|
Herbert Boyer
Herbert Wayne "Herb" Boyer (born July 10, 1936) is an American biotechnologist, researcher and entrepreneur in biotechnology. Along with Stanley N. Cohen and Paul Berg, he discovered recombinant DNA, a method to coax bacteria into producing foreign proteins, which aided in jump-starting the field of genetic engineering. By 1969, he had performed studies on a couple of restriction enzymes of ''E. coli'' with especially useful properties. He is recipient of the 1990 National Medal of Science, co-recipient of the 1996 Lemelson–MIT Prize, and a co-founder of Genentech. He was professor at the University of California, San Francisco (UCSF) and later served as vice president of Genentech from 1976 until his retirement in 1991. Early life and education Herbert Boyer was born in 1936 in Derry, Pennsylvania. He received his bachelor's degree in biology and chemistry from Saint Vincent College in Latrobe, Pennsylvania, in 1958. He married his wife Grace the following year. He rece ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Derry, Pennsylvania
:''There are also four Derry Township, Pennsylvania (other), Derry Townships in Pennsylvania.'' Derry is a borough (Pennsylvania), borough in Westmoreland County, Pennsylvania, Westmoreland County in Pennsylvania, east of Pittsburgh. The Borough of Derry, consisting of the town area, should not be confused with Derry Township, Westmoreland County, Pennsylvania, Derry Township, which is a separate municipality surrounding the borough. The population was 2,637 at the 2020 United States census, 2020 census. History 19th century Originally known as Derry Station, the borough was created in 1852 to serve the Pennsylvania Railroad. It was named after the village on Pennsylvania Route 982, PA Route 982 originally known as Derry and now known as New Derry (even though it is older than the community being discussed here). The original "Derry" in Westmoreland County, Pennsylvania, Westmoreland County, Pennsylvania, was named after the City of Derry in Ulster, the northern Provinc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Recombinant DNA
Recombinant DNA (rDNA) molecules are DNA molecules formed by laboratory methods of genetic recombination (such as molecular cloning) that bring together genetic material from multiple sources, creating sequences that would not otherwise be found in the genome. Recombinant DNA is the general name for a piece of DNA that has been created by combining two or more fragments from different sources. Recombinant DNA is possible because DNA molecules from all organisms share the same chemical structure, differing only in the nucleotide sequence. Recombinant DNA molecules are sometimes called chimeric DNA because they can be made of material from two different species like the mythical chimera. rDNA technology uses palindromic sequences and leads to the production of sticky and blunt ends. The DNA sequences used in the construction of recombinant DNA molecules can originate from any species. For example, plant DNA can be joined to bacterial DNA, or human DNA can be joined with fun ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nucleotide
Nucleotides are Organic compound, organic molecules composed of a nitrogenous base, a pentose sugar and a phosphate. They serve as monomeric units of the nucleic acid polymers – deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) and ribonucleic acid (RNA), both of which are essential biomolecules within all Life, life-forms on Earth. Nucleotides are obtained in the diet and are also synthesized from common Nutrient, nutrients by the liver. Nucleotides are composed of three subunit molecules: a nucleobase, a pentose, five-carbon sugar (ribose or deoxyribose), and a phosphate group consisting of one to three phosphates. The four nucleobases in DNA are guanine, adenine, cytosine, and thymine; in RNA, uracil is used in place of thymine. Nucleotides also play a central role in metabolism at a fundamental, cellular level. They provide chemical energy—in the form of the nucleoside triphosphates, adenosine triphosphate (ATP), guanosine triphosphate (GTP), cytidine triphosphate (CTP), and uridine triph ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gene
In biology, the word gene has two meanings. The Mendelian gene is a basic unit of heredity. The molecular gene is a sequence of nucleotides in DNA that is transcribed to produce a functional RNA. There are two types of molecular genes: protein-coding genes and non-coding genes. During gene expression (the synthesis of Gene product, RNA or protein from a gene), DNA is first transcription (biology), copied into RNA. RNA can be non-coding RNA, directly functional or be the intermediate protein biosynthesis, template for the synthesis of a protein. The transmission of genes to an organism's offspring, is the basis of the inheritance of phenotypic traits from one generation to the next. These genes make up different DNA sequences, together called a genotype, that is specific to every given individual, within the gene pool of the population (biology), population of a given species. The genotype, along with environmental and developmental factors, ultimately determines the phenotype ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Biogen
Biogen Inc. is an American multinational biotechnology company based in Cambridge, Massachusetts, United States specializing in the discovery, development, and delivery of the treatment of neurological diseases to patients worldwide. Biogen operates in Argentina, Brazil, Canada, China, France, Germany, Hungary, India, Italy, Japan, Mexico, Netherlands, Poland, Sweden, and Switzerland. History Biogen was founded in 1978 in Geneva as ''Biotechnology Geneva'' by several prominent biologists, including Kenneth Murray from the University of Edinburgh, Phillip Allen Sharp from the Massachusetts Institute of Technology, Walter Gilbert from Harvard University (Gilbert served as CEO during the start-up phase of Biogen), Heinz Schaller from the University of Heidelberg, and Charles Weissmann from the University of Zurich (Weissmann contributed the first product interferon alpha).Werner Grundlehner''Zürcher Antikörper gegen Alzheimer hat Milliardenpotenzial – und Gegenwind.''Neu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Walter Gilbert
Walter Gilbert (born March 21, 1932) is an American biochemist, physicist, molecular biology pioneer, and Nobel laureate. Education and early life Walter Gilbert was born in Boston, Massachusetts, on March 21, 1932, into a Jewish family, the son of Emma (Cohen), a child psychologist, and Richard V. Gilbert, an economist. When Gilbert was seven years old, the family moved to the Washington D.C. area so his father could work under Harry Hopkins on the New Deal brain trust. While living in Washington the family became friends with the family of I.F. Stone and Wally met Stone's oldest daughter, Celia, when they were both 8. They later married at age 21. He was educated at the Sidwell Friends School, and attended Harvard University for undergraduate and graduate studies, earning a baccalaureate in chemistry and physics in 1953 and a master's degree in physics in 1954. He studied for his doctorate at the University of Cambridge, where he earned a PhD in physics supervised by the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Robert A
The name Robert is an ancient Germanic given name, from Proto-Germanic "fame" and "bright" (''Hrōþiberhtaz''). Compare Old Dutch ''Robrecht'' and Old High German ''Hrodebert'' (a compound of ''Hrōþ, Hruod'' () "fame, glory, honour, praise, renown, godlike" and ''berht'' "bright, light, shining"). It is the second most frequently used given name of ancient Germanic origin.Reaney & Wilson, 1997. ''Dictionary of English Surnames''. Oxford University Press. It is also in use Robert (surname), as a surname. Another commonly used form of the name is Rupert (name), Rupert. After becoming widely used in Continental Europe, the name entered England in its Old French form ''Robert'', where an Old English cognate form (''Hrēodbēorht'', ''Hrodberht'', ''Hrēodbēorð'', ''Hrœdbœrð'', ''Hrœdberð'', ''Hrōðberχtŕ'') had existed before the Norman Conquest. The feminine version is Roberta (given name), Roberta. The Italian, Portuguese, and Spanish form is Roberto (given name), ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Venture Capitalist
Venture capital (VC) is a form of private equity financing provided by firms or funds to startup, early-stage, and emerging companies, that have been deemed to have high growth potential or that have demonstrated high growth in terms of number of employees, annual revenue, scale of operations, etc. Venture capital firms or funds invest in these early-stage companies in exchange for equity, or an ownership stake. Venture capitalists take on the risk of financing start-ups in the hopes that some of the companies they support will become successful. Because startups face high uncertainty, VC investments have high rates of failure. Start-ups are usually based on an innovative technology or business model and often come from high technology industries such as information technology (IT) or biotechnology. Pre-seed and seed rounds are the initial stages of funding for a startup company, typically occurring early in its development. During a seed round, entrepreneurs seek investment fr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
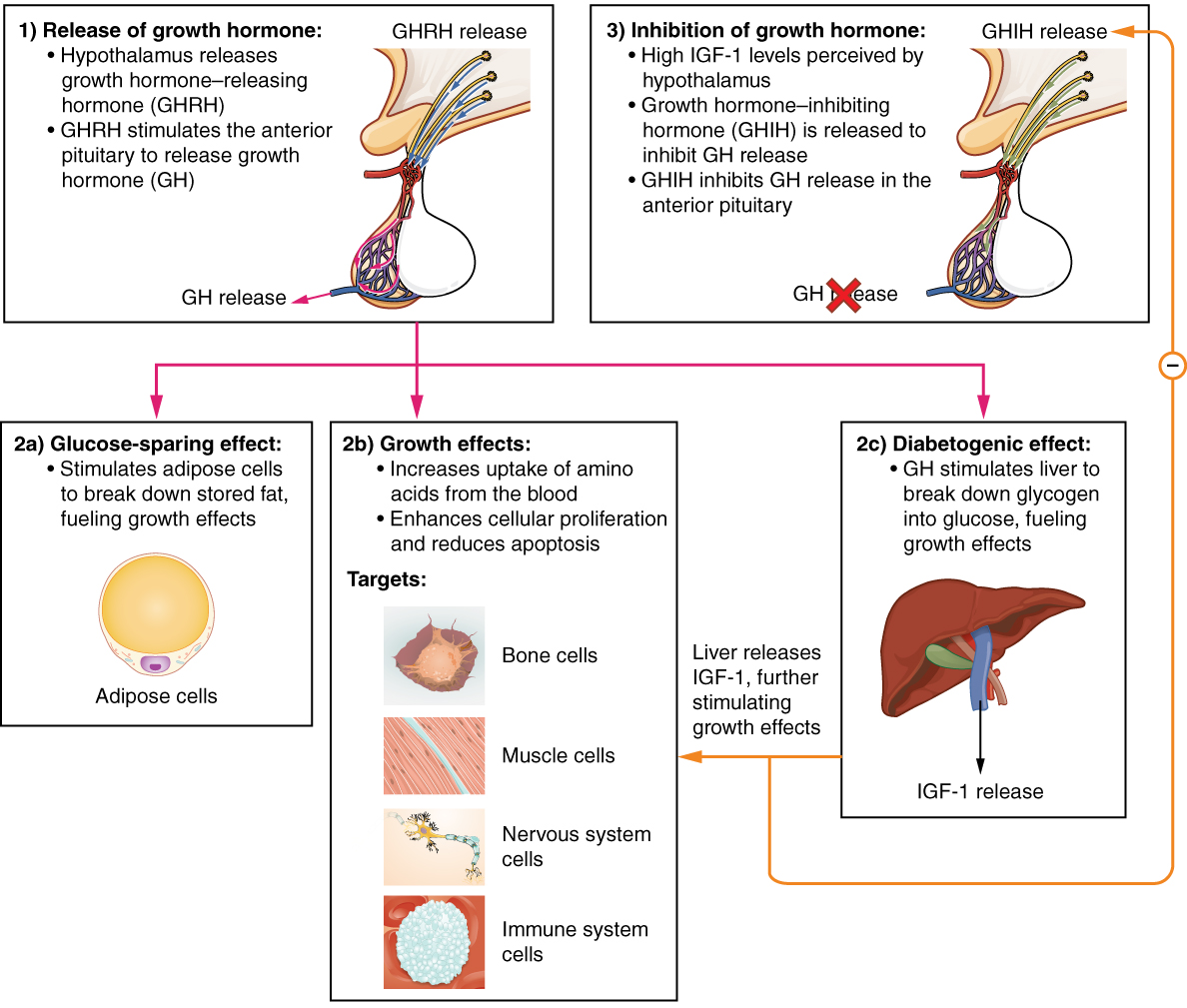
Growth Hormone
Growth hormone (GH) or somatotropin, also known as human growth hormone (hGH or HGH) in its human form, is a peptide hormone that stimulates growth, cell reproduction, and cell regeneration in humans and other animals. It is thus important in human development. GH also stimulates production of insulin-like growth factor 1 (IGF-1) and increases the concentration of glucose and free fatty acids. It is a type of mitogen which is specific only to the receptors on certain types of cells. GH is a 191-amino acid, single-chain polypeptide that is synthesized, stored and secreted by somatotropic cells within the lateral wings of the anterior pituitary gland. A recombinant form of HGH called somatropin ( INN) is used as a prescription drug to treat children's growth disorders and adult growth hormone deficiency. In the United States, it is only available legally from pharmacies by prescription from a licensed health care provider. In recent years in the United States, some health ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Genetically Modified Bacteria
Genetically modified bacteria were the first organisms to be modified in the laboratory, due to their simple genetics. These organisms are now used for several purposes, and are particularly important in producing large amounts of pure human proteins for use in medicine. History The first example of this occurred in 1978 when Herbert Boyer, working at a University of California laboratory, took a version of the human insulin gene and inserted into the bacterium ''Escherichia coli'' to produce synthetic "human" insulin. Four years later, it was approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration. Research Bacteria were the first organisms to be genetically modified in the laboratory, due to the relative ease of modifying their chromosomes. This ease made them important tools for the creation of other GMOs. Genes and other genetic information from a wide range of organisms can be added to a plasmid and inserted into bacteria for storage and modification. Bacteria are cheap, e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Insulin
Insulin (, from Latin ''insula'', 'island') is a peptide hormone produced by beta cells of the pancreatic islets encoded in humans by the insulin (''INS)'' gene. It is the main Anabolism, anabolic hormone of the body. It regulates the metabolism of carbohydrates, fats, and protein by promoting the absorption of glucose from the blood into cells of the liver, fat cell, fat, and skeletal muscles. In these tissues the absorbed glucose is converted into either glycogen, via glycogenesis, or Fatty acid metabolism#Glycolytic end products are used in the conversion of carbohydrates into fatty acids, fats (triglycerides), via lipogenesis; in the liver, glucose is converted into both. Glucose production and secretion by the liver are strongly inhibited by high concentrations of insulin in the blood. Circulating insulin also affects the synthesis of proteins in a wide variety of tissues. It is thus an anabolic hormone, promoting the conversion of small molecules in the blood into large ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
City Of Hope National Medical Center
City of Hope is a private, non-profit clinical research center, hospital and graduate school located in Duarte, California, United States. The center's main campus resides on of land adjacent to the boundaries of Duarte and Irwindale, California, Irwindale, with a network of clinical practice locations throughout Southern California, satellite offices in Monrovia, California, Monrovia and Irwindale, and regional fundraising offices throughout the United States. City of Hope is best known as a cancer treatment center. It has been designated a NCI-designated Cancer Center, Comprehensive Cancer Center by the National Cancer Institute. City of Hope has also been ranked one of the nation's Best Cancer Hospitals by ''U.S. News & World Report'' for over ten years and is a founding member of the National Comprehensive Cancer Network. City of Hope played a role in the development of insulin, synthetic human insulin in 1978. The center has performed 13,000 hematopoietic stem cell transpla ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |