|
Heinrich Obersteiner
Heinrich Obersteiner (13 November 1847 – 19 November 1922) was an Austrian neurologist born in Vienna. In 1870 earned his doctorate from the University of Vienna, where he worked in the laboratory of Ernst Wilhelm von Brücke (1819–1892). In 1873 he earned his habilitation for pathology and anatomy of the nervous system at the University of Vienna, becoming an associate professor in 1880, and receiving the title of "full professor" in 1898. He was also director of a private mental institution at Oberdöbling, outside of Vienna. In 1882 he established an internationally known neurological institute in Vienna. The eponymous Obersteiner–Redlich line is named after him, along with Emil Redlich (1866–1930). This zone is where the central nervous system and peripheral nervous system meet, as well as the place where Schwann cells meet oligodendroglia cells. Written works * '' Anleitung beim Studium des baues der nervösen Centralorgane im gesunden und kranken Zustande''. Le ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
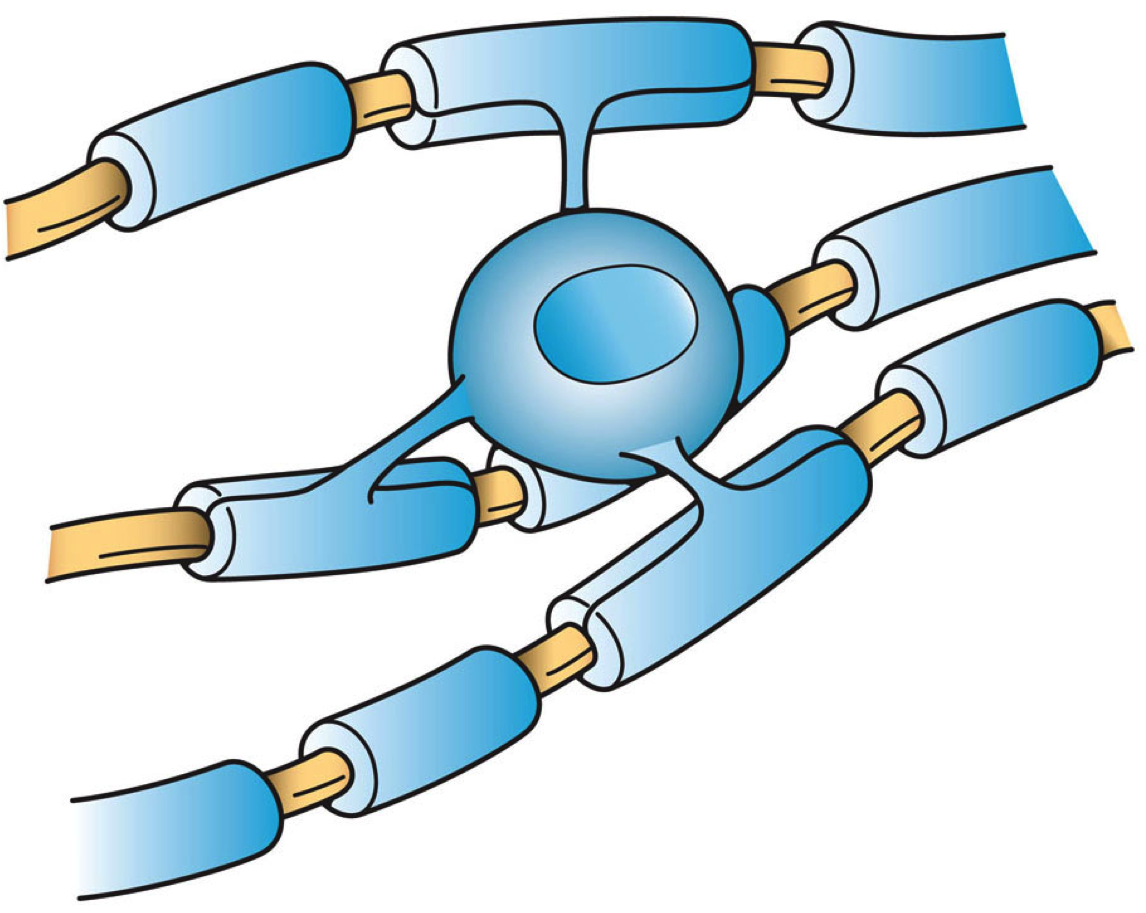
Oligodendrocyte
Oligodendrocytes (), also known as oligodendroglia, are a type of neuroglia whose main function is to provide the myelin sheath to neuronal axons in the central nervous system (CNS). Myelination gives metabolic support to, and insulates the axons of most vertebrates. A single oligodendrocyte can extend its Cellular extensions, processes to cover up to 40 axons, that can include multiple adjacent axons. The myelin sheath is segmented along the axon's length at gaps known as the nodes of Ranvier. In the peripheral nervous system the myelination of axons is carried out by Schwann cells. Oligodendrocytes are found exclusively in the CNS, which comprises the brain and spinal cord. They are the most widespread cell lineage, including oligodendrocyte progenitor cells, pre-myelinating cells, and mature myelinating oligodendrocytes in the CNS white matter. Non-myelinating oligodendrocytes are found in the grey matter surrounding and lying next to neuronal cell bodies. They are known as neu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Austrian Neurologists
Austrian may refer to: * Austrians, someone from Austria or of Austrian descent ** Someone who is considered an Austrian citizen * Austrian German dialect * Something associated with the country Austria, for example: ** Austria-Hungary ** Austrian Airlines (AUA) ** Austrian cuisine ** Austrian Empire ** Austrian monarchy ** Austrian German (language/dialects) ** Austrian literature ** Austrian nationality law ** Austrian Service Abroad ** Music of Austria **Austrian School of Economics * Economists of the Austrian school of economic thought * The Austrian Attack variation of the Pirc Defence chess opening. See also * * * Austria (other) * Australian (other) * L'Autrichienne (other) is the feminine form of the French word , meaning "The Austrian". It may refer to: *A derogatory nickname for Queen Marie Antoinette of France ** ''L'Autrichienne'' (film), a 1990 French film on Marie Antoinette with Ute Lemper * ''L'Autrichienn ... {{disambig Lang ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Physicians From Vienna
A physician, medical practitioner (British English), medical doctor, or simply doctor is a health professional who practices medicine, which is concerned with promoting, maintaining or restoring health through the study, diagnosis, prognosis and treatment of disease, injury, and other physical and mental impairments. Physicians may focus their practice on certain disease categories, types of patients, and methods of treatment—known as specialities—or they may assume responsibility for the provision of continuing and comprehensive medical care to individuals, families, and communities—known as general practice. Medical practice properly requires both a detailed knowledge of the academic disciplines, such as anatomy and physiology, underlying diseases, and their treatment, which is the science of medicine, and a decent competence in its applied practice, which is the art or craft of the profession. Both the role of the physician and the meaning of the word itself vary ar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1922 Deaths
Events January * January 7 – Dáil Éireann (Irish Republic), Dáil Éireann, the parliament of the Irish Republic, ratifies the Anglo-Irish Treaty by 64–57 votes. * January 10 – Arthur Griffith is elected President of Dáil Éireann, the day after Éamon de Valera resigns. * January 11 – The first successful insulin treatment of diabetes is made, by Frederick Banting in Toronto. * January 15 – Michael Collins (Irish leader), Michael Collins becomes Chairman of the Provisional Government of the Irish Free State. * January 26 – Italian forces occupy Misrata, Italian Libya, Libya; the Pacification of Libya, reconquest of Libya begins. February * February 6 ** Pope Pius XI (Achille Ratti) succeeds Pope Benedict XV, to become the 259th pope. ** The Washington Naval Treaty, Five Power Naval Disarmament Treaty is signed between the United States, United Kingdom, Empire of Japan, Japan, French Third Republic, France and Kingdom of Italy, Italy. Japan returns some ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1847 Births
Events January–March * January 4 – Samuel Colt sells his first revolver pistol to the U.S. government. * January 13 – The Treaty of Cahuenga ends fighting in the Mexican–American War in California. * January 16 – John C. Frémont is appointed Governor of the new California Territory. * January 17 – St. Anthony Hall fraternity is founded at Columbia University, New York City. * January 30 – Yerba Buena, California, is renamed San Francisco. * February 5 – A rescue effort, called the First Relief, leaves Johnson's Ranch to save the ill-fated Donner Party of California-bound migrants who became snowbound in the Sierra Nevada earlier this winter. Some have resorted to survival by cannibalism. * February 22 – Mexican–American War: Battle of Buena Vista – 5,000 American troops under General Zachary Taylor use their superiority in artillery to drive off 15,000 Mexican troops under Antonio López de Santa Anna, defeating the Mexicans the next day. * Febr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Who Named It
''Whonamedit?'' is an online English-language dictionary of medical eponyms and the people associated with their identification. Though it is a dictionary, many eponyms and persons are presented in extensive articles with comprehensive bibliographies. The dictionary is hosted in Norway Norway, officially the Kingdom of Norway, is a Nordic countries, Nordic country located on the Scandinavian Peninsula in Northern Europe. The remote Arctic island of Jan Mayen and the archipelago of Svalbard also form part of the Kingdom of ... and was developed by medical historian Ole Daniel Enersen. References External links * Medical websites Medical dictionaries Eponyms in medicine {{online-dict-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Berlin
Berlin ( ; ) is the Capital of Germany, capital and largest city of Germany, by both area and List of cities in Germany by population, population. With 3.7 million inhabitants, it has the List of cities in the European Union by population within city limits, highest population within its city limits of any city in the European Union. The city is also one of the states of Germany, being the List of German states by area, third smallest state in the country by area. Berlin is surrounded by the state of Brandenburg, and Brandenburg's capital Potsdam is nearby. The urban area of Berlin has a population of over 4.6 million and is therefore the most populous urban area in Germany. The Berlin/Brandenburg Metropolitan Region, Berlin-Brandenburg capital region has around 6.2 million inhabitants and is Germany's second-largest metropolitan region after the Rhine-Ruhr region, as well as the List of EU metropolitan areas by GDP, fifth-biggest metropolitan region by GDP in the European Union. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Emil Abderhalden
Emil Abderhalden (9 March 1877 – 5 August 1950) was a Swiss biochemist and physiologist. His main findings, though disputed already in the 1910s, were not finally rejected until the late 1990s. Whether his misleading findings were based on fraud or simply the result of a lack of scientific rigour remains unclear. Abderhalden's drying pistol, used in chemistry, was first described by one of his students in a textbook Abderhalden edited. Biography Emil Abderhalden was born in Oberuzwil in the Canton of St. Gallen in Switzerland. He moved to Basel to study at the University of Basel. During his time in Basel, he joined the rowing club and was a founding member of FC Basel. Eleven men attended the meeting of founding Fussball Club Basel on 15 November 1893. Abderhalden played his first game for the club in the home game in the Stadion Schützenmatte on 22 September 1894 as Basel won 2–0 against FC Gymnasia. Abderhalden left the club in January 1895. Abderhalden studied medi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gustav Albert Schwalbe
Gustav Albert Schwalbe, M.D. (1 August 1844 – 23 April 1916) was a German anatomist and anthropologist from Quedlinburg. He was educated at the universities of Humboldt University of Berlin, Berlin, University of Zurich, Zurich, and University of Bonn, Bonn (Doctor of Medicine, M.D. 1866), he became in 1870 privat-docent at the University of Halle, in 1871 privatdozent and prosector at the University of Freiburg in Baden, in 1872 assistant professor at the University of Leipzig, and then professor of anatomy successively at the universities of University of Jena, Jena (1873), University of Königsberg, Königsberg (1881), and University of Strasbourg, Strassburg (1883) — at that time a German university, Alsace having been annexed to Germany. There he died. Known for his anthropological research of primitive man, Schwalbe considered the Neanderthal to be a direct ancestor of modern humans. Much to the dismay of the Dutch paleontologist Eugène Dubois (1858–1940) who ha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wilhelm Ebstein
Wilhelm Ebstein (27 November 1836, Jauer, Prussian Silesia – 22 October 1912) was a German physician. He proposed a low-carbohydrate high-fat diet to treat obesity. Ebstein's anomaly is named for him. Biography Ebstein was born to a Jewish family in Jauer, Prussian Silesia (modern Jawor, Poland).Hurst, J. Willis. (1995)''Portrait of a Contributor: Wilhelm Ebstein (1836-1912)'' ''Clinical Cardiology'' 18: 115-116. He studied medicine at the University of Breslau under Friedrich Theodor von Frerichs and at the University of Berlin under Rudolf Virchow and Moritz Heinrich Romberg,Wilhelm Ebstein @ graduating from the latter institution in 1859. During the same year he was named physician at the < ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hypnotism
Hypnosis is a human condition involving focused attention (the selective attention/selective inattention hypothesis, SASI), reduced peripheral awareness, and an enhanced capacity to respond to suggestion.In 2015, the American Psychological Association Division 30 defined hypnosis as a "state of consciousness involving focused attention and reduced peripheral awareness characterized by an enhanced capacity for response to suggestion". For critical commentary on this definition, see: There are competing theories explaining hypnosis and related phenomena. ''Altered state'' theories see hypnosis as an altered state of mind or trance, marked by a level of awareness different from the ordinary state of consciousness. In contrast, ''non-state'' theories see hypnosis as, variously, a type of placebo effect,Kirsch, I., "Clinical Hypnosis as a Nondeceptive Placebo", pp. 211–25 in Kirsch, I., Capafons, A., Cardeña-Buelna, E., Amigó, S. (eds.), ''Clinical Hypnosis and Self-Regulat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |