|
L-selectin
L-selectin, also known as CD62L, is a cell adhesion molecule found on the cell surface of leukocytes, and the blastocyst. It is coded for in the human by the ''SELL'' gene. L-selectin belongs to the selectin family of proteins, which recognize sialylated carbohydrate groups containing a Sialyl LewisX (sLeX) determinant. L-selectin plays an important role in both the innate and adaptive immune responses by facilitating leukocyte-endothelial cell adhesion events. These tethering interactions are essential for the trafficking of monocytes and neutrophils into inflamed tissue as well as the homing of lymphocytes to secondary lymphoid organs. L-selectin is also expressed by lymphoid primed hematopoietic stem cells and may participate in the migration of these stem cells to the primary lymphoid organs. In addition to its function in the immune response, L-selectin is expressed on embryonic cells and facilitates the attachment of the blastocyst to the endometrial endothelium during human ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
High Endothelial Venule
High endothelial venules (HEV) are specialized post-capillary venules characterized by plump endothelial cells as opposed to the usual flatter endothelial cells found in regular venules. HEVs enable lymphocytes circulating in the blood to directly enter a lymph node (by crossing through the HEV). Table 14-1 In humans, HEVs are found in all secondary lymphoid organs (with the exception of spleen, where blood exits through open arterioles and enters the red pulp), including hundreds of lymph nodes dispersed in the body, tonsils and adenoids in the pharynx, Peyer's patches (PIs) in the small intestine, appendix, and small aggregates of lymphoid tissue in the stomach and large intestine. In contrast to the endothelial cells from other vessels, the high endothelial cells of HEVs have a distinctive appearance, consisting of a cuboidal morphology and with various receptors to interact with leukocytes (express specialized ligands for lymphocytes and are able to support high levels of lymph ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Selectins
The selectins (cluster of differentiation 62 or CD62) are a family of cell adhesion molecules (or CAMs). All selectins are single-chain transmembrane glycoproteins that share similar properties to C-type lectins due to a related amino terminus and calcium-dependent binding. Selectins bind to sugar moieties and so are considered to be a type of lectin, cell adhesion proteins that bind sugar polymers. Structure All three known members of the selectin family (L-, E-, and P-selectin) share a similar cassette structure: an N-terminal, calcium-dependent lectin domain, an epidermal growth factor (EGF)-like domain, a variable number of consensus repeat units (2, 6, and 9 for L-, E-, and P-selectin, respectively), a transmembrane domain (TM) and an intracellular cytoplasmic tail (cyto). The transmembrane and cytoplasmic parts are not conserved across the selectins being responsible for their targeting to different compartments. Though they share common elements, their tissue distribu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Selectin
The selectins ( cluster of differentiation 62 or CD62) are a family of cell adhesion molecules (or CAMs). All selectins are single-chain transmembrane glycoproteins that share similar properties to C-type lectins due to a related amino terminus and calcium-dependent binding. Selectins bind to sugar moieties and so are considered to be a type of lectin, cell adhesion proteins that bind sugar polymers. Structure All three known members of the selectin family (L-, E-, and P-selectin) share a similar cassette structure: an N-terminal, calcium-dependent lectin domain, an epidermal growth factor (EGF)-like domain, a variable number of consensus repeat units (2, 6, and 9 for L-, E-, and P-selectin, respectively), a transmembrane domain (TM) and an intracellular cytoplasmic tail (cyto). The transmembrane and cytoplasmic parts are not conserved across the selectins being responsible for their targeting to different compartments. Though they share common elements, their tissue d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
PSGL-1
Selectin P ligand, also known as SELPLG or CD162 (cluster of differentiation 162), is a human gene. SELPLG codes for PSGL-1, the high affinity counter-receptor for P-selectin on myeloid cells and stimulated T lymphocytes. As such, it plays a critical role in the tethering of these cells to activated platelets or endothelia expressing P-selectin. Naive and stimulated lymphocytes appear to use PSGL-1 for trafficking into and out of lymph nodes. The gene and structure of human PSGL-1 was first reported in 1993. In 1995, most of the binding activity of PSGL-1 was localized within its N-terminal 19 amino acids, including the sulfotyrosines (Tys) at positions 5, 7 and 10 and the critical O-linked glycan attached to the threonine at position 16 of the mature, fully processed PSGL-1 present on a cell's surface. The co-crystal structure of human PSGL-1 bound to human P-selectin was published in 2000. https://www.cell.com/cms/10.1016/S0092-8674(00)00138-0/asset/b4d95b05-fc96-4a34-837a-48b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Implantation (embryology)
Implantation, also known as nidation, is the stage in the mammalian embryonic development in which the blastocyst hatches, attaches, adheres, and penetrates into the endometrium of the female's uterus. Implantation is the first stage of gestation, and, when successful, the female is considered to be pregnant. An implanted embryo is detected by the presence of increased levels of human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG) in a pregnancy test. The implanted embryo will receive oxygen and nutrients in order to grow. For implantation to take place the uterus must become receptive. Uterine receptivity involves much cross-talk between the embryo and the uterus, initiating changes to the endometrium. This stage gives a synchrony that opens a window of implantation that enables successful implantation of a viable embryo. The endocannabinoid system plays a vital role in this synchrony in the uterus, influencing uterine receptivity, and embryo implantation. The embryo expresses cannabinoid r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
CD34
CD34 is a transmembrane phosphoglycoprotein protein encoded by the CD34 gene in humans, mice, rats and other species. CD34 derives its name from the cluster of differentiation protocol that identifies cell surface antigens. CD34 was first described on hematopoietic stem cells independently by Civin et al. and Tindle et al. as a cell surface glycoprotein and functions as a cell-cell adhesion factor. It may also mediate the attachment of hematopoietic stem cells to bone marrow extracellular matrix or directly to stromal cells. Clinically, it is associated with the selection and enrichment of hematopoietic stem cells for bone marrow transplants. Due to these historical and clinical associations, CD34 expression is almost ubiquitously related to hematopoietic cells; however, it is actually found on many other cell types as well. Function The CD34 protein is a member of a family of single-pass transmembrane sialomucin proteins that show expression on early haematopoietic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
T-lymphocytes
T cells (also known as T lymphocytes) are an important part of the immune system and play a central role in the adaptive immune response. T cells can be distinguished from other lymphocytes by the presence of a T-cell receptor (TCR) on their cell surface. T cells are born from hematopoietic stem cells, found in the bone marrow. Developing T cells then migrate to the thymus gland to develop (or mature). T cells derive their name from the thymus. After migration to the thymus, the precursor cells mature into several distinct types of T cells. T cell differentiation also continues after they have left the thymus. Groups of specific, differentiated T cell subtypes have a variety of important functions in controlling and shaping the immune response. One of these functions is immune-mediated cell death, and it is carried out by two major subtypes: CD8+ "killer" (cytotoxic) and CD4+ "helper" T cells. (These are named for the presence of the cell surface proteins CD8 or CD4.) CD8+ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
MadCAM-1
Mucosal vascular addressin cell adhesion molecule 1 (MAdCAM-1) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''MADCAM1'' gene. The protein encoded by this gene is an endothelial cell adhesion molecule that interacts preferentially with the leukocyte beta7 integrin LPAM-1 ( alpha4 / beta7), L-selectin, and VLA-4 (alpha4 / beta1) on myeloid cells to direct leukocytes into mucosal and inflamed tissues. It is a member of the immunoglobulin superfamily and is similar to ICAM-1 and VCAM-1. Nomenclature Addressin is a lesser-used term to describe the group of adhesion molecules that are involved with lymphocyte homing, commonly found at high-endothelial venules (HEVs) where lymphocytes exit the blood and enter the lymph node. Addressins are the ligands to the homing receptors of lymphocytes. The task of these ligands and their receptors is to determine which tissue the lymphocyte will enter next. They carry carbohydrates in order to be recognized by L-selectin. Addressins physi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
T Cell
T cells (also known as T lymphocytes) are an important part of the immune system and play a central role in the adaptive immune response. T cells can be distinguished from other lymphocytes by the presence of a T-cell receptor (TCR) on their cell surface receptor, cell surface. T cells are born from hematopoietic stem cells, found in the bone marrow. Developing T cells then migrate to the thymus gland to develop (or mature). T cells derive their name from the thymus. After migration to the thymus, the precursor cells mature into several distinct types of T cells. T cell differentiation also continues after they have left the thymus. Groups of specific, differentiated T cell subtypes have a variety of important functions in controlling and shaping the immune response. One of these functions is immune-mediated cell death, and it is carried out by two major subtypes: Cytotoxic T cell, CD8+ "killer" (cytotoxic) and T helper cell, CD4+ "helper" T cells. (These are named for the presen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ADAM17
A disintegrin and metalloprotease 17 (ADAM17), also called TACE (''tumor necrosis factor-α-converting enzyme''), is a 70-kDa enzyme that belongs to the ADAM protein family of disintegrins and metalloproteases, activated by substrate presentation. Structure ADAM17 is an 824-amino acid polypeptide. ADAM17 has multidomain structure that includes a pro-domain, a metallo-protease domain, a disintegrin domain, a cysteine-rich domain, an EGF-like domain, a transmembrane domain, and a cytoplasmic tail. The metalloprotease domain is responsible for the enzyme's catalytic activity, cleaving membrane-bound proteins, including cytokines like TNF-alpha, to release their soluble forms. The disintegrin and cysteine-rich domains are implicated in cell adhesion and interaction with integrins, while the transmembrane domain anchors the protein in the membrane. The cytoplasmic tail is involved in intracellular signaling and protein-protein interactions. ADAM17's activity is tightly regulated ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
GlyCAM-1
Glycosylation-dependent cell adhesion molecule-1 (GLYCAM1) is a proteoglycan ligand expressed on cells of the high endothelial venules in lymphoid tissues. It is the ligand for the receptor L-selectin L-selectin, also known as CD62L, is a cell adhesion molecule found on the cell surface of leukocytes, and the blastocyst. It is coded for in the human by the ''SELL'' gene. L-selectin belongs to the selectin family of proteins, which recognize si ... allowing for naive lymphocytes to exit the bloodstream into lymphoid tissues. GLYCAM1 binds to L-selectin by presenting one or more O-linked carbohydrates to the lectin domain of the leukocyte cell surface selectin. Data suggests that GLYCAM1 is a hormone-regulated milk protein that is part of the milk mucin complex. GlyCAM-1 is expressed exclusively on high endothelial venules. It is unclear how GlyCAM-1 is attached to the membrane as it lacks a transmembrane region. External links * References {{immunology-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
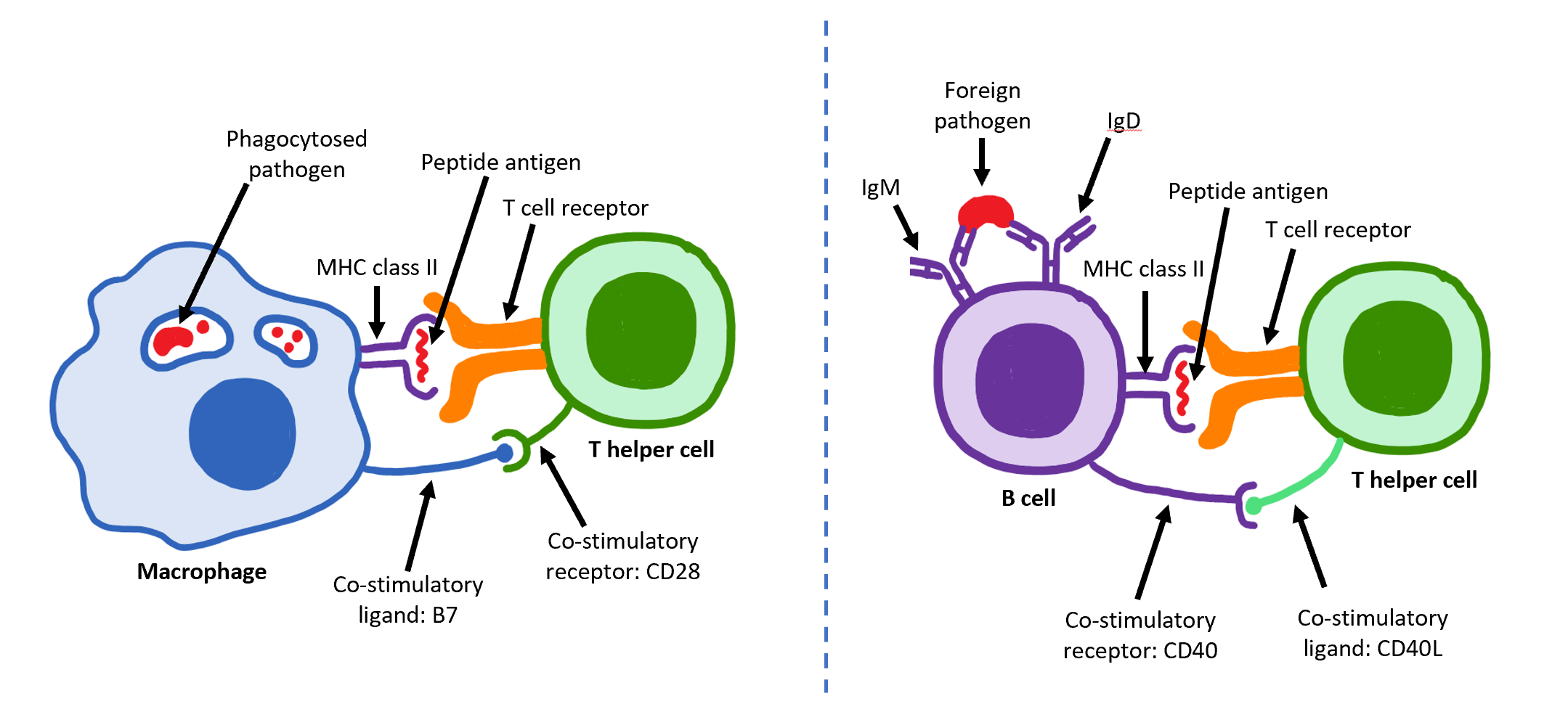
Cd4 T Cell
The T helper cells (Th cells), also known as CD4+ cells or CD4-positive cells, are a type of T cell that play an important role in the adaptive immune system. They aid the activity of other immune cells by releasing cytokines. They are considered essential in B cell antibody class switching, breaking cross-tolerance in dendritic cells, in the activation and growth of cytotoxic T cells, and in maximizing bactericidal activity of phagocytes such as macrophages and neutrophils. CD4+ cells are mature Th cells that express the surface protein CD4. Genetic variation in regulatory elements expressed by CD4+ cells determines susceptibility to a broad class of autoimmune diseases. Structure and function Th cells contain and release cytokines to aid other immune cells. Cytokines are small protein mediators that alter the behavior of target cells that express receptors for those cytokines. These cells help polarize the immune response depending on the nature of the immunological insult ( ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |