothelial cell adhesion events. These tethering interactions are essential for the trafficking of monocytes and neutrophils into inflamed tissue as well as the homing of lymphocytes to secondary lymphoid organs. L-selectin is also expressed by lymphoid primed hematopoietic stem cells and may participate in the migration of these stem cells to the primary lymphoid organs. In addition to its function in the immune response, L-selectin is expressed on embryonic cells and facilitates the attachment of the blastocyst to the endometrial endothelium during human ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sialyl-Lewis X
Sialyl LewisX (sLeX), also known as cluster of differentiation 15s (CD15s) or stage-specific embryonic antigen 1 (SSEA-1), is a tetrasaccharide carbohydrate which is usually attached to O-glycans on the surface of cells. It is known to play a vital role in cell-to-cell recognition processes. It is also the means by which an egg attracts sperm; first, to stick to it, then bond with it and eventually form a zygote. Sialyl-LewisX is also one of the most important blood group antigens and is displayed on the terminus of glycolipids that are present on the cell surface. The sialyl-LewisX determinant, E-selectin ligand carbohydrate structure, is constitutively expressed on granulocytes and monocytes and mediates inflammatory extravasation of these cells. Resting T and B lymphocytes lack its expression and are induced to strongly express sialyl-LewisX upon activation. The sialyl-LewisX determinant is expressed preferentially on activated Th1 cells but not on Th2 cells. Structure Sia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
CC Chemokine Receptors
CC chemokine receptors (or beta chemokine receptors) are integral membrane proteins that specifically bind and respond to cytokines of the CC chemokine family. They represent one subfamily of chemokine receptors, a large family of G protein-linked receptors that are known as seven transmembrane (7-TM) proteins since they span the cell membrane seven times. To date, ten true members of the CC chemokine receptor subfamily have been described. These are named CCR1 to CCR10 according to the IUIS/WHO Subcommittee on Chemokine Nomenclature. Mechanism The CC chemokine receptors all work by activating the G protein Gi. Types Overview table CCR1 CCR1 was the first CC chemokine receptor identified and binds multiple inflammatory/inducible (see inducible gene) CC chemokines (including CCL4, CCL5, CCL6, CCL14, CCL15, CCL16 and CCL23). In humans, this receptor can be found on peripheral blood lymphocytes and monocytes. There is some suggestion that this c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
CCL21
Chemokine (C-C motif) ligand 21 (CCL21) is a small cytokine belonging to the CC chemokine family. This chemokine is also known as 6Ckine (because it has six conserved cysteine residues instead of the four cysteines typical to chemokines), exodus-2, and secondary lymphoid-tissue chemokine (SLC). CCL21 elicits its effects by binding to a cell surface chemokine receptor known as CCR7. The main function of CCL21 is to guide CCR7 expressing leukocytes to the secondary lymphoid organs, such as lymph nodes and Peyer's patches. Gene The gene for CCL21 is located on human chromosome 9. CCL21 is classified as a homeostatic chemokine, it is produced constitutively. However, its expression increases during inflammation. Protein structure Chemokine CCL21 contains an extended C-terminus which is not found in CCL19, another ligand of CCR7. C-terminal tail is composed of 37 amino acids rich in positively charged residues and therefore, it has high affinity for negatively charged molecul ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chemokine
Chemokines (), or chemotactic cytokines, are a family of small cytokines or signaling proteins secreted by cells that induce directional movement of leukocytes, as well as other cell types, including endothelial and epithelial cells. In addition to playing a major role in the activation of host immune responses, chemokines are important for biological processes, including morphogenesis and wound healing, as well as in the pathogenesis of diseases like cancers. Cytokine proteins are classified as chemokines according to behavior and structural characteristics. In addition to being known for mediating chemotaxis, chemokines are all approximately 8–10 kilodaltons in mass and have four cysteine residues in conserved locations that are key to forming their 3-dimensional shape. These proteins have historically been known under several other names including the ''SIS family of cytokines'', ''SIG family of cytokines'', ''SCY family of cytokines'', ''Platelet factor-4 superfamily'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
CD34
CD34 is a transmembrane phosphoglycoprotein protein encoded by the CD34 gene in humans, mice, rats and other species. CD34 derives its name from the cluster of differentiation protocol that identifies cell surface antigens. CD34 was first described on hematopoietic stem cells independently by Civin et al. and Tindle et al. as a cell surface glycoprotein and functions as a cell-cell adhesion factor. It may also mediate the attachment of hematopoietic stem cells to bone marrow extracellular matrix or directly to stromal cells. Clinically, it is associated with the selection and enrichment of hematopoietic stem cells for bone marrow transplants. Due to these historical and clinical associations, CD34 expression is almost ubiquitously related to hematopoietic cells; however, it is actually found on many other cell types as well. Function The CD34 protein is a member of a family of single-pass transmembrane sialomucin proteins that show expression on early haematopoietic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ICAM-1
ICAM-1 (Intercellular adhesion molecule, Intercellular Adhesion Molecule 1) also known as CD54 (Cluster of Differentiation 54) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''ICAM1'' gene. This gene encodes a cell surface glycoprotein which is typically expressed on endothelium, endothelial cells and cells of the immune system. It binds to integrins of type CD11a / CD18, or Integrin alpha M, CD11b / CD18 and is also exploited by rhinovirus as a receptor for entry into respiratory epithelium. Structure ICAM-1 is a member of the immunoglobulin superfamily, the superfamily of proteins including antibody, antibodies and T cell receptor, T-cell receptors. ICAM-1 is a transmembrane protein possessing an N-terminus, amino-terminus extracellular domain, a single transmembrane domain, and a C-terminus, carboxy-terminus cytoplasmic domain. The structure of ICAM-1 is characterized by heavy glycosylation, and the protein’s extracellular domain is composed of multiple loops created by dis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Addressin
Mucosal vascular addressin cell adhesion molecule 1 (MAdCAM-1) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''MADCAM1'' gene. The protein encoded by this gene is an endothelium, endothelial cell adhesion molecule that interacts preferentially with the leukocyte beta7 integrin LPAM-1 (ITGA7, alpha4 / ITGB7, beta7), L-selectin, and VLA-4 (alpha4 / CD29, beta1) on myeloid cells to direct leukocytes into mucosal and inflamed tissues. It is a member of the immunoglobulin superfamily and is similar to ICAM-1 and VCAM-1. Nomenclature Addressin is a lesser-used term to describe the group of adhesion molecules that are involved with lymphocyte homing, commonly found at High endothelial venules, high-endothelial venules (HEVs) where lymphocytes exit the blood and enter the lymph node. Addressins are the ligands to the homing receptors of lymphocytes. The task of these ligands and their receptors is to determine which tissue the lymphocyte will enter next. They carry carbohydrates in o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lymphotoxin
Lymphotoxin is a member of the tumor necrosis factor (TNF) superfamily of cytokines, whose members are responsible for regulating the growth and function of lymphocytes and are expressed by a wide variety of cells in the body. Lymphotoxin plays a critical role in developing and preserving the framework of lymphoid organs and of gastrointestinal immune responses, as well as in the activation signaling of both the innate and adaptive immune responses. Lymphotoxin alpha (LT-α, previously known as TNF-beta) and lymphotoxin beta (LT-β), the two forms of lymphotoxin, each have distinctive structural characteristics and perform specific functions. Structure and function Each LT-α/LT-β subunit is a trimer and assembles into homotrimers or heterotrimers. LT-α binds with LT-β to form membrane-bound heterotrimers LT-α1-β2 and LT-α2-β1, which are commonly referred to as lymphotoxin beta. LT-α1-β2 is the most prevalent form of lymphotoxin beta. LT-α also forms a homotrim ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
CD11c
CD11c, also known as Integrin, alpha X (complement component 3 receptor 4 subunit) (ITGAX), is a gene that encodes for CD11c . CD11c is an integrin alpha X chain protein. Integrins are heterodimeric integral membrane proteins composed of an alpha chain and a beta chain. This protein combines with the beta 2 chain (ITGB2) to form a leukocyte-specific integrin referred to as inactivated-C3b (iC3b) receptor 4 (CR4). The alpha X beta 2 complex seems to overlap the properties of the alpha M beta 2 integrin in the adherence of neutrophils and monocytes to stimulated endothelium cells, and in the phagocytosis of complement coated particles. CD11c is a type I transmembrane protein found at high levels on most human dendritic cells, but also on monocytes, macrophages, neutrophils, and some B cells that induces cellular activation and helps trigger neutrophil respiratory burst; expressed in hairy cell leukemias, acute nonlymphocytic leukemias, and some B-cell chronic lymphocytic leuk ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dendritic Cells
A dendritic cell (DC) is an antigen-presenting cell (also known as an ''accessory cell'') of the mammalian immune system. A DC's main function is to process antigen material and present it on the cell surface to the T cells of the immune system. They act as messengers between the innate and adaptive immune systems. Dendritic cells are present in tissues that are in contact with the body's external environment, such as the skin, and the inner lining of the nose, lungs, stomach and intestines. They can also be found in an immature and mature state in the blood. Once activated, they migrate to the lymph nodes, where they interact with T cells and B cells to initiate and shape the adaptive immune response. At certain development stages they grow branched projections, the '' dendrites,'' that give the cell its name (δένδρον or déndron being Greek for 'tree'). While similar in appearance to the dendrites of neurons, these are structures distinct from them. Immature dendrit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |