|
Hazop
A hazard and operability study (HAZOP) is a structured and systematic examination of a complex system, usually a process facility, in order to identify hazards to personnel, equipment or the environment, as well as operability problems that could affect operations efficiency. It is the foremost hazard identification tool in the domain of process safety. The intention of performing a HAZOP is to review the design to pick up design and engineering issues that may otherwise not have been found. The technique is based on breaking the overall complex design of the process into a number of simpler sections called ''nodes'' which are then individually reviewed. It is carried out by a suitably experienced multi-disciplinary team during a series of meetings. The HAZOP technique is qualitative and aims to stimulate the imagination of participants to identify potential hazards and operability problems. Structure and direction are given to the review process by applying standardized guideword ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trevor Kletz
Trevor Asher Kletz (23 October 1922 – 31 October 2013) was a British author on the topic of chemical engineering safety. He was a central figure in establishing the discipline of process safety. He is credited with introducing the concept of inherent safety and was a major promoter of Hazop. He is listed in The Palgrave Dictionary of Anglo-Jewish History. Early life and education Kletz was born 23 October 1922 in Darlington of Jewish parents, from a Russian immigrant background. He attended The King's School, Chester, then the University of Liverpool, where he graduated in chemistry in 1944 and joined ICI the same year. During the Second World War, he was a member of the Home Guard. On 28 October 1958 he married Denise V. Winroope (died 1980) and they had two sons, Anthony and Nigel.Trevor Kletz (2000) ''By Accident… a Life Preventing them in industry'' PFV, Professional life In ICI he worked initially as a research chemist, then became plant manager (in turn) of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hazard Analysis
A hazard analysis is one of many methods that may be used to assess risk. At its core, the process entails describing a system object (such as a person or machine) that intends to conduct some activity. During the performance of that activity, an adverse event (referred to as a “ factor”) may be encountered that could cause or contribute to an occurrence (mishap, incident, accident). Finally, that occurrence will result in some outcome that may be measured in terms of the degree of loss or harm. This outcome may be measured on a continuous scale, such as an amount of monetary loss, or the outcomes may be categorized into various levels of severity. A Simple Hazard Analysis The first step in hazard analysis is to identify the hazards. If an automobile is an object performing an activity such as driving over a bridge, and that bridge may become icy, then an icy bridge might be identified as a hazard. If this hazard is encountered, it could cause or contribute to the occur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
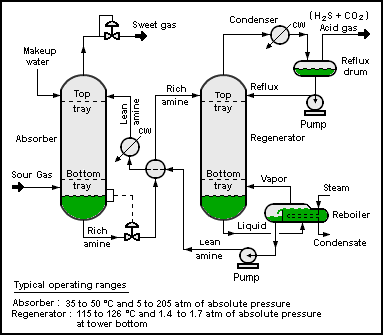
Process Flow Diagram
A process flow diagram (PFD) is a diagram commonly used in chemical and process engineering to indicate the general flow of plant processes and equipment. The PFD displays the relationship between ''major'' equipment of a plant facility and does not show minor details such as piping details and designations. Another commonly used term for a PFD is ''process'' ''flowsheet''. It is the key document in process design. Typical content of a process flow diagram Typically, process flow diagrams of a single unit process include the following: * Process piping * Major equipment items *Connections with other systems * Major bypass and recirculation (recycle) streams * Operational data (temperature, pressure, mass flow rate, density, etc.), often by stream references to a mass balance * Process stream names Process flow diagrams generally do not include: * Pipe classes or piping line numbers * Instrumentation details * Minor bypass lines * Instrumentation * Controllers like Level Con ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Piping And Instrumentation Diagram
A Piping and Instrumentation Diagram (P&ID) is a detailed diagram in the process industry which shows process equipment together with the instrumentation and control devices. It is also called as mechanical flow diagram (MFD). Superordinate to the P&ID is the process flow diagram (PFD) which indicates the more general flow of plant processes and the relationship between major equipment of a plant facility. Contents and function A piping and instrumentation diagram (P&ID) is defined as follows: # A diagram which shows the interconnection of process equipment and the instrumentation used to control the process. In the process industry, a Symbolic language (engineering), standard set of symbols is used to prepare drawings of processes. The instrument symbols used in these drawings are generally based on International Society of Automation (ISA) Standard S5.1 # The primary schematic drawing used for laying out a process control installation. They usually contain the following inf ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Maintenance (technical)
The technical meaning of maintenance involves functional checks, servicing, repairing or replacing of necessary devices, equipment, machinery, building infrastructure and supporting utilities in industrial, business, and residential installations. Terms such as "predictive" or "planned" maintenance describe various cost-effective practices aimed at keeping equipment operational; these activities occur either before or after a potential failure. Definitions Maintenance functions can be defined as maintenance, repair and overhaul (MRO), and MRO is also used for maintenance, repair and operations. Over time, the terminology of maintenance and MRO has begun to become standardized. The United States Department of Defense uses the following definitions: Federal Standard 1037C and from MIL-STD-188 and from the Department of Defense Dictionary of Military and Associated Terms * Any activity—such as tests, measurements, replacements, adjustments, and repairs—intended to retain ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Distributed Control System
A distributed control system (DCS) is a computerized control system for a process or plant usually with many control loops, in which autonomous controllers are distributed throughout the system, but there is no central operator supervisory control. This is in contrast to systems that use centralized controllers; either discrete controllers located at a central control room or within a central computer. The DCS concept increases reliability and reduces installation costs by localizing control functions near the process plant, with remote monitoring and supervision. Distributed control systems first emerged in large, high value, safety critical process industries, and were attractive because the DCS manufacturer would supply both the local control level and central supervisory equipment as an integrated package, thus reducing design integration risk. Today the functionality of Supervisory control and data acquisition (SCADA) and DCS systems are very similar, but DCS tends to be use ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Inerting (gas)
In fire and explosion prevention engineering, inerting refers to the introduction of an inert gas, inert (non-combustible) gas into a closed system (e.g. a container or a process vessel) to make a flammable atmosphere oxygen deficient and non-ignitable.NFPA 69. Standard on Explosion Prevention Systems. National Fire Protection Association.NFPA 77. Recommended Practice on Static Electricity. National Fire Protection Association. Inerting relies on the principle that a combustible (or flammable) gas is able to undergo combustion (explode) only if mixed with air in the right proportions. The flammability limits of the gas define those proportions, i.e. the ignitable range. In combustion engineering terms, the admission of inert gas can be said to dilute the oxygen below the limiting oxygen concentration. Inerting differs from Purging (gas), purging. Purging, by definition, ensures that an ignitable mixture ''never forms''. Inerting makes an ignitable mixture safe by introduction o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gas Venting
Gas venting, more specifically known as natural-gas venting or methane venting, is the intentional and controlled release of gases containing alkane hydrocarbons - predominately methane - into Earth's atmosphere. It is a widely used method for disposal of unwanted gases which are produced during the extraction of coal and crude oil. Such gases may lack value when they are not recyclable into the production process, have no export route to consumer markets, or are surplus to near-term demand. In cases where the gases have value to the producer, substantial amounts may also be vented from the equipment used for gas collection, pipeline transport, transport, and distribution. Gas venting contributes strongly to climate change. Nevertheless, many individual cases are sufficiently small and dispersed to be deemed "safe" with regard to immediate health hazards. Large and concentrated releases are usually abated with gas flares to produce relatively less-harmful carbon dioxide gas. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chemical Reaction
A chemical reaction is a process that leads to the chemistry, chemical transformation of one set of chemical substances to another. When chemical reactions occur, the atoms are rearranged and the reaction is accompanied by an Gibbs free energy, energy change as new products are generated. Classically, chemical reactions encompass changes that only involve the positions of electrons in the forming and breaking of chemical bonds between atoms, with no change to the Atomic nucleus, nuclei (no change to the elements present), and can often be described by a chemical equation. Nuclear chemistry is a sub-discipline of chemistry that involves the chemical reactions of unstable and radioactive Chemical element, elements where both electronic and nuclear changes can occur. The substance (or substances) initially involved in a chemical reaction are called reagent, reactants or reagents. Chemical reactions are usually characterized by a chemical change, and they yield one or more Product (c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Temperature
Temperature is a physical quantity that quantitatively expresses the attribute of hotness or coldness. Temperature is measurement, measured with a thermometer. It reflects the average kinetic energy of the vibrating and colliding atoms making up a substance. Thermometers are calibrated in various temperature scales that historically have relied on various reference points and thermometric substances for definition. The most common scales are the Celsius scale with the unit symbol °C (formerly called ''centigrade''), the Fahrenheit scale (°F), and the Kelvin scale (K), with the third being used predominantly for scientific purposes. The kelvin is one of the seven base units in the International System of Units (SI). Absolute zero, i.e., zero kelvin or −273.15 °C, is the lowest point in the thermodynamic temperature scale. Experimentally, it can be approached very closely but not actually reached, as recognized in the third law of thermodynamics. It would be impossible ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vacuum
A vacuum (: vacuums or vacua) is space devoid of matter. The word is derived from the Latin adjective (neuter ) meaning "vacant" or "void". An approximation to such vacuum is a region with a gaseous pressure much less than atmospheric pressure. Physicists often discuss ideal test results that would occur in a ''perfect'' vacuum, which they sometimes simply call "vacuum" or free space, and use the term partial vacuum to refer to an actual imperfect vacuum as one might have in a laboratory or in space. In engineering and applied physics on the other hand, vacuum refers to any space in which the pressure is considerably lower than atmospheric pressure. The Latin term ''in vacuo'' is used to describe an object that is surrounded by a vacuum. The ''quality'' of a partial vacuum refers to how closely it approaches a perfect vacuum. Other things equal, lower gas pressure means higher-quality vacuum. For example, a typical vacuum cleaner produces enough suction to reduce air pressur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |