Halite (oxyanion) on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
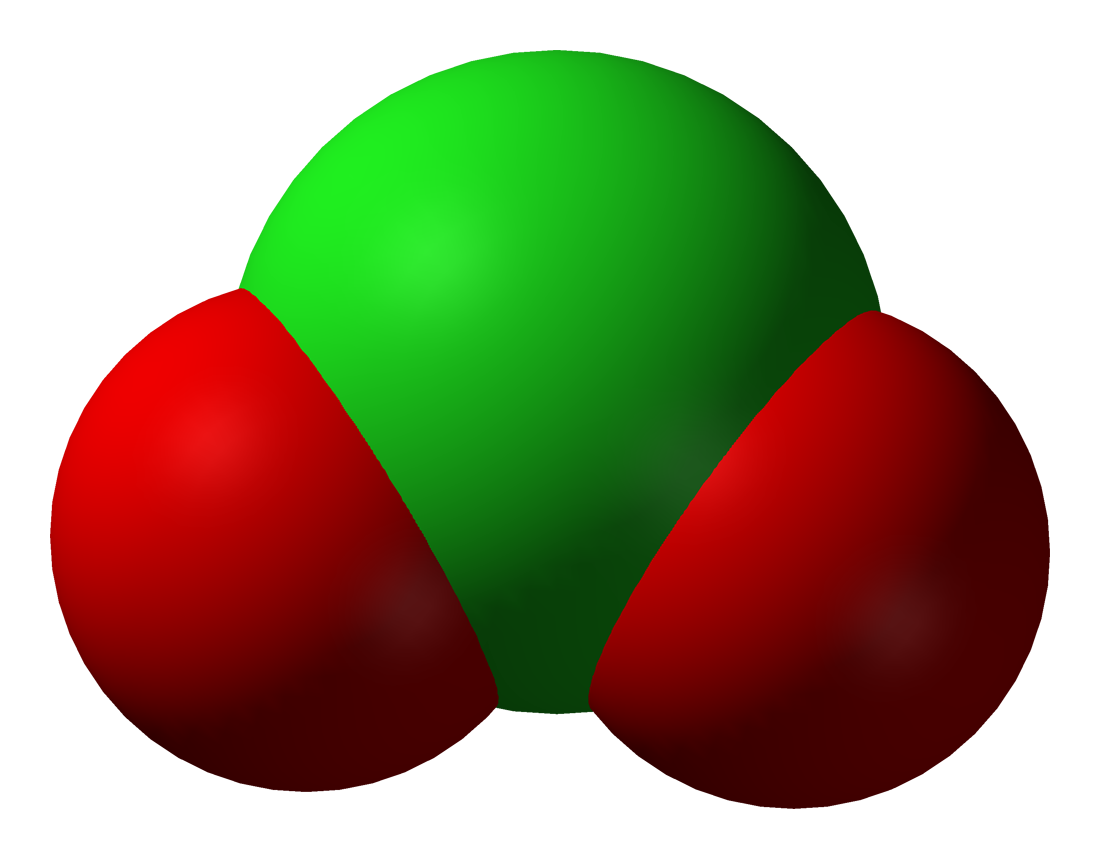 A halite, also known as a halogenite, is an
A halite, also known as a halogenite, is an
 A halite, also known as a halogenite, is an
A halite, also known as a halogenite, is an oxyanion An oxyanion, or oxoanion, is an ion with the generic formula (where A represents a chemical element and O represents an oxygen atom). Oxyanions are formed by a large majority of the chemical elements. The formulae of simple oxyanions are determine ...
containing a halogen
The halogens () are a group in the periodic table consisting of six chemically related elements: fluorine (F), chlorine (Cl), bromine (Br), iodine (I), and the radioactive elements astatine (At) and tennessine (Ts), though some authors would ...
in a +3 oxidation state
In chemistry, the oxidation state, or oxidation number, is the hypothetical Electrical charge, charge of an atom if all of its Chemical bond, bonds to other atoms are fully Ionic bond, ionic. It describes the degree of oxidation (loss of electrons ...
. It is the conjugate base of a halous acid. The known halites are chlorite
The chlorite ion, or chlorine dioxide anion, is the halite (oxyanion), halite with the chemical formula of . A chlorite (compound) is a compound that contains this group, with chlorine in the oxidation state of +3. Chlorites are also known as s ...
, bromite, and iodite.
Uses
Halites can be used to generate the respective halogen dioxides via a one-electron oxidation: : 5 NaClO2 + 4 HCl → 5 NaCl + 4 + 2 H2O : + HBrO3 + H+ → 2 + H2O This reaction in particular is used in bleach to generatechlorine dioxide
Chlorine dioxide is a chemical compound with the formula ClO2 that exists as yellowish-green gas above 11 °C, a reddish-brown liquid between 11 °C and −59 °C, and as bright orange crystals below −59 °C. It is usually ...
.
Stability
Chlorites tend to decompose rapidly, some even explosively, upon heating. A few bromites have been isolated, but no iodites have.Egon Wiberg, Arnold Frederick Holleman (2001) ''Inorganic Chemistry'', ElsevierReferences
{{chem-compound-stub