|
Haematin
Haematin (also known as hematin, ferriheme, hematosin, hydroxyhemin, oxyheme, phenodin, or oxyhemochromogen) is a dark bluish or brownish pigment containing iron in the ferric state, obtained by the oxidation of haem. Haematin inhibits the synthesis of porphyrin (by repressing ALAS1 synthesis), and stimulates the synthesis of globin. For this reason, it is used in the treatment of porphyrias. It is a component of cytochromes and peroxidases Peroxidases or peroxide reductases ( EC numberbr>1.11.1.x are a large group of enzymes which play a role in various biological processes. They are named after the fact that they commonly break up peroxides, and should not be confused with other .... Haematin derived synthetically from hemin is used as a reagent. References Iron(III) compounds Pigments {{organic-compound-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Haem
Heme (American English), or haem (Commonwealth English, both pronounced / hi:m/ ), is a ring-shaped iron-containing molecule that commonly serves as a ligand of various proteins, more notably as a component of hemoglobin, which is necessary to bind oxygen in the bloodstream. It is composed of four pyrrole rings with 2 vinyl and 2 propionic acid side chains. Heme is biosynthesized in both the bone marrow and the liver. Heme plays a critical role in multiple different redox reactions in mammals, due to its ability to carry the oxygen molecule. Reactions include oxidative metabolism (cytochrome c oxidase, succinate dehydrogenase), xenobiotic detoxification via cytochrome P450 pathways (including metabolism of some drugs), gas sensing ( guanyl cyclases, nitric oxide synthase), and microRNA processing (DGCR8). Heme is a coordination complex "consisting of an iron ion coordinated to a tetrapyrrole acting as a tetradentate ligand, and to one or two axial ligands". The definition is lo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Porphyrin
Porphyrins ( ) are heterocyclic, macrocyclic, organic compounds, composed of four modified pyrrole subunits interconnected at their α carbon atoms via methine bridges (). In vertebrates, an essential member of the porphyrin group is heme, which is a component of hemoproteins, whose functions include carrying oxygen in the bloodstream. In plants, an essential porphyrin derivative is chlorophyll, which is involved in light harvesting and electron transfer in photosynthesis. The parent of porphyrins is porphine, a rare chemical compound of exclusively theoretical interest. Substituted porphines are called porphyrins. With a total of 26 π-electrons the porphyrin ring structure is a coordinated aromatic system. One result of the large conjugated system is that porphyrins absorb strongly in the visible region of the electromagnetic spectrum, i.e. they are deeply colored. The name "porphyrin" derives . Structure Porphyrin complexes consist of a square planar MN4 core. The p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Globin
The globins are a superfamily of heme-containing globular proteins, involved in binding and/or transporting oxygen. These proteins all incorporate the globin fold, a series of eight alpha helical segments. Two prominent members include myoglobin and hemoglobin. Both of these proteins reversibly bind oxygen via a heme prosthetic group. They are widely distributed in many organisms. Structure Globin superfamily members share a common three-dimensional fold. This 'globin fold' typically consists of eight alpha helices, although some proteins have additional helix extensions at their termini. Since the globin fold contains only helices, it is classified as an all-alpha protein fold. The globin fold is found in its namesake globin families as well as in phycocyanins. The globin fold was thus the first protein fold discovered (myoglobin was the first protein whose structure was solved). Helix packaging The eight helices of the globin fold core share significant nonlocal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
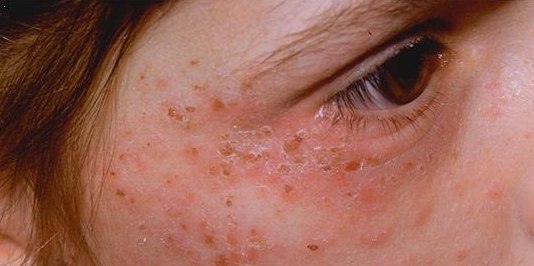
Porphyria
Porphyria ( or ) is a group of disorders in which substances called porphyrins build up in the body, adversely affecting the skin or nervous system. The types that affect the nervous system are also known as Porphyria#Acute porphyrias, acute porphyria, as symptoms are rapid in onset and short in duration. Symptoms of an attack include abdominal pain, chest pain, vomiting, confusion, constipation, fever, hypertension, high blood pressure, and tachycardia, high heart rate. The attacks usually last for days to weeks. Complications may include paralysis, hyponatraemia, low blood sodium levels, and seizures. Attacks may be triggered by Alcohol (drug), alcohol, smoking, hormonal changes, fasting, stress, or certain medications. If the skin is affected, blisters or itching may occur with sunlight exposure. Most types of porphyria are inherited from one or both of a person's parents and are due to a mutation in one of the genes that make heme. They may be inherited in an autosomal dom ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cytochrome
Cytochromes are redox-active proteins containing a heme, with a central iron (Fe) atom at its core, as a cofactor. They are involved in the electron transport chain and redox catalysis. They are classified according to the type of heme and its mode of binding. Four varieties are recognized by the International Union of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology (IUBMB), cytochromes a, cytochromes b, cytochromes c and cytochrome d. Cytochrome function is linked to the reversible redox change from ferrous (Fe(II)) to the ferric (Fe(III)) oxidation state of the iron found in the heme core. In addition to the classification by the IUBMB into four cytochrome classes, several additional classifications such as cytochrome o and cytochrome P450 can be found in biochemical literature. History Cytochromes were initially described in 1884 by Charles Alexander MacMunn as respiratory pigments (myohematin or histohematin). In the 1920s, Keilin rediscovered these respiratory pigments and na ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Peroxidase
Peroxidases or peroxide reductases ( EC numberbr>1.11.1.x are a large group of enzymes which play a role in various biological processes. They are named after the fact that they commonly break up peroxides, and should not be confused with other enzymes that ''produce'' peroxide, which are often oxidases. Functionality Peroxidases typically catalyze a reaction of the form: :ROOR' + \overset + 2H+ -> ce + R'OH Optimal substrates For many of these enzymes the optimal substrate is hydrogen peroxide, but others are more active with organic hydroperoxides such as lipid peroxides. Peroxidases can contain a heme cofactor in their active sites, or alternately redox-active cysteine or selenocysteine residues. The nature of the electron donor is very dependent on the structure of the enzyme. * For example, horseradish peroxidase can use a variety of organic compounds as electron donors and acceptors. Horseradish peroxidase has an accessible active site, and many compounds can re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Iron(III) Compounds
Iron is a chemical element; it has symbol Fe () and atomic number 26. It is a metal that belongs to the first transition series and group 8 of the periodic table. It is, by mass, the most common element on Earth, forming much of Earth's outer and inner core. It is the fourth most abundant element in the Earth's crust, being mainly deposited by meteorites in its metallic state. Extracting usable metal from iron ores requires kilns or furnaces capable of reaching , about 500 °C (900 °F) higher than that required to smelt copper. Humans started to master that process in Eurasia during the 2nd millennium BC and the use of iron tools and weapons began to displace copper alloys – in some regions, only around 1200 BC. That event is considered the transition from the Bronze Age to the Iron Age. In the modern world, iron alloys, such as steel, stainless steel, cast iron and special steels, are by far the most common industrial metals, due to their mechanical proper ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |