|
Halite (oxyanion)
A halite, also known as a halogenite, is an oxyanion containing a halogen in a III oxidation state. It is the conjugate base of a halous acid. The known halites are chlorite The chlorite ion, or chlorine dioxide anion, is the halite with the chemical formula of . A chlorite (compound) is a compound that contains this group, with chlorine in the oxidation state of +3. Chlorites are also known as salts of chlorous ac ..., bromite, and iodite. Uses Halites can be used to generate the respective halogen dioxides via a one-electron oxidation: : 5 NaClO2 + 4 HCl → 5 NaCl + 4 + 2 H2O : + HBrO3 + H+ → 2 + H2O This reaction in particular is used in bleach to generate chlorine dioxide. Stability Chlorites tend to decompose rapidly, some even explosively, upon heating. A few bromites have been isolated, but no iodites have.Egon Wiberg, Arnold Frederick Holleman (2001) ''Inorganic Chemistry'', Elsevier References Halites {{chem ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hydrochloric Acid
Hydrochloric acid, also known as muriatic acid, is an aqueous solution of hydrogen chloride. It is a colorless solution with a distinctive pungent smell. It is classified as a strong acid. It is a component of the gastric acid in the digestive systems of most animal species, including humans. Hydrochloric acid is an important laboratory reagent and industrial chemical. History In the early tenth century, the Persian physician and alchemist Abu Bakr al-Razi ( 865–925, Latin: Rhazes) conducted experiments with sal ammoniac ( ammonium chloride) and vitriol (hydrated sulfates of various metals), which he distilled together, thus producing the gas hydrogen chloride. In doing so, al-Razi may have stumbled upon a primitive method for producing hydrochloric acid, as perhaps manifested in the following recipe from his ("The Book of Secrets"): However, it appears that in most of his experiments al-Razi disregarded the gaseous products, concentrating instead on the color c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bromine Dioxide
Bromine dioxide is the chemical compound composed of bromine and oxygen with the formula BrO2. It forms unstable yellow to yellow-orange crystals. It was first isolated by R. Schwarz and M. Schmeißer in 1937 and is hypothesized to be important in the atmospheric reaction of bromine with ozone. It is similar to chlorine dioxide, the dioxide of its halogen neighbor one period higher on the periodic table. Reactions Bromine dioxide is formed when an electric current is passed through a mixture of bromine and oxygen gases at low temperature and pressure. Bromine dioxide can also be formed by the treatment of bromine gas with ozone in trichlorofluoromethane at −50 °C. When mixed with a base, bromine dioxide gives the bromide and bromate anions: :6 BrO2 + 6 NaOH → NaBr Sodium bromide is an inorganic compound with the formula Na Br. It is a high-melting white, crystalline solid that resembles sodium chloride. It is a widely used source of the bromide ion and has man ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bromic Acid
Bromic acid, also known as hydrogen bromate, is an oxoacid with the molecular formula HBrO3. It only exists in aqueous solution.''The Merck Index: An Encyclopedia of Chemicals, Drugs, and Biologicals''. 14th Edition. 2006.''Van Nostrand's Scientific Encyclopedia''. Glenn D. Considine. Ninth Edition. Volume 1. p 554 It is a colorless solution that turns yellow at room temperature as it decomposes to bromine.Recipes for Belousov–Zhabotinsky reagents. ''J. Chem. Educ.'', 1991, 68 (4), 320. DOI10.1021/ed068p320/ref> Bromic acid and bromates are powerful oxidizing agents and are common ingredients in Belousov–Zhabotinsky reactions.The Source of the Carbon Monoxide in the Classical Belousov–Zhabotinsky Reaction. ''J. Phys. Chem. A.'', 2007, 111 (32), 7805–12 DOI10.1021/jp073512+/ref> Belousov-Zhabotinsky reactions are a classic example of non-equilibrium thermodynamics Non-equilibrium thermodynamics is a branch of thermodynamics that deals with physical systems that are not in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bromite
Bromous acid is the inorganic compound with the formula of HBrO2. It is an unstable compound, although salts of its conjugate base – bromites – have been isolated. In acidic solution, bromites decompose to bromine.Egon Wiberg, Arnold Frederick Holleman (2001) ''Inorganic Chemistry'', Elsevier Discovery In 1905, Richards A. H. proved the existence of bromous acid through a series of experiments involving silver nitrate (AgNO3) and bromine. The reaction of excess cold aqueous to form hypobromous acid (HBrO), silver bromide (AgBr) and nitric acid (HNO3): :Br2 + AgNO3 + H2O → HBrO + AgBr + HNO3 Richards discovered that the effect of adding excess liquid bromine in a concentrated silver nitrate (AgNO3) resulted in a different reaction mechanism. From numbers of equivalent portions of acid bromine formed from the previous reaction, the ratio between oxygen and bromine was calculated, with the exact value of O:Br (0.149975:0.3745), suggesting the acid compound contains two oxyg ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
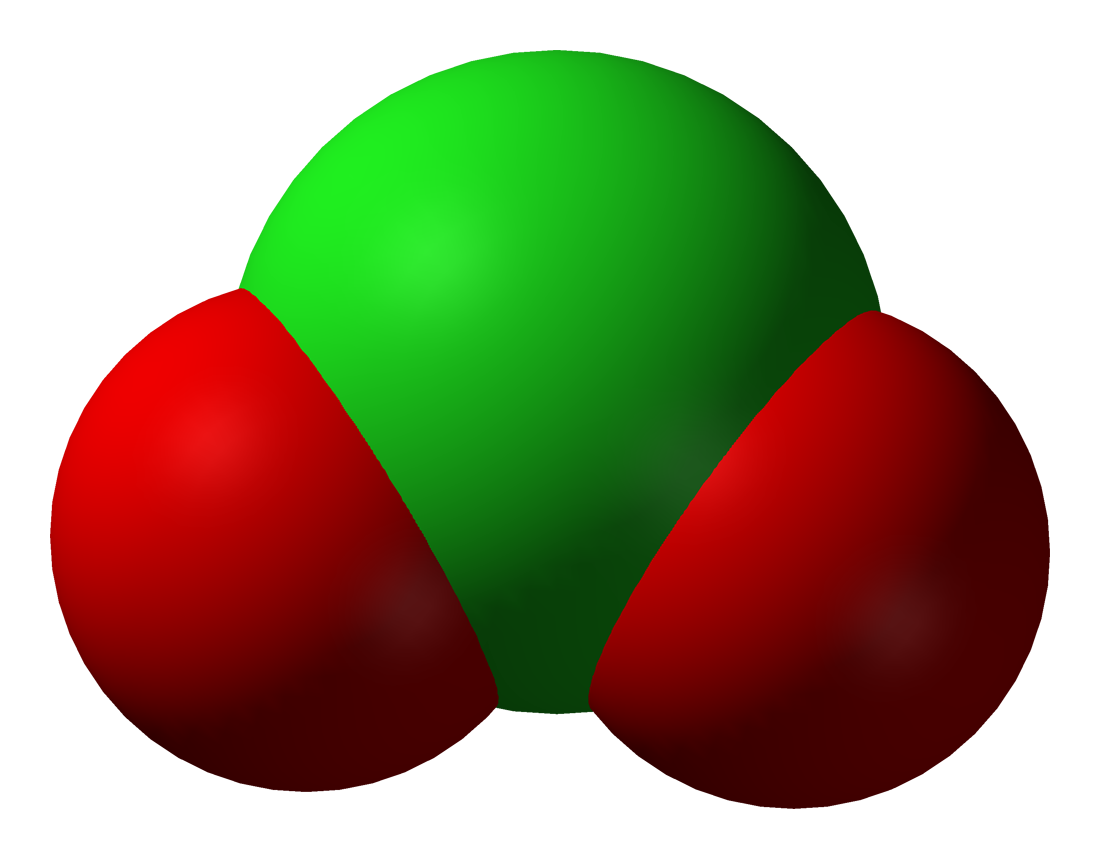
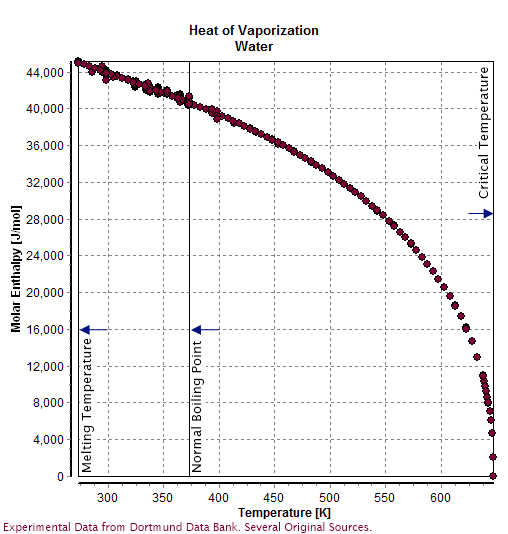
Properties Of Water
Water () is a polar inorganic compound that is at room temperature a tasteless and odorless liquid, which is nearly colorless apart from an inherent hint of blue. It is by far the most studied chemical compound and is described as the "universal solvent" and the "solvent of life". It is the most abundant substance on the surface of Earth and the only common substance to exist as a solid, liquid, and gas on Earth's surface. It is also the third most abundant molecule in the universe (behind molecular hydrogen and carbon monoxide). Water molecules form hydrogen bonds with each other and are strongly polar. This polarity allows it to dissociate ions in salts and bond to other polar substances such as alcohols and acids, thus dissolving them. Its hydrogen bonding causes its many unique properties, such as having a solid form less dense than its liquid form, a relatively high boiling point of 100 °C for its molar mass, and a high heat capacity. Water is amphoteric ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chlorine Dioxide
Chlorine dioxide is a chemical compound with the formula ClO2 that exists as yellowish-green gas above 11 °C, a reddish-brown liquid between 11 °C and −59 °C, and as bright orange crystals below −59 °C. It is usually handled as an aqueous solution. It is also commonly used as a bleach. More recent developments have extended its applications in food processing and as a disinfectant. Structure and bonding The molecule ClO2 has an odd number of valence electrons, and therefore, it is a paramagnetic radical. It is an unusual "example of an odd-electron molecule which is stable towards dimerization" (nitric oxide being another example). In 1933, Lawrence O. Brockway, a graduate student of Linus Pauling, proposed a structure that involved a three-electron bond and two single bonds. However, Pauling in his ''General Chemistry'' shows a double bond to one oxygen and a single bond plus a three-electron bond to the other. The valence bond structu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sodium Chloride
Sodium chloride , commonly known as salt (although sea salt also contains other chemical salts), is an ionic compound with the chemical formula NaCl, representing a 1:1 ratio of sodium and chloride ions. With molar masses of 22.99 and 35.45 g/mol respectively, 100 g of NaCl contains 39.34 g Na and 60.66 g Cl. Sodium chloride is the salt most responsible for the salinity of seawater and of the extracellular fluid of many multicellular organisms. In its edible form, salt (also known as '' table salt'') is commonly used as a condiment and food preservative. Large quantities of sodium chloride are used in many industrial processes, and it is a major source of sodium and chlorine compounds used as feedstocks for further chemical syntheses. Another major application of sodium chloride is de-icing of roadways in sub-freezing weather. Uses In addition to the familiar domestic uses of salt, more dominant applications of the approximately 250 million tonnes per year productio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sodium Chlorite
Sodium chlorite (NaClO2) is a chemical compound used in the manufacturing of paper and as a disinfectant. Use The main application of sodium chlorite is the generation of chlorine dioxide for bleaching and stripping of textiles, pulp, and paper. It is also used for disinfection of municipal water treatment plants after conversion to chlorine dioxide. An advantage in this application, as compared to the more commonly used chlorine, is that trihalomethanes (such as chloroform) are not produced from organic contaminants. Chlorine dioxide generated from sodium chlorite is approved by FDA under some conditions for disinfecting water used to wash fruits, vegetables, and poultry. Sodium chlorite, NaClO2, sometimes in combination with zinc chloride, also finds application as a component in therapeutic rinses, mouthwashes, toothpastes and gels, mouth sprays, as preservative in eye drops, and in contact lens cleaning solution under the trade name Purite. It is also used for sanitizi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oxyanion
An oxyanion, or oxoanion, is an ion with the generic formula (where A represents a chemical element and O represents an oxygen atom). Oxyanions are formed by a large majority of the chemical elements. The formulae of simple oxyanions are determined by the octet rule. The corresponding oxyacid of an oxyanion is the compound . The structures of condensed oxyanions can be rationalized in terms of AO''n'' polyhedral units with sharing of corners or edges between polyhedra. The oxyanions (specifically, phosphate and polyphosphate esters) adenosine monophosphate ( AMP), adenosine diphosphate (ADP) and adenosine triphosphate (ATP) are important in biology. Monomeric oxyanions The formula of monomeric oxyanions, , is dictated by the oxidation state of the element A and its position in the periodic table. Elements of the first row are limited to a maximum coordination number of 4. However, none of the first row elements has a monomeric oxyanion with that coordination number. Instead, ca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Iodite
The iodite ion, or iodine dioxide anion, is the halite with the chemical formula . Within the ion the Iodine exists in the oxidation state of +3. Iodite anion Iodites (including iodous acid) are highly unstable and have been observed but never isolated. They will rapidly disproportionate to molecular Iodine and Iodates. However, they have been detected as intermediates in the conversion between iodide and iodate. Iodous acid Iodous acid is acid form of the iodite ion, with the formula HIO2. Other oxyanions Iodine can assume oxidation state In chemistry, the oxidation state, or oxidation number, is the hypothetical charge of an atom if all of its bonds to different atoms were fully ionic. It describes the degree of oxidation (loss of electrons) of an atom in a chemical compound. ...s of −1, +1, +3, +5, or +7. A number of neutral iodine oxides are also known. References {{reflist Iodine oxyanions Oxygen compounds Halites ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bromite
Bromous acid is the inorganic compound with the formula of HBrO2. It is an unstable compound, although salts of its conjugate base – bromites – have been isolated. In acidic solution, bromites decompose to bromine.Egon Wiberg, Arnold Frederick Holleman (2001) ''Inorganic Chemistry'', Elsevier Discovery In 1905, Richards A. H. proved the existence of bromous acid through a series of experiments involving silver nitrate (AgNO3) and bromine. The reaction of excess cold aqueous to form hypobromous acid (HBrO), silver bromide (AgBr) and nitric acid (HNO3): :Br2 + AgNO3 + H2O → HBrO + AgBr + HNO3 Richards discovered that the effect of adding excess liquid bromine in a concentrated silver nitrate (AgNO3) resulted in a different reaction mechanism. From numbers of equivalent portions of acid bromine formed from the previous reaction, the ratio between oxygen and bromine was calculated, with the exact value of O:Br (0.149975:0.3745), suggesting the acid compound contains two oxyg ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |