|
Herpes Simplex Virus 2
Herpes simplex virus 2 (HHV-2 or HSV-2) is a species of virus in the genus '' Simplexvirus'', subfamily ''Alphaherpesvirinae'', family ''Herpesviridae'', and order ''Herpesvirales''. Evolution Herpes simplex virus 2 can be divided into two clades: one is globally distributed and the other is mostly limited to sub Saharan Africa.Burrel S, Boutolleau D, Ryu D, Agut H, Merkel K, Leendertz FH, Calvignac-Spencer S (2017) Ancient recombination events between human herpes simplex viruses. Mol Biol Evol Pathology Herpes simplex virus 2 infects humans, most often as genital herpes. In the United States more than one in six people have the virus. It is primarily a sexually transmitted infection. Herpes simplex virus 2 tends to reside in the sacral ganglia. Herpes simplex virus 2 is periodically shed in the human genital tract, most often asymptomatically. Most sexual transmissions occur during periods of asymptomatic shedding. Asymptomatic reactivation means that the virus causes at ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Simplexvirus
''Simplexvirus'' is a genus of viruses in the order ''Herpesvirales'', in the family ''Herpesviridae'', in the subfamily ''Alphaherpesvirinae''. Humans and mammals A mammal () is a vertebrate animal of the class Mammalia (). Mammals are characterised by the presence of milk-producing mammary glands for feeding their young, a broad neocortex region of the brain, fur or hair, and three middle e ... serve as natural hosts. Diseases associated with this genus include skin vesicles or mucosal ulcers, rarely encephalitis, and meningitis. Species The following 17 species are assigned to the genus in ICTV 2022: * '' Simplexvirus atelinealpha1'' * '' Simplexvirus bovinealpha2'' * '' Simplexvirus cercopithecinealpha2'' * '' Simplexvirus humanalpha1'' * '' Simplexvirus humanalpha2'' * '' Simplexvirus leporidalpha4'' * '' Simplexvirus macacinealpha1'' * '' Simplexvirus macacinealpha2'' * '' Simplexvirus macacinealpha3'' * '' Simplexvirus macropodidalpha1'' * '' Simplexvirus ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alphaherpesvirinae
''Alphaherpesvirinae'' is a subfamily of viruses in the family ''Herpesviridae'', primarily distinguished by reproducing more quickly than other subfamilies in the ''Herpesviridae''. In animal virology the most important herpesviruses belong to the Alphaherpesvirinae. Pseudorabies virus is the causative agent of Aujeszky's disease in pigs, and '' Bovine herpesvirus 1'' is the causative agent of bovine infectious rhinotracheitis and pustular vulvovaginitis. Mammals serve as natural hosts. There are currently 45 species in this subfamily, divided among 5 genera, with one species unassigned to a genus. Diseases associated with this subfamily include: HHV-1 and HHV-2: skin vesicles or mucosal ulcers, rarely encephalitis and meningitis, HHV-3: chickenpox (varicella) and shingles, GaHV-2: Marek's disease. Genera ''Alphaherpesvirinae'' consists of the following five genera: * '' Iltovirus'' * ''Mardivirus'' * '' Scutavirus'' * '' Simplexvirus'' * '' Varicellovirus'' The species ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Herpesviridae
''Orthoherpesviridae'', previously named and more widely known as ''Herpesviridae'', is a large family of DNA viruses that cause infections and certain diseases in animals, including humans. The members of this family are commonly known as herpesviruses. The family name is derived from the Greek word ἕρπειν ( 'to creep'), referring to spreading cutaneous lesions, usually involving blisters, seen in flares of herpes simplex 1, herpes simplex 2 and herpes zoster ( shingles). In 1971, the International Committee on the Taxonomy of Viruses (ICTV) established ''Herpesvirus'' as a genus with 23 viruses among four groups. Since then, the number of identified herpesviruses has grown to more than 100. Herpesviruses can cause both latent and lytic infections. Nine herpesvirus types are known to primarily infect humans, at least five of which are extremely widespread among most human populations, and which cause common diseases: herpes simplex 1 and 2 (HSV-1 and HSV-2, also know ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Herpesvirales
''Herpesvirales'' is an order of dsDNA viruses (Baltimore group I) with animal hosts, characterised by a common morphology consisting of an icosahedral capsid enclosed in a glycoprotein-containing lipid envelope. Common infections in humans caused by members of this order include cold sores, genital herpes, chickenpox, shingles, and glandular fever. ''Herpesvirales'' is the sole order in the class ''Herviviricetes'', which is the sole class in the phylum ''Peploviricota''. Virology Morphology All members of the order have a virion structure that consists of a DNA core surrounded by an icosahedral capsid composed of 12 pentavalent and 150 hexavalent capsomeres (T = 16). The capsid has a diameter of ~110 nanometers (nm) and is embedded in a proteinaceous matrix called the tegument, which in its turn is enclosed by a glycoprotein-containing lipid envelope with a diameter of about 200 nm. The DNA genome is linear and double stranded, with sizes in the range 125–290 kbp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Clade
In biology, a clade (), also known as a Monophyly, monophyletic group or natural group, is a group of organisms that is composed of a common ancestor and all of its descendants. Clades are the fundamental unit of cladistics, a modern approach to taxonomy adopted by most biological fields. The common ancestor may be an individual, a population, or a species (extinct or Extant taxon, extant). Clades are nested, one in another, as each branch in turn splits into smaller branches. These splits reflect evolutionary history as populations diverged and evolved independently. Clades are termed ''monophyletic'' (Greek: "one clan") groups. Over the last few decades, the cladistic approach has revolutionized biological classification and revealed surprising evolutionary relationships among organisms. Increasingly, taxonomists try to avoid naming Taxon, taxa that are not clades; that is, taxa that are not Monophyly, monophyletic. Some of the relationships between organisms that the molecul ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sub Saharan Africa
Sub-Saharan Africa is the area and regions of the continent of Africa that lie south of the Sahara. These include Central Africa, East Africa, Southern Africa, and West Africa. Geopolitically, in addition to the African countries and territories that are situated fully in that specified region, the term may also include polities that only have part of their territory located in that region, per the definition of the United Nations (UN). This is considered a non-standardised geographical region with the number of countries included varying from 46 to 48 depending on the organisation describing the region (e.g. UN, WHO, World Bank, etc.). The African Union (AU) uses a different regional breakdown, recognising all 55 member states on the continent—grouping them into five distinct and standard regions. The term serves as a grouping counterpart to North Africa, which is instead grouped with the definition of MENA (i.e. Middle East and North Africa) as it is part of the Arab wo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Genital Herpes
Genital herpes is a herpes infection of the genitals caused by the herpes simplex virus (HSV). Most people either have no or mild symptoms and thus do not know they are infected. When symptoms do occur, they typically include small blisters that break open to form painful ulcers. Flu-like symptoms, such as fever, aching, or swollen lymph nodes, may also occur. Onset is typically around 4 days after exposure with symptoms lasting up to 4 weeks. Once infected further outbreaks may occur but are generally milder. The disease is typically spread by direct genital contact with the skin surface or secretions of someone who is infected. This may occur during sex, including anal, oral, and manual sex. Sores are not required for transmission to occur. The risk of spread between a couple is about 7.5% over a year. HSV is classified into two types, HSV-1 and HSV-2. While historically HSV-2 was more common, genital HSV-1 has become more common in the developed world. Diagnosis may o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sacral Ganglia
The sacral ganglia are paravertebral ganglia of the sympathetic trunk.:39 As the sympathetic trunk heads inferiorly down the sacrum, it turns medially. There are generally four or five sacral ganglia. In addition to gray rami communicantes, the ganglia send off sacral splanchnic nerves to join the inferior hypogastric plexus. Near the coccyx, the right and left sympathetic trunks join to form the ganglion impar. The sacral ganglia innervate blood vessels and sweat glands of the lower limbs. Clinical significance Recurrences of genital herpes are caused by herpes simplex virus Herpes simplex virus 1 and 2 (HSV-1 and HSV-2) are two members of the Herpesviridae#Human herpesvirus types, human ''Herpesviridae'' family, a set of viruses that produce Viral disease, viral infections in the majority of humans. Both HSV-1 a ... (either HSV-1 or HSV-2) which lies dormant in the sacral ganglia between bouts of active infection. Either primary infection or reactivation may be silent ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Valaciclovir
Valaciclovir, also spelled valacyclovir, is an antiviral medication used to treat outbreaks of herpes simplex or herpes zoster (shingles). It is also used to prevent cytomegalovirus following a kidney transplant in high risk cases. It is taken by mouth. Common side effects include headache and vomiting. Severe side effects may include kidney problems. Use in pregnancy appears to be safe. It is a prodrug, which works after being converted to aciclovir in a person's body. Valaciclovir was patented in 1987 and came into medical use in 1995. It is on the World Health Organization's List of Essential Medicines. It is available as a generic medication. In 2022, it was the 113th most commonly prescribed medication in the United States, with more than 5million prescriptions. Medical uses Valaciclovir is used for the treatment of HSV and VZV infections, including:Rossi S, editor. Australian Medicines Handbook 2006. Adelaide: Australian Medicines Handbook; 2006. * Oral and genita ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Crossover Design
In medicine, a crossover study or crossover trial is a longitudinal study in which subjects receive a sequence of different treatments (or exposures). While crossover studies can be observational studies, many important crossover studies are controlled experiments, which are discussed in this article. Crossover designs are common for experiments in many scientific disciplines, for example Psychology#Research methods, psychology, pharmaceutical science, and medicine. Randomization, Randomized, controlled crossover experiments are especially important in health care. In a randomized clinical trial, the subjects are Random assignment, randomly assigned to different arms of the study which receive different treatments. When the trial has a repeated measures design, the same measures are collected multiple times for each subject. A crossover trial has a repeated measures design in which each patient is assigned to a sequence of two or more treatments, of which one may be a standard ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yeast Infection
Candidiasis is a fungal infection due to any species of the genus '' Candida'' (a yeast). When it affects the mouth, in some countries it is commonly called thrush. Signs and symptoms include white patches on the tongue or other areas of the mouth and throat. Other symptoms may include soreness and problems swallowing. When it affects the vagina, it may be referred to as a yeast infection or thrush. Signs and symptoms include genital itching, burning, and sometimes a white "cottage cheese-like" discharge from the vagina. Yeast infections of the penis are less common and typically present with an itchy rash. Very rarely, yeast infections may become invasive, spreading to other parts of the body. This may result in fevers, among other symptoms. Finally, candiasis of the esophagus is an important risk factor for contracting esophageal cancer in individuals with achalasia. More than 20 types of ''Candida'' may cause infection with '' Candida albicans'' being the most common. Inf ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
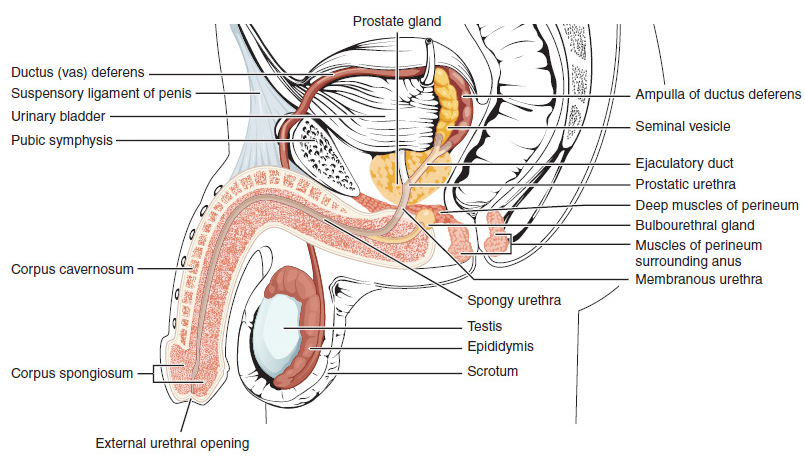
Human Penis
In Human body, human anatomy, the penis (; : penises or penes; from the Latin ''pēnis'', initially 'tail') is an external sex organ (intromittent organ) through which males urination, urinate and ejaculation, ejaculate, as Penis, on other animals. Together with the testes and surrounding structures, the penis functions as part of the male reproductive system. The main parts of the penis are the Root of penis, root, Body of penis, body, the epithelium of the penis, including the shaft skin, and the foreskin covering the glans penis, glans. The body of the penis is made up of three columns of tissue (biology), tissue: two Corpus cavernosum penis, corpora cavernosa on the dorsal side and corpus spongiosum penis, corpus spongiosum between them on the ventral side. The Urethra#Male, urethra passes through the prostate gland, where it is joined by the ejaculatory ducts, and then through the penis. The urethra goes across the corpus spongiosum and ends at the tip of the glans as the o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |