|
Heilbronn Stadtbahn
The Heilbronn Stadtbahn is a three line tram-train system in city of Heilbronn in the German state of Baden-Württemberg. It is based on the Karlsruhe model and operated jointly by the Albtal-Verkehrs-Gesellschaft (AVG), the Stadtwerke Heilbronn (SWH) and Deutsche Bahn (DB). It operates on normal railways under the Eisenbahn-Bau- und Betriebsordnung (Ordinance on the Construction and Operation of Railways, ''EBO'') and within Heilbronn under the Verordnung über den Bau und Betrieb der Straßenbahnen (Ordinance on the Construction and Operation of Street Railways, ''BOStrab''). The oldest line of the system, the S4, was an extension of an existing line that had been operated by the Karlsruhe Stadtbahn since 1992. It was extended in 1999 from Eppingen to Heilbronn and since 2001 it has continued over the new Heilbronn inner-city line (''Heilbronner Innenstadtstrecke''). In 2005, the line was extended to Öhringen, which is integrated into the Heilbronner Hohenloher Haller ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Heilbronn
Heilbronn () is a List of cities and towns in Germany, city in northern Baden-Württemberg, Germany, surrounded by Heilbronn (district), Heilbronn District. From the late Middle Ages on, it developed into an important trading centre. At the beginning of the 19th century, Heilbronn became one of the centres of early industrialisation in Württemberg. Heilbronn's old town was completely destroyed during the air raid of 4 December 1944 and rebuilt in the 1950s. Today Heilbronn is the economic centre of the Heilbronn-Franconia, Heilbronn-Franken region. Heilbronn is known for its wine industry and is nicknamed ''Käthchenstadt'', after Heinrich von Kleist's ''Das Käthchen von Heilbronn''. Geography Heilbronn is located in the northern corner of the Neckar Sedimentary basin, basin at the bottom of the Wartberg (Heilbronn), Wartberg (308 m). It occupies both banks of the Neckar, and the highest spot inside city limits is the Schweinsberg (mountain), Schweinsberg with a height of 372 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Verordnung über Den Bau Und Betrieb Der Straßenbahnen
The ("Ordinance on the Construction and Operation of Street Railways" / light railway regulations), abbreviated as BOStrab, is a German law regulation governing the field of tramway, metro and light rail operations. The orders are enacted by the Federal Ministry of Transport based on enabling act through the General Railway Law ("", first issued on 29. March 1951). The supervisory authority is delegated to the Federal Railway Authority of Germany. The BOStrab regulations are not as strict as the EBO main railway regulations; for example the BOStrab does not specify a strict loading gauge to follow. A third law ESBO () covers narrow-gauge railway regulations. The distinctions for these light rail systems are slightly different from in the UK Tramways Act 1870 ( 33 & 34 Vict. c. 78) / Light Railways Act 1896. Some Stadtbahn systems are subject to both BOStrab and EBO regulations as their vehicles use both types of networks. This is common with tram-train systems - apart from ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Karlsruhe Model
The Karlsruhe model is a tram-train system which consists of tram/light rail trains and commuter/regional rail trains running on the same set of tracks, generally between or outside of urban areas. It was initially developed and implemented in the city of Karlsruhe, Germany, by the local transit authority, ''Karlsruher Verkehrsverbund'' (KVV). Overview Commencing service in 1992, the system in Karlsruhe has provided a connection between the regular railway network and the city's local tram network. The whole system is now called the Karlsruhe Stadtbahn. Passengers may travel from distant towns such as Baden-Baden directly into the city centre of Karlsruhe, bridging the inconvenient distance between the main station and the city centre. For most trips, the number of train transfers has been reduced significantly. This model has led to the creation of similar tram-train systems in other locations. Other examples A similar model has been connecting the city of Vienna with the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tram-train
A tram-train or dual-system tram is a type of light rail vehicle that both meets the standards of a light rail system, and also national mainline standards. Tramcars are adapted to be capable of running on streets like an urban tramway but also be permitted operation alongside mainline trains. This allows services that can utilise both existing urban light rail systems and mainline railway networks and stations. It combines the urban accessibility of a tram or light rail with a mainline train's greater speed in the suburbs. The modern tram-train concept was pioneered by the German city of Karlsruhe in the late 1980s, resulting in the creation of the Karlsruhe Stadtbahn. This concept is often referred to as the Karlsruhe model, and it has since been adopted in other cities such as Mulhouse in France and in Kassel, Nordhausen and Saarbrücken in Germany. An inversion of the concept is a train-tram – a mainline train adapted to run on-street in an urban tramway, also know ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bad Friedrichshall
Bad Friedrichshall () is a town in the district of Heilbronn in Baden-Württemberg in southern Germany. It is situated at the confluences of the Jagst and of the Kocher into the Neckar, some north of Heilbronn. Bad Friedrichshall arose by the connection of Kochendorf and Jagstfeld in 1933, and is famous for its salt mine. Geography Bad Friedrichshall is a town in the district of Heilbronn in Baden-Württemberg in southern Germany. It is situated at the confluences of the Jagst and of the Kocher into the Neckar. Neighbouring municipalities Neighbouring towns and villages of Bad Friedrichshall are (clockwise from the south): Neckarsulm, Untereisesheim, Bad Wimpfen, Offenau, Gundelsheim, Neudenau, Neuenstadt am Kocher and Oedheim, which all belong to the district of Heilbronn. It is north of the city of Heilbronn Bad Friedrichshall has combined its administration with Oedheim and Offenau. Town structure Bad Friedrichshall is subdivided into the villages of Kochendo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neckarsulm
Neckarsulm () is a city in northern Baden-Württemberg, Germany, near Heilbronn, and part of the district of Heilbronn. , Neckarsulm had 26,800 inhabitants. The name Neckarsulm derives from the city's location where the Neckar and Sulm rivers meet. Neckarsulm is known for its renewable energy projects and wine. The Weingärtnergenossenschaft Neckarsulm-Gundelsheim (winegrower's cooperative of Neckarsulm and Gundelsheim) is the oldest winegrower's collective in Germany. The wine Trollinger and Lemberger are the principal varieties of grape grown in this region. The Schwarz Gruppe (Schwarz Group) who leads both companies Lidl and Kaufland has its headquarters in Neckarsulm. Neckarsulm was first mentioned in a document in 771 and was granted city status around 1300. The city celebrated its 1250th birthday in 2021. Geography Neckarsulm is located on the eastern side of the Neckar River Valley. The town is approximately from the Löwenstein Mountains and is part of the Swabian- ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kaufland
Kaufland () is a German hypermarket chain, part of the Schwarz Gruppe which also owns Lidl. The hypermarket directly translates to English as "buy-land." It opened its first store in 1984 in Neckarsulm and quickly expanded to become a major chain in what was formerly West Germany. It operates over 1,500 stores in Germany, Croatia, the Czech Republic, Slovakia, Poland, Romania, Bulgaria and Moldova. History The history of Kaufland began when Joseph Schwarz entered the ''Südfrüchte Großhandlung Lidl & Co.'' company as a shareholder in 1930, which was then renamed ''Lidl & Schwarz KG''. The company expanded its range from fruit to a food and goods wholesaler for the Heilbronn-Franken region. During World War II, along with the city of Heilbronn, the company was destroyed and needed rebuilding. Within ten years, the company was rebuilt and, in 1954, moved into its own property in Heilbronn in addition to joining the ''A & O'' retail chain (today: Markant). With ''Handels- un ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gauntlet Track
Gauntlet track or interlaced track, also gantlet track () is an arrangement in which Rail tracks, railway tracks run parallel on a single track bed and are interlaced (i.e., overlapped) in such a way that only one pair of rails can be used at any time. Since this requires only slightly more Structure gauge, width than a Single track (rail), single track, all rails can be carried on the same Railroad tie, crossties/sleepers. Trains run on the pair of rails appropriate to their direction, track gauge or loading gauge. The term ''Gauntlet (glove), gauntlet'' refers to the expression ''running the gauntlet'', which means running between two confining rows of adversaries. Configurations Frog gauntlet (double-gauntlet-double) Gauntlet tracks can be used to provide horizontal clearance to a fixed obstruction adjacent to a track such as a Cutting (transportation), cutting, bridge, or tunnel. Frog gauntlets are also commonly used when a rail line's capacity is increased by the provisi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bottwar Valley Railway
The Bottwar is a river in Baden-Württemberg, Germany. It passes through Großbottwar and flows into the Murr in Steinheim an der Murr. See also *List of rivers of Baden-Württemberg A list of rivers of Baden-Württemberg, Germany: A *Aal (Kocher), Aal *Aalbach (Main), Aalbach *Aalenbach *Ablach (Danube), Ablach *Ach (Blau), Ach *Acher *Adelbach *Aich (river), Aich *Aid (Würm), Aid *Aischbach (Kinzig), Aischbach, tributary ... References Rivers of Baden-Württemberg Rivers of Germany {{BadenWürttemberg-river-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Northern Branch
The Northern Branch is a railroad line that runs from Jersey City to Northvale in northeastern New Jersey, and formerly extended further into New York State. The line was constructed in 1859 by the Northern Railroad of New Jersey to connect the New York and Erie Railroad's Piermont Branch terminus in Piermont, New York, directly to Erie's primary terminal in Jersey City, initially Exchange Place, later Pavonia Terminal. In 1870 the line was extended to Nyack, New York, and continued to provide passenger service until 1966. After the Erie's unsuccessful merger with the Lackawanna Railroad to form the Erie-Lackawanna, ownership of the line passed into the hands of Conrail upon its formation in 1976 from a number of bankrupt railroads (including the E-L). The line survives as two separate but connected sections. The Northern Running Track is an approximately two-mile-long freight railroad line in Hudson County, New Jersey. It runs from the Passaic and Harsimus Line at ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
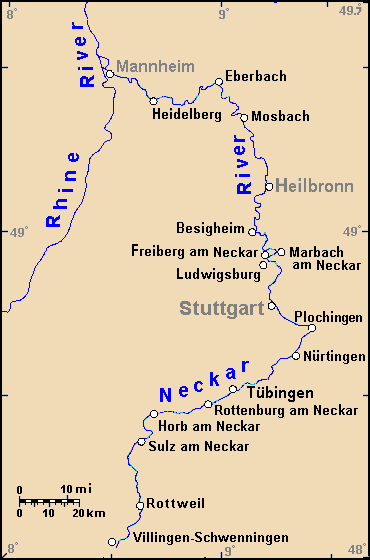
Neckar
The Neckar () is a river in Germany, mainly flowing through the southwestern States of Germany, state of Baden-Württemberg, with a short section through Hesse. The Neckar is a major right tributary of the Rhine. Rising in the Schwarzwald-Baar-Kreis near Villingen-Schwenningen, Schwenningen in the ''Schwenninger Moos'' conservation area at a height of above sea level, it passes through Rottweil, Rottenburg am Neckar, Kilchberg (Tübingen), Kilchberg, Tübingen, Wernau, Nürtingen, Plochingen, Esslingen am Neckar, Esslingen, Stuttgart, Ludwigsburg, Marbach am Neckar, Marbach, Heilbronn and Heidelberg, before discharging on average of water into the Rhine at Mannheim, at above sea level, making the Neckar its 4th largest tributary, and the 10th largest river in Germany. Since 1968, the Neckar has been navigable for cargo ships via 27 locks for about upstream from Mannheim to the river port of Plochingen, at the confluence with the Fils (river), Fils. From Plochingen to Stuttg ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |