|
Hartog Jacob Hamburger
Hartog Jakob or Hartog Jacob Hamburger (9 March 1859 – 4 January 1924) was a Dutch physiologist, born in Alkmaar. After completing the Hogere Burgerschool in Alkmaar, Hamburger studied chemistry at Utrecht University, where he received his doctorate in 1883, on the determination of urea in urine. He subsequently worked with Utrecht ophthalmologist and physiologist Franciscus Cornelis Donders for seven years, and completed a medical degree. From 1888 he lectured in physiology and pathology at the National Veterinary School, also in Utrecht. In 1896, he invented the crystalloid solution known as Hamburger's solution or saline (medicine), normal saline. Based on plant-based experiments by botanist Hugo de Vries, he developed a salt solution that was thought to have the same osmolality as human blood and therefore did not cause haemolysis of red blood cells. It is uncertain whether the saline was ever originally intended for intravenous administration. In 1901, he joined the Univ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alkmaar
Alkmaar () is a List of cities in the Netherlands by province, city and List of municipalities of the Netherlands, municipality in the Netherlands, located in the Provinces of the Netherlands, province of North Holland. Alkmaar is well known for its traditional cheese market. For tourists, it is a popular cultural destination. The municipality has a population of 111,766 as of 2023. History The earliest mention of the name Alkmaar is in a 10th-century document. As the village grew into a town, it was granted City rights in the Netherlands, city rights in 1254. The oldest part of Alkmaar lies on an ancient sand bank a couple of meters (yards) above the surrounding region; it afforded some protection from inundation during medieval times. Its vicinage consists of some of the Achtermeer, oldest polders in existence. Older spellings include Alckmar. On 24 June 1572, after the Geuzen captured the town, five Franciscans from Alkmaar were taken to Enkhuizen and hanged, becoming the m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Red Blood Cell
Red blood cells (RBCs), referred to as erythrocytes (, with -''cyte'' translated as 'cell' in modern usage) in academia and medical publishing, also known as red cells, erythroid cells, and rarely haematids, are the most common type of blood cell and the vertebrate's principal means of delivering oxygen () to the body tissue (biology), tissues—via blood flow through the circulatory system. Erythrocytes take up oxygen in the lungs, or in fish the gills, and release it into tissues while squeezing through the body's capillary, capillaries. The cytoplasm of a red blood cell is rich in hemoglobin (Hb), an iron-containing biomolecule that can bind oxygen and is responsible for the red color of the cells and the blood. Each human red blood cell contains approximately 270 million hemoglobin molecules. The cell membrane is composed of proteins and lipids, and this structure provides properties essential for physiological Cell (biology), cell function such as erythrocyte deformabil ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Royal Netherlands Academy Of Arts And Sciences
The Royal Netherlands Academy of Arts and Sciences (, KNAW) is an organization dedicated to the advancement of science and literature in the Netherlands. The academy is housed in the Trippenhuis in Amsterdam. In addition to various advisory and administrative functions it operates a number of research institutes and awards many prizes, including the Lorentz Medal in theoretical physics, the Dr Hendrik Muller Prize for Behavioural and Social Science and the Heineken Prizes. Main functions The academy advises the Dutch government on scientific matters. While its advice often pertains to genuine scientific concerns, it also counsels the government on such topics as policy on careers for researchers or the Netherlands' contribution to major international projects. The academy offers solicited and unsolicited advice to parliament, ministries, universities and research institutes, funding agencies and international organizations. * Advising the government on matters related to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
White Blood Cell
White blood cells (scientific name leukocytes), also called immune cells or immunocytes, are cells of the immune system that are involved in protecting the body against both infectious disease and foreign entities. White blood cells are generally larger than red blood cells. They include three main subtypes: granulocytes, lymphocytes and monocytes. All white blood cells are produced and derived from multipotent cells in the bone marrow known as hematopoietic stem cells. Leukocytes are found throughout the body, including the blood and lymphatic system. All white blood cells have nuclei, which distinguishes them from the other blood cells, the anucleated red blood cells (RBCs) and platelets. The different white blood cells are usually classified by cell lineage ( myeloid cells or lymphoid cells). White blood cells are part of the body's immune system. They help the body fight infection and other diseases. Types of white blood cells are granulocytes (neutrophils, eosino ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neutrophil Granulocyte
Neutrophils are a type of phagocytic white blood cell and part of innate immunity. More specifically, they form the most abundant type of granulocytes and make up 40% to 70% of all white blood cells in humans. Their functions vary in different animals. They are also known as neutrocytes, heterophils or polymorphonuclear leukocytes. They are formed from stem cells in the bone marrow and differentiated into subpopulations of neutrophil-killers and neutrophil-cagers. They are short-lived (between 5 and 135 hours, see ) and highly mobile, as they can enter parts of tissue where other cells/molecules cannot. Neutrophils may be subdivided into segmented neutrophils and banded neutrophils (or bands). They form part of the polymorphonuclear cells family (PMNs) together with basophils and eosinophils. The name ''neutrophil'' derives from staining characteristics on hematoxylin and eosin ( H&E) histological or cytological preparations. Whereas basophilic white blood cells st ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phagocytosis
Phagocytosis () is the process by which a cell (biology), cell uses its plasma membrane to engulf a large particle (≥ 0.5 μm), giving rise to an internal compartment called the phagosome. It is one type of endocytosis. A cell that performs phagocytosis is called a phagocyte. In a Multicellular organism, multicellular organism's immune system, phagocytosis is a major mechanism used to remove pathogens and cell debris. The ingested material is then digested in the phagosome. Bacteria, dead tissue cells, and small mineral particles are all examples of objects that may be phagocytized. Some protozoa use phagocytosis as means to obtain nutrients. The two main cells that do this are the Macrophages and the Neutrophils of the immune system. Where phagocytosis is used as a means of feeding and provides the organism part or all of its nourishment, it is called phagotrophy and is distinguished from osmotrophy, which is nutrition taking place by absorption. History The history of phag ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Band 3
Band 3 anion transport protein, also known as anion exchanger 1 (AE1) or band 3 or solute carrier family 4 member 1 (SLC4A1), is a protein that is encoded by the gene in humans. Band 3 anion transport protein is a phylogenetically-preserved transport protein responsible for mediating the exchange of chloride (Cl−) with bicarbonate (HCO3−) across plasma membranes. Functionally similar members of the AE clade are AE2 and AE3. Function Band 3 is present in the basolateral face of the α-intercalated cells of the collecting ducts of the nephron, which are the main acid-secreting cells of the kidney. They generate hydrogen ions and bicarbonate ions from carbon dioxide and water – a reaction catalysed by carbonic anhydrase. The hydrogen ions are pumped into the collecting duct tubule by vacuolar H+ ATPase, the apical proton pump, which thus excretes acid into the urine. kAE1, the kidney isoform of AE1, exchanges bicarbonate for chloride on the basolateral surfac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chloride
The term chloride refers to a compound or molecule that contains either a chlorine anion (), which is a negatively charged chlorine atom, or a non-charged chlorine atom covalently bonded to the rest of the molecule by a single bond (). The pronunciation of the word "chloride" is . Chloride salts such as sodium chloride are often soluble in water.Green, John, and Sadru Damji. "Chapter 3." ''Chemistry''. Camberwell, Vic.: IBID, 2001. Print. It is an essential electrolyte located in all body fluids responsible for maintaining acid/base balance, transmitting nerve impulses and regulating liquid flow in and out of cells. Other examples of ionic chlorides include potassium chloride (), calcium chloride (), and ammonium chloride (). Examples of covalent chlorides include methyl chloride (), carbon tetrachloride (), sulfuryl chloride (), and monochloramine (). Electronic properties A chloride ion (diameter 167 pm) is much larger than a chlorine atom (diameter 99 pm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bicarbonate
In inorganic chemistry, bicarbonate (IUPAC-recommended nomenclature: hydrogencarbonate) is an intermediate form in the deprotonation of carbonic acid. It is a polyatomic anion with the chemical formula . Bicarbonate serves a crucial biochemical role in the physiological pH buffering system. The term "bicarbonate" was coined in 1814 by the English chemist William Hyde Wollaston. The name lives on as a trivial name. Chemical properties The bicarbonate ion (hydrogencarbonate ion) is an anion with the empirical formula and a molecular mass of 61.01 daltons; it consists of one central carbon atom surrounded by three oxygen atoms in a trigonal planar arrangement, with a hydrogen atom attached to one of the oxygens. It is isoelectronic with nitric acid (). The bicarbonate ion carries a negative one formal charge and is an amphiprotic species which has both acidic and basic properties. It is both the conjugate base of carbonic acid (); and the conjugate acid of , t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
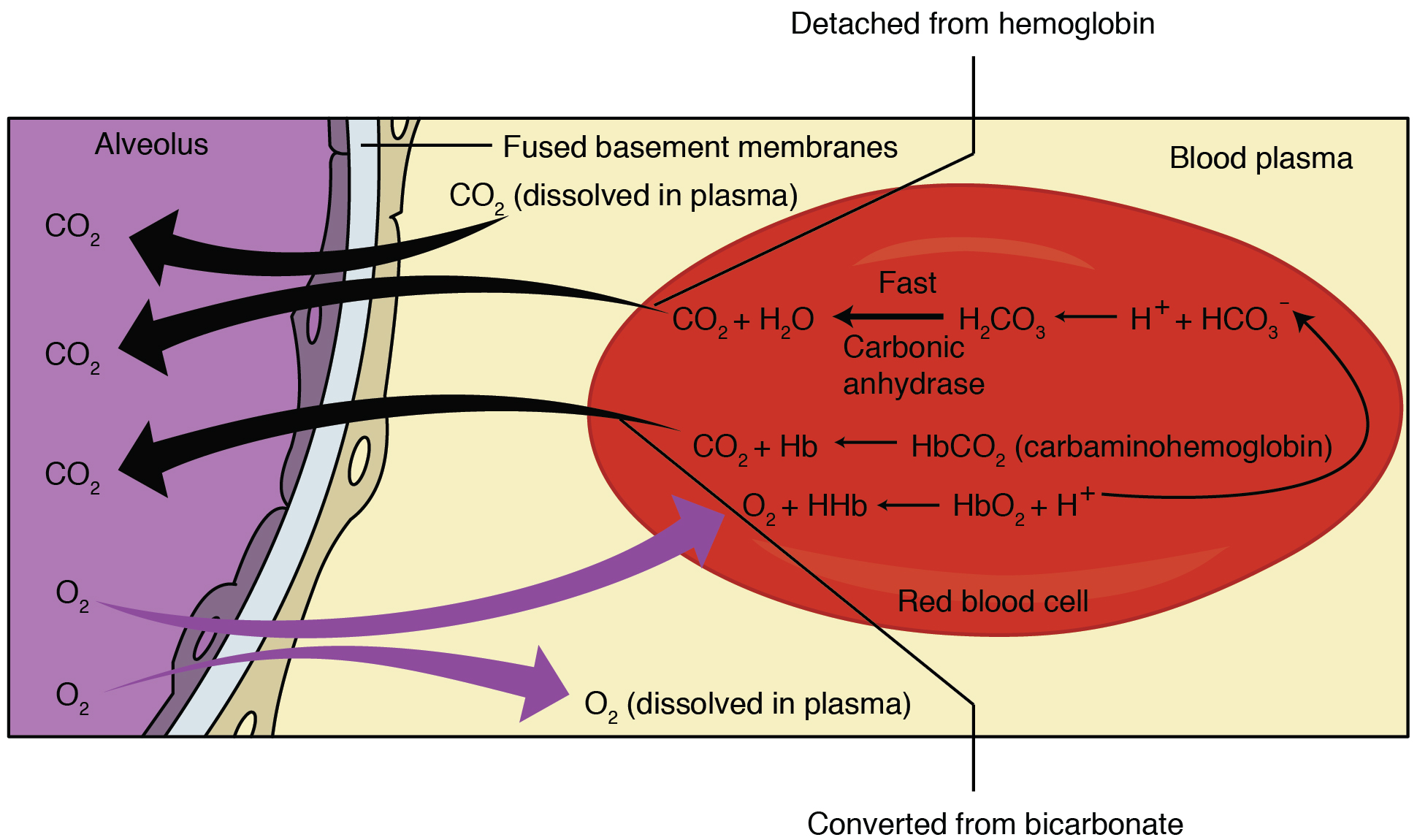
Chloride Shift
Chloride shift (also known as the Hamburger phenomenon or lineas phenomenon, named after Hartog Jakob Hamburger) is a process which occurs in a cardiovascular system and refers to the exchange of bicarbonate (HCO3−) and chloride (Cl−) across the membrane of red blood cells (RBCs). Mechanism Carbon dioxide (CO2) is produced in tissues as a byproduct of normal aerobic metabolism. It dissolves in the solution of blood plasma and into red blood cells (RBC), where carbonic anhydrase catalyzes its hydration to carbonic acid (H2CO3). Carbonic acid then spontaneously dissociates to form bicarbonate Ions (HCO3−) and a hydrogen ion (H+). In response to the decrease in intracellular pCO2, more CO2 passively diffuses into the cell. Cell membranes are generally impermeable to charged ions (i.e. H+, HCO3− ) but RBCs are able to exchange bicarbonate for chloride using the anion exchanger protein Band 3. Thus, the rise in intracellular bicarbonate leads to bicarbonate export and chlor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vitalism
Vitalism is a belief that starts from the premise that "living organisms are fundamentally different from non-living entities because they contain some non-physical element or are governed by different principles than are inanimate things." Where vitalism explicitly invokes a vital principle, that element is often referred to as the "vital spark", "energy", "'' élan vital''" (coined by vitalist Henri Bergson), "vital force", or "''vis vitalis''", which some equate with the soul. In the 18th and 19th centuries, vitalism was discussed among biologists, between those who felt that the known mechanics of physics would eventually explain the difference between life and non-life and vitalists who argued that the processes of life could not be reduced to a mechanistic process. Vitalist biologists such as Johannes Reinke proposed testable hypotheses meant to show inadequacies with mechanistic explanations, but their experiments failed to provide support for vitalism. Biologists now ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Health Science
The following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to health sciences: Health sciences – those sciences that focus on health, or health care, as core parts of their subject matter. Health sciences relate to multiple academic disciplines, including STEM disciplines and emerging patient safety disciplines (such as social care research). Medicine and its branches Medicine is an applied science or practice of the diagnosis, treatment, and prevention of disease. It encompasses a variety of health care practices evolved to maintain and restore health by the prevention and treatment of illness. Below are some of the branches of medicine. * Anesthesiology is the brand of medicine that deals with life support and anesthesia during surgery. * Angiology deals with the diseases of the circulatory system. * Audiology focuses on preventing and curing hearing damage. * Bariatrics deals with the causes, prevention, and treatment of obesity. * Cardiology ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |