|
Harmodius And Aristogiton
Harmodius (Greek: Ἁρμόδιος, ''Harmódios'') and Aristogeiton (Ἀριστογείτων, ''Aristogeíton''; both died 514 BC) were two lovers in Classical Athens who became known as the Tyrannicides (τυραννόκτονοι, ''tyrannoktonoi'') for their assassination of Hipparchus, the brother of the tyrant Hippias, for which they were executed. A few years later, in 510 BC, the Spartan king Cleomenes I forced Hippias to go into exile, thereby opening the way to the subsequent democratic reforms of Cleisthenes. The Athenian democrats later celebrated Harmodius and Aristogeiton as national heroes, partially to conceal the role played by Sparta in the removal of the Athenian tyranny. Cleisthenes notably commissioned the famous statues of the Tyrannicides. Background The two principal historical sources covering Harmodius and Aristogeiton are the ''History of the Peloponnesian War'' (VI, 56–59) by Thucydides, and '' The Constitution of the Athenians'' (XVIII) attribute ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Concubine
Concubinage is an interpersonal relationship, interpersonal and Intimate relationship, sexual relationship between two people in which the couple does not want to, or cannot, enter into a full marriage. Concubinage and marriage are often regarded as similar, but mutually exclusive. During the early stages of European colonialism, administrators often encouraged European men to practice concubinage to discourage them from paying prostitutes for sex (which could spread venereal disease) and from homosexuality. Colonial administrators also believed that having an intimate relationship with a native woman would enhance white men's understanding of native culture and would provide them with essential domestic labor. The latter was critical, as it meant white men did not require wives from the metropole, hence did not require a family wage. Colonial administrators eventually discouraged the practice when these liaisons resulted in offspring who threatened colonial rule by producing a m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ancient Argos
Argos (; ; ) is a city and former municipality in Argolis, Peloponnese, Greece and is one of the oldest continuously inhabited cities in the world, and the oldest in Europe. It is the largest city in Argolis and a major center in the same prefecture, having nearly twice the population of the prefectural capital, Nafplio. Since the 2011 local government reform it has been part of the municipality of Argos-Mykines, of which it is a municipal unit. The municipal unit has an area of 138.138 km2. It is from Nafplion, which was its historic harbour. A settlement of great antiquity, Argos has been continuously inhabited as at least a substantial village for the past 7,000 years. A resident of the city of Argos is known as an Argive ( , ; ). However, this term is also used to refer to those ancient Greeks generally who assaulted the city of Troy during the Trojan War; the term is more widely applied by the Homeric bards. Numerous ancient monuments can be found in the cit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Panathenaea
The Panathenaea (or Panathenaia) was a multi-day ancient Greek festival held annually in Athens that would always conclude on 28 Hekatombaion, the first month of the Attic calendar.Shear, Julia L. "Hadrian, the Panathenaia, and the Athenian Calendar". ''Zeitschrift Für Papyrologie Und Epigraphik'' 180 (2012): 159. . The main purpose of the festival was for Athenians and non-Athenians to celebrate the goddess Athena. Every four years, the festival was celebrated in a larger manner over a longer time period with increased festivities and was known as the Great (or Greater) Panathenaea. In the years that the festival occurred that were not considered the Great Panathenaea, the festival was known as the Lesser Panathenaea. The festival consisted of various competitions and ceremonies, culminating with a religious procession that ended in the Acropolis of Athens.Shear, Julia L. Serving Athena: The Festival of the Panathenaia and the Construction of Athenian Identities. (New York: Camb ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kanephoros
The Kanephoros (, , pl. Kanephoroi (Greek: ); latinate plural form Canephorae; lit. "Basket Bearers") was an honorific office given to unmarried young women in ancient Greece, which involved the privilege of leading the procession to sacrifice at festivals; the highest honour was to lead the () at the Panathenaic Festival. The role was given to a virgin selected from amongst the aristocratic or Eupatrid families of Athens whose purity and youth was thought essential to ensure a successful sacrifice. Her task was to carry a basket or ''kanoun'' (), which contained the offering of barley or first fruits, the sacrificial knife and fillets to decorate the bull, in procession through the city up to the altar on the acropolis. From Aristophanes’s ''Lysistrata'' we have evidence that the office of kanephoros was the last in a sequence of religious duties that an unmarried Athenian girl might undertake; first as an ''arrephoros, arrhephoros'', later an ''aletris'', then as an ''arktos' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eromenos
In ancient Greece, an ''eromenos'' was the younger and passive (or 'receptive') partner in a male homosexual relationship. The partner of an ''eromenos'' was the ''erastes'', the older and active partner. The ''eromenos'' was often depicted as beautiful, beardless and more youthful-looking than the ''erastes''. Terminology ''Erômenos'' (ἐρώμενος) means 'one who is sexually desired' in Greek language and is the past participle of the verb ''eramai'', to have sexual desire. In '' Greek Homosexuality'', the first modern scholarly work on this topic, Kenneth Dover used the literal translation of the Greek word as an English word to refer to the passive partner in Greek homosexual relationship. Though in many contexts the younger man is also called ''pais'', 'boy', the word can also be used for child, girl, son, daughter and slave, and therefore ''eromenos'' would be more specific and can "avoid the cumbrousness and…imprecision of 'boy'". It is in contrast to the mascul ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Archon
''Archon'' (, plural: , ''árchontes'') is a Greek word that means "ruler", frequently used as the title of a specific public office. It is the masculine present participle of the verb stem , meaning "to be first, to rule", derived from the same root as words such as monarch and hierarchy. Ancient Greece In the early literary period of ancient Greece, the chief magistrates of various Greek city states were called ''archontes''. The term was also used throughout Greek history in a more general sense, ranging from "club leader" to "master of the tables" at '' syssitia'' to "Roman governor". In Athens, a system of three concurrent archons evolved, the three office holders being known as ''archon eponymos'' (), the '' polemarch'' (), and the '' archon basileus'' (). According to Aristotle's '' Constitution of the Athenians'', the power of the king first devolved to the archons, and these offices were filled from the aristocracy by elections every ten years. During this period, the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hippias (son Of Pisistratus)
Hippias (; 490 BC) was the last tyrant of Athens, ruling from 527 to 510 BC. He was one of the Peisistratids, a group of tyrants from the same family in ancient Greece. His father was Pisistratus, who preceded him as ruler of Athens, while his brother Hipparchus may have ruled jointly with him. Hippias also had an illegitimate son, Hegesistratus, whom he made tyrant of Sigeion. He was deposed when Cleomenes I of Sparta successfully invaded Athens and forced him to flee to the Achaemenid Empire. Early life Hippias was born around 570 BC as the eldest son of Pisistratus, the first tyrant of Athens. When his father was forced to flee to Eretria after insulting Megakles by having intercourse with his daughter in an indecent way, Peisistratos held counsel with his sons. Hippias suggested that they should retake the tyranny, which his father agreed to. Preparations began for which Athens fell to Peisistratos for the third time in 546 BC. Tyrant of Athens Hippias suc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Peisistratos (Athens)
Pisistratus (also spelled Peisistratus or Peisistratos; ; – 527 BC) was a politician in ancient Athens, ruling as tyrant in the late 560s, the early 550s and from 546 BC until his death. His unification of Attica, the triangular peninsula of Greece containing Athens, along with economic and cultural improvements laid the groundwork for the later pre-eminence of Athens in ancient Greece. His legacy lies primarily in his institution of the Panathenaic Games, historically assigned the date of 566 BC, and the consequent first attempt at producing a definitive version of the Homeric epics. Pisistratus' championing of the lower class of Athens is an early example of populism. While in power, he did not hesitate to confront the aristocracy and greatly reduce their privileges, confiscating their lands and giving them to the poor. Pisistratus funded many religious and artistic programs, in order to improve the economy and spread the wealth more equally among the Athenian peo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
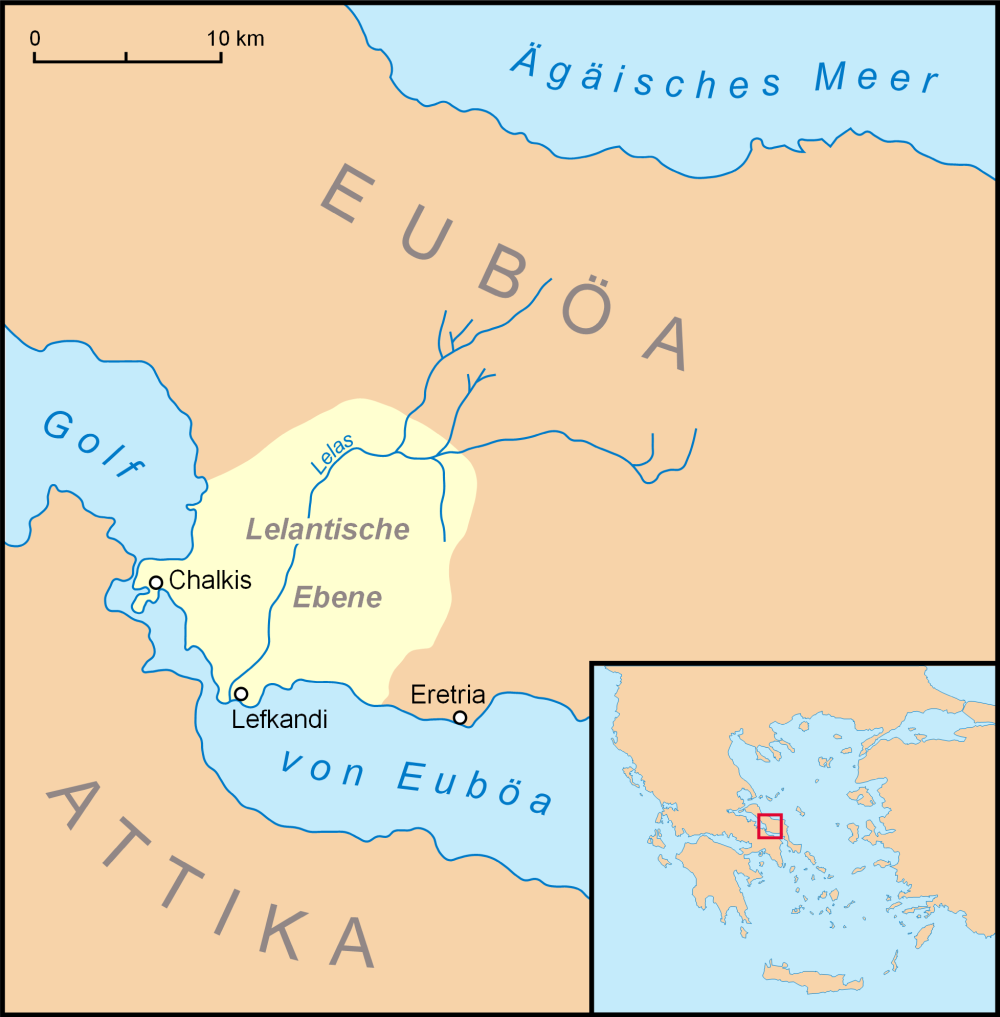
Eretria
Eretria (; , , , , literally 'city of the rowers') is a town in Euboea, Greece, facing the coast of Attica across the narrow South Euboean Gulf. It was an important Greek polis in the 6th and 5th century BC, mentioned by many famous writers and actively involved in significant historical events. Excavations of the ancient city began in the 1890s and have been conducted since 1964 by the Greek Archaeological Service (11th Ephorate of Antiquities) and the Swiss School of Archaeology in Greece. History of Eretria Prehistory The first evidence for human activity in the area of Eretria are pottery shards and stone artifacts from the late Neolithic period (3500–3000 BC) found on the Acropolis as well as in the plain. No permanent structures have yet been found. It is therefore unclear whether a permanent settlement existed at that time. The first known settlement from the Early Helladic period (3000–2000 BC) was located on the plain. A granary and several other buildi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |