|
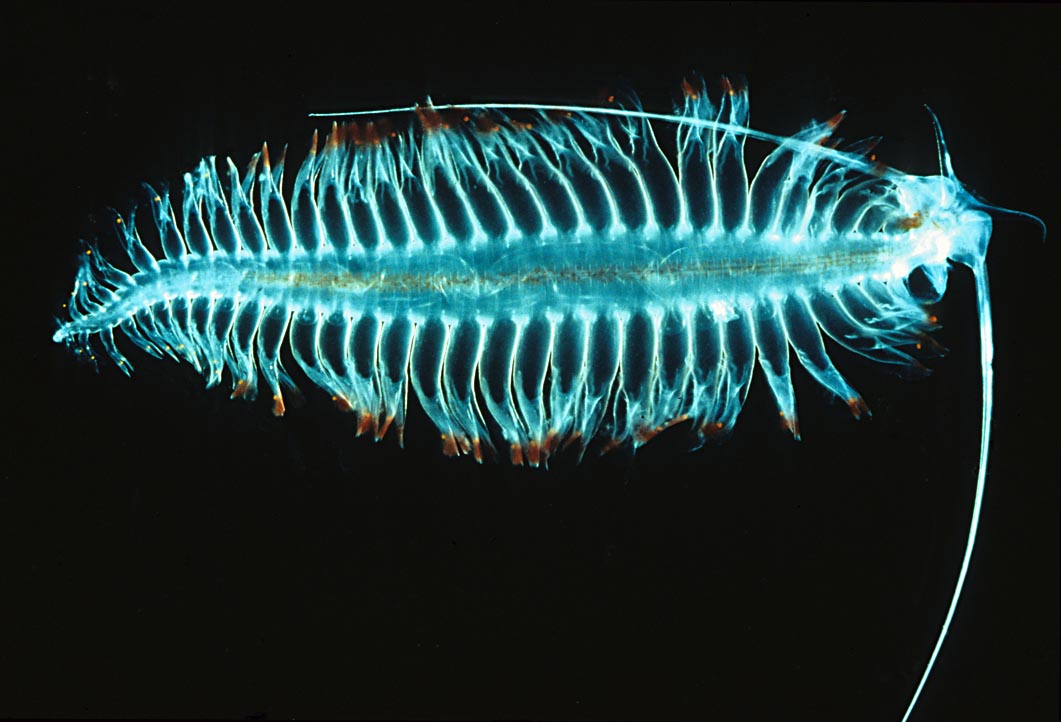
Heteropod
The Pterotracheoidea is, according to the Taxonomy of the Gastropoda (Bouchet & Rocroi, 2005), a taxonomic superfamily of sea snails or sea slugs, marine gastropod molluscs in the clade Littorinimorpha. They are commonly called heteropods or sea elephants. Taxonomy This superfamily comprises four families (classification based on Newman (superfamily Carinarioidea, pp. 804–808. In: Beesley ''et al''., 1998), that is also used by the taxonomy of the Gastropoda by Bouchet & Rocroi (2005): * Family Pterotracheidae Rafinesque, 1814 * Family Atlantidae Rang, 1829 * † Family Bellerophinidae Destombes, 1984 * Family Carinariidae Blainville 1818 Habitat These holoplanktonic snails are found floating or swimming in tropical to subtropical open oceans and seas at a depth of maximum 200 to 300 m Anatomy These snails have adapted themselves to a pelagic living : * a transparent body and shell * the foot has evolved into a swimming fin that produces motion through u ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Littorinimorpha
Littorinimorpha is a large order of snails, gastropods, consisting primarily of sea snails ( marine species), but also including some freshwater snails ( aquatic species) and land snails ( terrestrial species).Bouchet P. & Rocroi J.-P. (Ed.); Frýda J., Hausdorf B., Ponder W., Valdes A. & Warén A. 2005. ''Classification and nomenclator of gastropod families''. Malacologia: International Journal of Malacology, 47(1-2). ConchBooks: Hackenheim, Germany. . . 397 pp. http://www.vliz.be/Vmdcdata/imis2/ref.php?refid=78278 Previously, the Linnaean taxonomy used in the taxonomy of the Gastropoda by Ponder & Lindberg (1997) ranked like this: subclass Orthogastropoda, superorder Caenogastropoda, order Sorbeoconcha, suborder Hypsogastropoda, infraorder Littorinimorpha. The order Littorinimorpha contains many gastropoda families that were formerly placed in the order Mesogastropoda, as introduced by J. Thiele in his work from 1921. Evidence for this group being monophyletic is scanty. In ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Constantine Samuel Rafinesque
Constantine Samuel Rafinesque-Schmaltz (; October 22, 1783September 18, 1840) was a French 19th-century polymath born near Constantinople in the Ottoman Empire and self-educated in France. He traveled as a young man in the United States, ultimately settling in Ohio in 1815, where he made notable contributions to botany, zoology, and the study of prehistoric earthworks in North America. He also contributed to the study of ancient Mesoamerican linguistics, in addition to work he had already completed in Europe. Rafinesque was an eccentric and erratic genius. He was an autodidact, who excelled in various fields of knowledge, as a zoologist, botanist, writer and polyglot. He wrote prolifically on such diverse topics as anthropology, biology, geology, and linguistics, but was honored in none of these fields during his lifetime. Indeed, he was an outcast in the American scientific community whose submissions were rejected automatically by leading journals. Among his theories were ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Holoplankton
Holoplankton are organisms that are planktic (they live in the water column and cannot swim against a current) for their entire life cycle. Holoplankton can be contrasted with meroplankton, which are planktic organisms that spend part of their life cycle in the benthic zone. Examples of holoplankton include some diatoms, radiolarians, some dinoflagellates, foraminifera, amphipods, krill, copepods, and salps, as well as some gastropod mollusk species. Holoplankton dwell in the pelagic zone as opposed to the benthic zone. Holoplankton include both phytoplankton and zooplankton and vary in size. The most common plankton are protists. Reproduction Holoplankton have unique traits that make reproduction in the water column possible. Both sexual and asexual reproduction are used depending on the type of plankton. Some invertebrate holoplankton release sperm into the water column which are then taken up by the females for fertilization. Other species release both sperm and egg to increa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Metamorphosis
Metamorphosis is a biological process by which an animal physically develops including birth or hatching, involving a conspicuous and relatively abrupt change in the animal's body structure through cell growth and differentiation. Some insects, fish, amphibians, mollusks, crustaceans, cnidarians, echinoderms, and tunicates undergo metamorphosis, which is often accompanied by a change of nutrition source or behavior. Animals can be divided into species that undergo complete metamorphosis (" holometaboly"), incomplete metamorphosis (" hemimetaboly"), or no metamorphosis (" ametaboly"). Scientific usage of the term is technically precise, and it is not applied to general aspects of cell growth, including rapid growth spurts. Generally organisms with a larva stage undergo metamorphosis, and during metamorphosis the organism loses larval characteristics. References to "metamorphosis" in mammals are imprecise and only colloquial, but historically idealist ideas of transf ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Veliger
A veliger is the planktonic larva of many kinds of sea snails and freshwater snails, as well as most bivalve molluscs (clams) and tusk shells. Description The veliger is the characteristic larva of the gastropod, bivalve and scaphopod taxonomic classes. It is produced following either the embryonic or trochophore larval stage of development. In bivalves the veliger is sometimes referred to as a D-stage (early in its development) or pediveliger (late in its development) larva. This stage in the life history of these groups is a free-living planktonic organism; this mode of life potentially enhances dispersal to new regions far removed from the adult mollusks that produced the larvae. The general structure of the veliger includes a shell that surrounds the visceral organs of the larva (e.g., digestive tract, much of the nervous system, excretory organs) and a ciliated velum that extends beyond the shell as a single or multi-lobed structure used for swimming and particu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anatomical Terms Of Location
Standard anatomical terms of location are used to unambiguously describe the anatomy of animals, including humans. The terms, typically derived from Latin or Greek roots, describe something in its standard anatomical position. This position provides a definition of what is at the front ("anterior"), behind ("posterior") and so on. As part of defining and describing terms, the body is described through the use of anatomical planes and anatomical axes. The meaning of terms that are used can change depending on whether an organism is bipedal or quadrupedal. Additionally, for some animals such as invertebrates, some terms may not have any meaning at all; for example, an animal that is radially symmetrical will have no anterior surface, but can still have a description that a part is close to the middle ("proximal") or further from the middle ("distal"). International organisations have determined vocabularies that are often used as standard vocabularies for subdisciplines o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Statocyst
The statocyst is a balance sensory receptor present in some aquatic invertebrates, including bivalves, cnidarians, ctenophorans, echinoderms, cephalopods, and crustaceans. A similar structure is also found in ''Xenoturbella''. The statocyst consists of a sac-like structure containing a mineralised mass (statolith) and numerous innervated sensory hairs (setae). The statolith's inertia causes it to push against the setae when the animal accelerates. Deflection of setae by the statolith in response to gravity activates neurons, providing feedback to the animal on change in orientation and allowing balance to be maintained. In other words, the statolith shifts as the animal moves. Any movement large enough to throw the organism off balance causes the statolith to brush against tiny bristles which in turn send a message to the brain to correct its balance. It may have been present in the common ancestor of cnidarians and bilaterians. Hearing In cephalopods like squids, statocysts ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Radula
The radula (, ; plural radulae or radulas) is an anatomical structure used by molluscs for feeding, sometimes compared to a tongue. It is a minutely toothed, chitinous ribbon, which is typically used for scraping or cutting food before the food enters the esophagus. The radula is unique to the molluscs, and is found in every class of mollusc except the bivalves, which instead use cilia, waving filaments that bring minute organisms to the mouth. Within the gastropods, the radula is used in feeding by both herbivorous and carnivorous snails and slugs. The arrangement of teeth ( denticles) on the radular ribbon varies considerably from one group to another. In most of the more ancient lineages of gastropods, the radula is used to graze, by scraping diatoms and other microscopic algae off rock surfaces and other substrates. Predatory marine snails such as the Naticidae use the radula plus an acidic secretion to bore through the shell of other molluscs. Other predatory marine sn ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Proboscis
A proboscis () is an elongated appendage from the head of an animal, either a vertebrate or an invertebrate. In invertebrates, the term usually refers to tubular mouthparts used for feeding and sucking. In vertebrates, a proboscis is an elongated nose or snout. Etymology First attested in English in 1609 from Latin , the latinisation of the Ancient Greek (), which comes from () 'forth, forward, before' + (), 'to feed, to nourish'. The plural as derived from the Greek is , but in English the plural form ''proboscises'' occurs frequently. Invertebrates The most common usage is to refer to the tubular feeding and sucking organ of certain invertebrates such as insects (e.g., moths, butterflies, and mosquitoes), worms (including Acanthocephala, proboscis worms) and gastropod molluscs. Acanthocephala The Acanthocephala or thorny-headed worms, or spiny-headed worms are characterized by the presence of an eversible proboscis, armed with spines, which it uses to pierce an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pelagic
The pelagic zone consists of the water column of the open ocean, and can be further divided into regions by depth (as illustrated on the right). The word ''pelagic'' is derived . The pelagic zone can be thought of as an imaginary cylinder or water column between the surface of the sea and the bottom. Conditions in the water column change with depth: pressure increases; temperature and light decrease; salinity, oxygen, micronutrients (such as iron, magnesium and calcium) all change. Marine life is affected by bathymetry (underwater topography) such as the seafloor, shoreline, or a submarine seamount, as well as by proximity to the boundary between the ocean and the atmosphere at the ocean surface, which brings light for photosynthesis, predation from above, and wind stirring up waves and setting currents in motion. The pelagic zone refers to the open, free waters away from the shore, where marine life can swim freely in any direction unhindered by topographical constraints. Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scripta Geologica
''Scripta Geologica'' is a peer-reviewed scientific journal that publishes on vertebrate and invertebrate palaeontology, palaeobotany/palynology, stratigraphy, petrology, and mineralogy, including gemmology with a focus on systematics. It is published by the Dutch National Museum of Natural History, Naturalis. ''Scripta Geologica'' was established in 1881 as ''Sammlungen des geologischen Reichsmuseums in Leiden'' (1881-1923), changing its title to ''Leidse Geologische Mededelingen'' in 1925 (originally spelled as ''Leidsche Geologische Mededeelingen''). From 1971, the latter title was published in parallel with ''Scripta Geologica'' until they were merged in 1985. Abstracting and indexing ''Scripta Geologica'' is abstracted and indexed in PASCAL, GeoBase, GeoAbstracts and GeoRef __NOTOC__ The GeoRef database is a bibliographic database that indexes scientific literature in the geosciences, including geology. Coverage ranges from 1666 to the present for North American liter ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bellerophinidae
Bellerophinidae is an extinct family of sea snails, marine gastropod molluscs in the clade Littorinimorpha Littorinimorpha is a large order of snails, gastropods, consisting primarily of sea snails ( marine species), but also including some freshwater snails ( aquatic species) and land snails ( terrestrial species).Bouchet P. & Rocroi J.-P. (Ed.); Fr .... According to taxonomy of the Gastropoda by Bouchet & Rocroi (2005) the family Pterotracheidae has no subfamilies. References {{paleo-gastropod-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |




_2.jpg)