statocyst on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
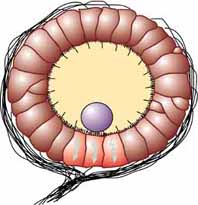
 The statocyst is a balance sensory receptor present in some aquatic
The statocyst is a balance sensory receptor present in some aquatic

 The statocyst is a balance sensory receptor present in some aquatic
The statocyst is a balance sensory receptor present in some aquatic invertebrate
Invertebrates are animals that neither develop nor retain a vertebral column (commonly known as a ''spine'' or ''backbone''), which evolved from the notochord. It is a paraphyletic grouping including all animals excluding the chordata, chordate s ...
s, including bivalve
Bivalvia () or bivalves, in previous centuries referred to as the Lamellibranchiata and Pelecypoda, is a class (biology), class of aquatic animal, aquatic molluscs (marine and freshwater) that have laterally compressed soft bodies enclosed b ...
s, cnidaria
Cnidaria ( ) is a phylum under kingdom Animalia containing over 11,000 species of aquatic invertebrates found both in fresh water, freshwater and marine environments (predominantly the latter), including jellyfish, hydroid (zoology), hydroids, ...
ns, ctenophorans, echinoderm
An echinoderm () is any animal of the phylum Echinodermata (), which includes starfish, brittle stars, sea urchins, sand dollars and sea cucumbers, as well as the sessile sea lilies or "stone lilies". While bilaterally symmetrical as ...
s, cephalopod
A cephalopod is any member of the molluscan Taxonomic rank, class Cephalopoda (Greek language, Greek plural , ; "head-feet") such as a squid, octopus, cuttlefish, or nautilus. These exclusively marine animals are characterized by bilateral symm ...
s, crustaceans, and gastropods
Gastropods (), commonly known as slugs and snails, belong to a large taxonomic class of invertebrates within the phylum Mollusca called Gastropoda ().
This class comprises snails and slugs from saltwater, freshwater, and from the land. Ther ...
, A similar structure is also found in '' Xenoturbella''. The statocyst consists of a sac-like structure containing a mineralised mass (statolith) and numerous innervated sensory hairs ( setae). The statolith's inertia
Inertia is the natural tendency of objects in motion to stay in motion and objects at rest to stay at rest, unless a force causes the velocity to change. It is one of the fundamental principles in classical physics, and described by Isaac Newto ...
causes it to push against the setae when the animal accelerates. Deflection of setae by the statolith in response to gravity
In physics, gravity (), also known as gravitation or a gravitational interaction, is a fundamental interaction, a mutual attraction between all massive particles. On Earth, gravity takes a slightly different meaning: the observed force b ...
activates neuron
A neuron (American English), neurone (British English), or nerve cell, is an membrane potential#Cell excitability, excitable cell (biology), cell that fires electric signals called action potentials across a neural network (biology), neural net ...
s, providing feedback to the animal on change in orientation and allowing balance to be maintained.
In other words, the statolith shifts as the animal moves. Any movement large enough to throw the organism off balance causes the statolith to brush against tiny bristles which in turn send a message to the brain to correct its balance.
It may have been present in the common ancestor of cnidarians and bilaterians.
Hearing
Incephalopod
A cephalopod is any member of the molluscan Taxonomic rank, class Cephalopoda (Greek language, Greek plural , ; "head-feet") such as a squid, octopus, cuttlefish, or nautilus. These exclusively marine animals are characterized by bilateral symm ...
s like squid
A squid (: squid) is a mollusc with an elongated soft body, large eyes, eight cephalopod limb, arms, and two tentacles in the orders Myopsida, Oegopsida, and Bathyteuthida (though many other molluscs within the broader Neocoleoidea are also ...
s, statocysts provide a cochlea
The cochlea is the part of the inner ear involved in hearing. It is a spiral-shaped cavity in the bony labyrinth, in humans making 2.75 turns around its axis, the modiolus (cochlea), modiolus. A core component of the cochlea is the organ of Cort ...
-like mechanism to hear. As a result, the longfin inshore squid for instance can hear low-frequency sounds between 30 and 500 Hz when the water temperature is above .
See also
*Accelerometer
An accelerometer is a device that measures the proper acceleration of an object. Proper acceleration is the acceleration (the rate of change (mathematics), rate of change of velocity) of the object relative to an observer who is in free fall (tha ...
* Inertial guidance
* Müllerian vesicle, similar structure in loxodid ciliates
* Otolith, an equivalent structure in vertebrates.
* Statocyte, a similar structure in plants
* Sensory organs of gastropods
References
{{Cephalopod anatomy Vestibular system Cnidarian anatomy Arthropod anatomy Mollusc anatomy