|
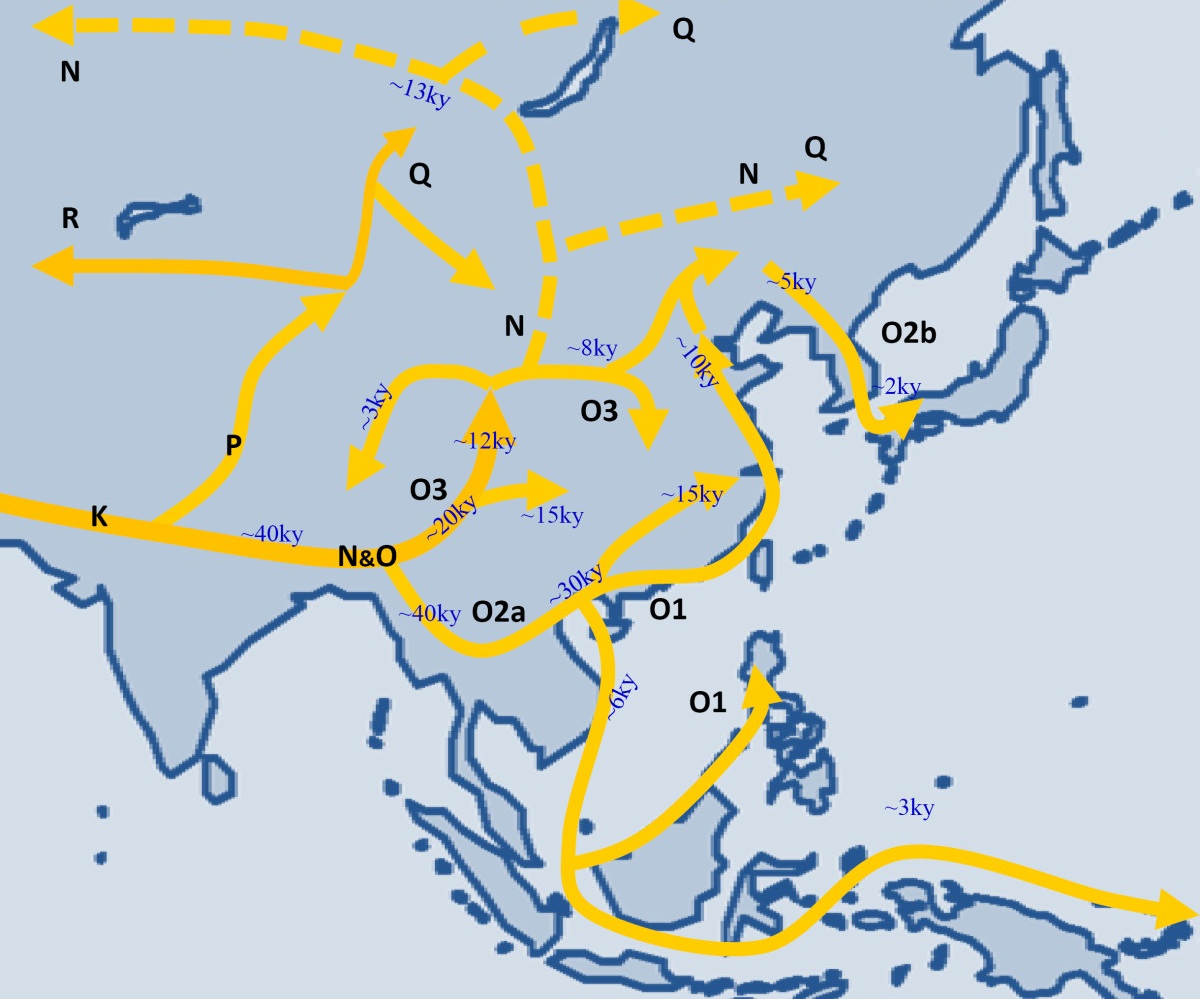
Haplogroup Q1a3a (Y-DNA)
Haplogroup Q-M3 (Y-DNA) is a Y-chromosome DNA haplogroup. Haplogroup Q-M3 is a subclade of Haplogroup Q-L54. Haplogroup Q-M3 was previously known as Haplogroup Q3; currently Q-M3 is Q1b1a1a below Q1b-M346. In 1996 the research group at Stanford University headed by Dr. Peter Underhill first discovered the SNP that was to become known as M3. At the time, it was called DYS191. Later studies completed the genetic bridge by determining that Q-M3 was related to Q-M242-bearing populations who traveled through Central Asia to East Asia. Origin and distribution Haplogroup Q-M3 is one of the Y-Chromosome haplogroups linked to the indigenous peoples of the Americas (over 90% of indigenous people in Meso & South America). Today, such lineages also include other Q-M242 branches ( Q-M346, Q-L54, Q-P89.1, Q-NWT01, and Q-Z780), haplogroup C-M130 branches ( C-M217 and C-P39), and R-M207, which are almost exclusively found in North America. Haplogroup Q-M3 is defined by the presence of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
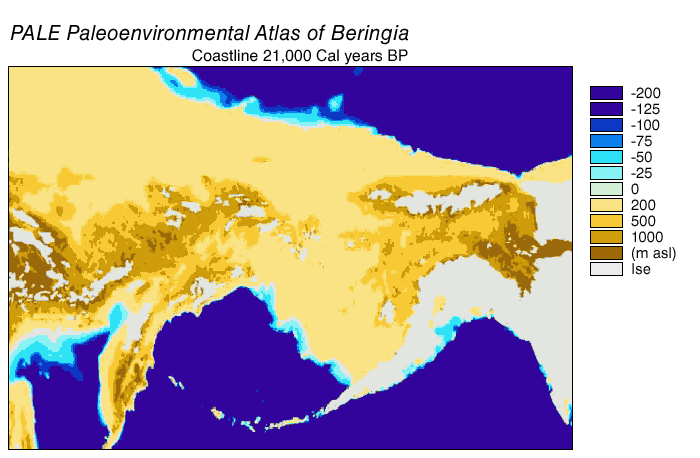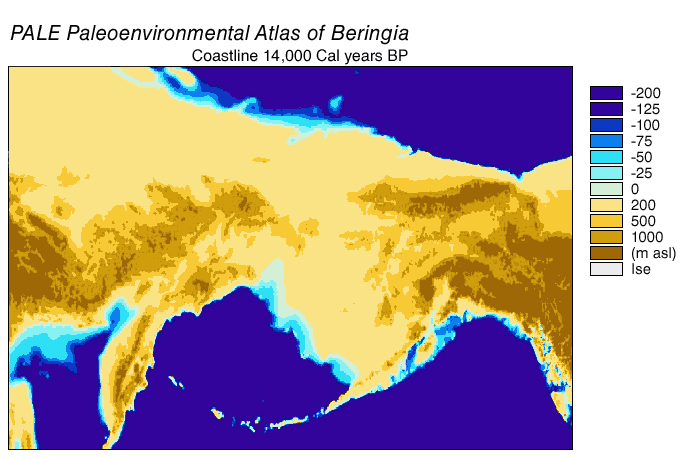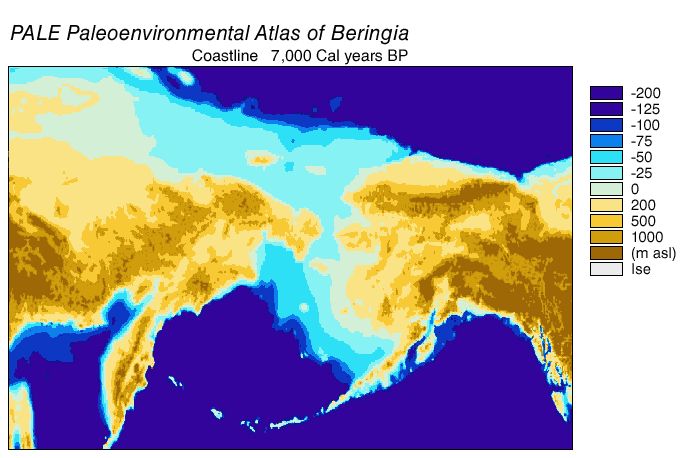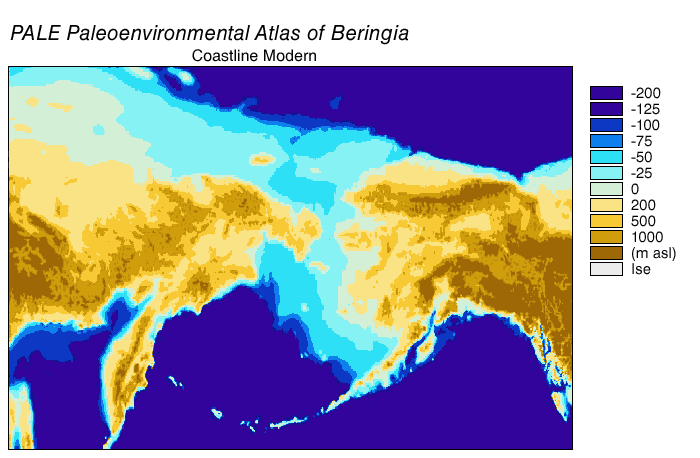
Beringia
Beringia is defined today as the land and maritime area bounded on the west by the Lena River in Russia; on the east by the Mackenzie River in Canada; on the north by 70th parallel north, 72° north latitude in the Chukchi Sea; and on the south by the tip of the Kamchatka Peninsula. It includes the Chukchi Sea, the Bering Sea, the Bering Strait, the Chukchi Peninsula, Chukchi and Kamchatka peninsulas in Russia as well as Alaska in the United States and Yukon in Canada. The area includes land lying on the North American Plate and Siberian land east of the Chersky Range. At various times, it formed a land bridge referred to as the Bering land bridge, that was up to wide at its greatest extent and which covered an area as large as British Columbia and Alberta together, totaling about , allowing biological dispersal to occur between Asia and North America. Today, the only land that is visible from the central part of the Bering land bridge are the Diomede Islands, the Pribilof Isla ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Haplogroup R-M207 (Y-DNA)
Haplogroup R, or R-M207, is a Human Y-chromosome DNA haplogroup, Y-chromosome DNA haplogroup. It is both numerous and widespread among modern populations. Some descendant subclades have been found since pre-history in Europe, Central Asia and South Asia. Others have long been present, at lower levels, in parts of West Asia and Africa. Some authorities have also suggested, more controversially, that R-M207 has long been present among Indigenous peoples of the Americas, Native Americans in North America – a theory that has not yet been widely accepted. According to geneticist Spencer Wells, haplogroup K originated in the Middle East or Central Asia. "Given the widespread distribution of K, it probably arose somewhere in the Middle East or Central Asia, perhaps in the region of Iran or Pakistan." However, Karafet et al. (2014) proposed that "rapid diversification ... of Haplogroup K2, K-M526", also known as K2, likely occurred in Southeast Asia (near Indonesia) and later expande ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Haplogroup Q-L54 (Y-DNA)
Haplogroup Q-L54 is a subclade of Y-DNA haplogroup Q-L53. Q1a3a-L54 is defined by the presence of the L54 Single Nucleotide Polymorphism (SNP). Distribution Q-L54 has descendants across Western and Central Europe, the North and East of Asia, and the Americas. It includes two of the major pre-Columbian paternal lineages in the Americas: Q-M3 and Q-M971. The boy Anzick-1, who lived 12,600 years ago and was found in the state of Montana, has a Y-chromosome that refers to haplogroup Q-M971 (Q-L54*(xM3)). Q-L54 descendant lines also include two Eurasian paternal lineages, the Central Asian Q-L330 lineage and the Scandinavian Q-L804. Q-L330 is also found in some men with Romaniote Jewish paternal lines from Greece. Q-L804 is Scandinavian and the TMRCA is just over 3000 years. Haplogroup Q‐L54 is dominant in two North Siberian populations, the Kets and Selkups, with frequencies of 97.7% and 66.7%, respectively. Associated SNP's Q-L54 is currently defined by the L54 SNP alone ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Single-nucleotide Polymorphism
In genetics and bioinformatics, a single-nucleotide polymorphism (SNP ; plural SNPs ) is a germline substitution of a single nucleotide at a specific position in the genome. Although certain definitions require the substitution to be present in a sufficiently large fraction of the population (e.g. 1% or more), many publications do not apply such a frequency threshold. For example, a Guanine, G nucleotide present at a specific location in a reference genome may be replaced by an Adenine, A in a minority of individuals. The two possible nucleotide variations of this SNP – G or A – are called alleles. SNPs can help explain differences in susceptibility to a wide range of diseases across a population. For example, a common SNP in the Factor H, CFH gene is associated with increased risk of age-related macular degeneration. Differences in the severity of an illness or response to treatments may also be manifestations of genetic variations caused by SNPs. For example, two ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Theodore G
Theodore may refer to: Places * Theodore, Australian Capital Territory, Australia * Theodore, Queensland, Australia * Theodore, Saskatchewan, Canada * Theodore, Alabama, United States * Theodore Reservoir, in Saskatchewan People * Theodore (given name), including a list of people with the name ** Theodore Roosevelt, 26th President of the United States **Grand Wizzard Theodore, American musician and DJ * Theodore (surname), including a list of people with the name Fictional characters * T-Bag (''Prison Break'') (Theodore Bagwell), in ''Prison Break'' * T-Dog (''The Walking Dead'') (Theodore Douglas), in ''The Walking Dead'' * Theodore Huxtable, in ''The Cosby Show'' * Theodore, in ''Alvin and the Chipmunks'' * Theodore Grambell, or CatNap, in video game ''Poppy Playtime'' * Theodore "The Roach" Roachmont, from Supernoobs Other uses * Theodore (horse), a British Thoroughbred racehorse * Theodore Racing, a Formula One constructor See also * Theodoros, or Theodorus * Principa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
David C
David (; , "beloved one") was a king of ancient Israel and Judah and the third king of the United Monarchy, according to the Hebrew Bible and Old Testament. The Tel Dan stele, an Aramaic-inscribed stone erected by a king of Aram-Damascus in the late 9th/early 8th centuries BCE to commemorate a victory over two enemy kings, contains the phrase (), which is translated as " House of David" by most scholars. The Mesha Stele, erected by King Mesha of Moab in the 9th century BCE, may also refer to the "House of David", although this is disputed. According to Jewish works such as the '' Seder Olam Rabbah'', '' Seder Olam Zutta'', and '' Sefer ha-Qabbalah'' (all written over a thousand years later), David ascended the throne as the king of Judah in 885 BCE. Apart from this, all that is known of David comes from biblical literature, the historicity of which has been extensively challenged,Writing and Rewriting the Story of Solomon in Ancient Israel; by Isaac Kalimi; page 3 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Whitehead Institute
Whitehead Institute for Biomedical Research is a non-profit research institute located in Cambridge, Massachusetts, United States that is dedicated to improving human health through basic biomedical research. It was founded as a fiscally independent entity from the Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT), where its 19 members all hold faculty appointments in the MIT Department of Biology or the MIT Department of Bioengineering. , Ruth Lehmann is its director; she succeeded David C. Page. History Whitehead Institute was founded in 1982 by industrialist and philanthropist Edwin C. “Jack” Whitehead (1920–1992), who sought to establish a research institute "dedicated to improving human health through basic biomedical science". Whitehead believed that while such an institution should be closely affiliated with an academic institution, it should remain wholly independent and self-governing. In David Baltimore (1975 Nobel Laureate in Physiology or Medicine), Whitehead ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ticuna
The Ticuna (also Magüta, Tucuna, Tikuna, or Tukuna, ) are an indigenous people of Brazil (36,000'')'', indigenous peoples of Colombia, Colombia (6,000), and indigenous peoples in Peru, Peru (7,000). They are the most numerous tribe in the Brazilian Amazon Basin, Amazon. History Ticuna were originally a tribe that lived far away from the rivers and whose expansion was kept in check by neighboring people. Their historical lack of access to waterways and their practice of endogamy has led to the Ticuna being culturally and genetically distinct from other Amazonian tribes. The first contact with outsiders occurred on the colonization of Brazil when a Portuguese fleet exploring the Amazon came into contact with the Ticuna. Sustained contact with the Portuguese and other outsiders began in 1649. Since the Ticuna lived relatively inland compared to other tribes they were less affected by the diseases and violence caused by colonialism, hence why the Ticuna today have the largest popu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Indigenous Peoples Of South America
In South America, Indigenous peoples comprise the Pre-Columbian peoples and their descendants, as contrasted with people of European ancestry and those of African descent. In Spanish, Indigenous peoples are referred to as (), or (). The term () is used in Argentina, and () is commonly used in Colombia. The English term ''Amerindian'' (short for "Indians of the Americas") is often used in the Guianas. Latin Americans of mixed European and Indigenous descent are usually referred to as (Spanish) and (Portuguese), while those of mixed African and Indigenous ancestry are referred to as . It is believed that the first human populations of South America either arrived from Asia into North America via the Bering Land Bridge and migrated southwards or alternatively from Polynesia across the Pacific. The earliest generally accepted archaeological evidence for human habitation in South America dates to 14,000 years ago, and is located at the Monte Verde site in southern Chile. T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Evens
The Evens /əˈvɛn/ ( Even: эвэн; pl. эвэсэл, ''evesel'' in Even and эвены, ''eveny'' in Russian; formerly called ''Lamuts'') are a people in Siberia and the Russian Far East. They live in regions of the Magadan Oblast and Kamchatka Krai and northern parts of Sakha east of the Lena River, although they are a nomadic people. According to the 2002 census, there were 19,071 Evens in Russia. According to the 2010 census, there were 22,383 Evens in Russia. They speak their own language called Even, one of the Tungusic languages; it is heavily influenced by their lifestyle and reindeer herding. It is also closely related to the language of their neighbors, the Evenks. The Evens are close to the Evenks by their origins and culture, having migrated with them from central China over 10,000 years ago. Officially, they have been considered to be of Orthodox faith since the 19th century, though the Evens have retained some pre-Christian practices, such as shamanism. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Siberian
Siberia ( ; , ) is an extensive geographical region comprising all of North Asia, from the Ural Mountains in the west to the Pacific Ocean in the east. It has formed a part of the sovereign territory of Russia and its predecessor states since the lengthy conquest of Siberia, which began with the fall of the Khanate of Sibir in 1582 and concluded with the annexation of Chukotka in 1778. Siberia is vast and sparsely populated, covering an area of over , but home to roughly a quarter of Russia's population. Novosibirsk, Krasnoyarsk, and Omsk are the largest cities in the area. Because Siberia is a geographic and historic concept and not a political entity, there is no single precise definition of its territorial borders. Traditionally, Siberia spans the entire expanse of land from the Ural Mountains to the Pacific Ocean, with the Ural River usually forming the southernmost portion of its western boundary, and includes most of the drainage basin of the Arctic Ocean. It is fu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kennewick Man
Kennewick Man or Ancient One was a Native American man who lived during the early Holocene, whose skeletal remains were found in 1996 washed out on a bank of the Columbia River near Kennewick, Washington. Radiocarbon tests show the man lived about 8,400 to 8,690 years Before Present, making his skeleton one of the most complete ever found this old in the Americas, and thus of high scientific interest for understanding the peopling of the Americas. The discovery precipitated a nearly twenty-year-long dispute involving the Federal government, Native Americans, and the science community. The Federal government, through the United States Army Corps of Engineers, held jurisdiction over the land where the remains were found and thus had legal custody. However, Native American tribes asserted legal rights to rebury the man under the Native American Graves Protection and Repatriation Act (NAGPRA), a federal law to repatriate Indian remains. Nevertheless, some members of the scientif ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |