|
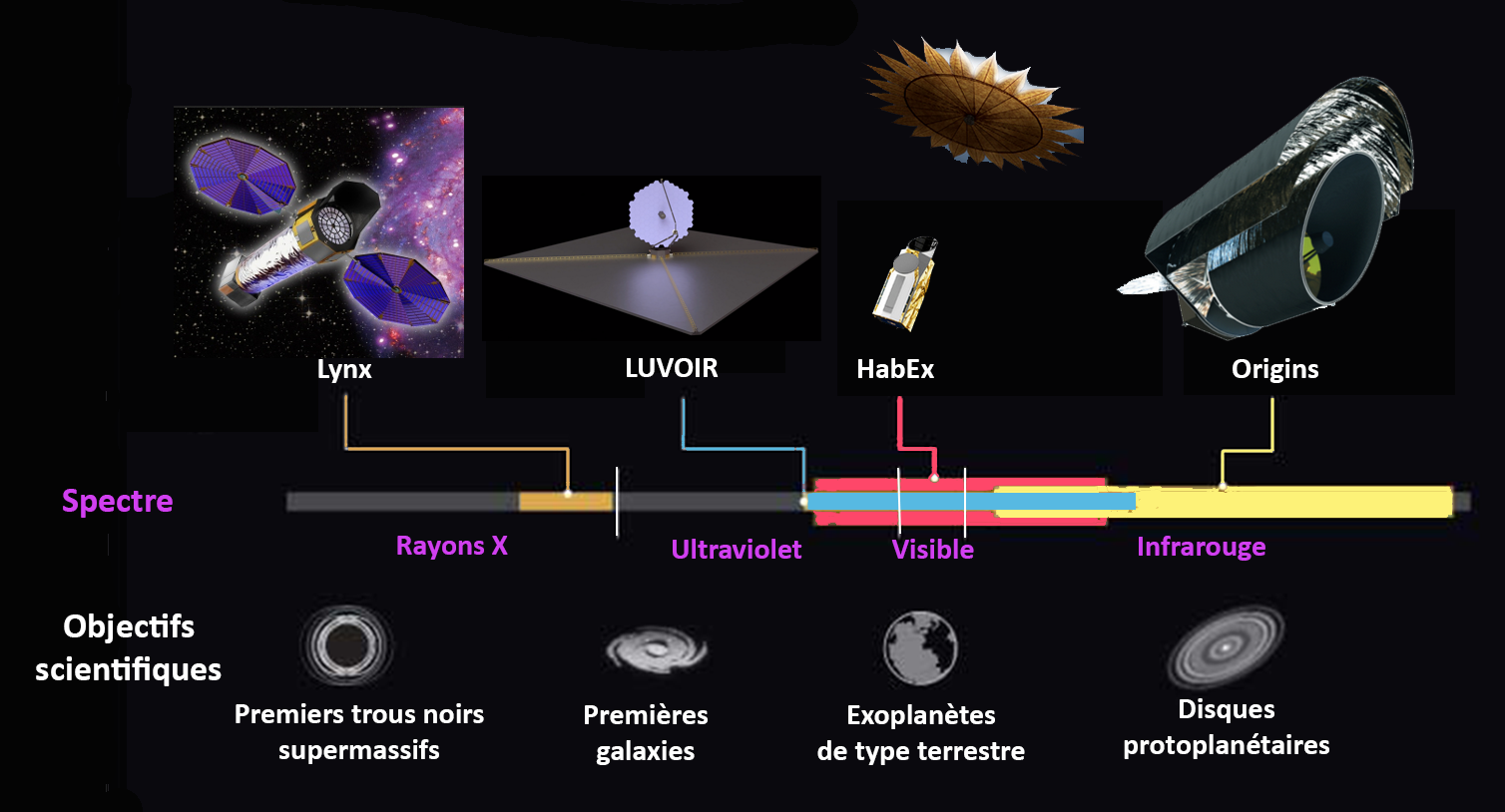
Habitable Exoplanets Observatory
The Habitable Exoplanet Observatory (HabEx) is a space telescope concept that would be optimized to search for and image Earth-size Planetary habitability, habitable exoplanets in the Circumstellar habitable zone, habitable zones of their stars, where Extraterrestrial liquid water, liquid water can exist. HabEx would aim to understand how common Terrestrial planet, terrestrial worlds beyond the Solar System may be and determine the range of their characteristics. It would be an optical, Ultraviolet, UV and infrared telescope that would also use Astronomical spectroscopy, spectrographs to study planetary atmospheres and eclipse starlight with either an internal coronagraph or an external New Worlds Mission, starshade. The proposal, first made in 2016, is for a large strategic science missions NASA mission. It would operate at the Lagrange point, Lagrange point L2. In January 2023, a new space telescope concept was proposed called the Habitable Worlds Observatory (HWO), which draw ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Space Observatory
A space telescope (also known as space observatory) is a telescope in outer space used to observe astronomical objects. Suggested by Lyman Spitzer in 1946, the first operational telescopes were the American Orbiting Astronomical Observatory, OAO-2 launched in 1968, and the Soviet Orion (space telescope), Orion 1 ultraviolet telescope aboard space station Salyut 1 in 1971. Space telescopes avoid several problems caused by the atmosphere, including the absorption or scattering of certain wavelengths of light, obstruction by clouds, and distortions due to atmospheric refraction such as twinkling. Space telescopes can also observe dim objects during the daytime, and they avoid light pollution which Observatory#Ground-based observatories, ground-based observatories encounter. They are divided into two types: Satellites which map the entire sky (astronomical survey), and satellites which focus on selected astronomical objects or parts of the sky and beyond. Space telescopes are distinct ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Starlight
Starlight is the light emitted by stars. It typically refers to visible electromagnetic radiation from stars other than the Sun, observable from Earth at night, although a component of starlight is observable from Earth during daytime. Sunlight is the term used for the Sun's starlight observed during daytime. During nighttime, albedo describes solar reflections from other Solar System objects, including moonlight, planetshine, and zodiacal light. Observation Observation and measurement of starlight through telescopes is the basis for many fields of astronomy, including photometry and stellar spectroscopy. Hipparchus did not have a telescope or any instrument that could measure apparent brightness accurately, so he simply made estimates with his eyes. He sorted the stars into six brightness categories, which he called magnitudes.''Astronomy''. https://d3bxy9euw4e147.cloudfront.net/oscms-prodcms/media/documents/Astronomy-Draft-20160817.pdf: Rice University. 2016. p. 761. - v ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Extraterrestrial Atmosphere
The study of extraterrestrial atmospheres is an active field of research, both as an aspect of astronomy and to gain insight into Earth's atmosphere. In addition to Earth, many of the other astronomical objects in the Solar System have atmospheres. These include all the giant planets, as well as Atmosphere of Mars, Mars, Atmosphere of Venus, Venus and Titan (moon), Titan. Several Natural satellite, moons and other bodies also have atmospheres, as do comets and the Sun. There is evidence that extrasolar planets can have an atmosphere. Comparisons of these atmospheres to one another and to Earth's atmosphere broaden our basic understanding of atmospheric processes such as the greenhouse effect, aerosol and cloud physics, and atmospheric chemistry and dynamics. In September 2022, astronomers were reported to have formed a new group, called "Categorizing Atmospheric Technosignatures" (CATS), to list the results of exoplanet atmosphere studies for biosignatures, technosignatures and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Planetary Science Decadal Survey
The Planetary Science Decadal Survey is a serial publication of the United States National Research Council produced for NASA and other United States Government Agencies such as the National Science Foundation.National Academy of Sciences, National Academies Press, http://www.nap.edu/download.php?record_id=13117 , ''Vision and Voyages for Planetary Science in the Decade 2013–2022'', 2011; . Retrieved February 23, 2015 The documents identify key questions facing planetary science and outlines recommendations for space and ground-based exploration ten years into the future. Missions to gather data to answer these big questions are described and prioritized, where appropriate. Similar decadal surveys cover astronomy and astrophysics, earth science, and heliophysics. As of 2022 there have been three "Decadals", one published in April 2002 for the decade from 2003 to 2013, one published on March 7, 2011 for the decade from 2013 to 2022, and one published on April 19, 2022 for the de ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
National Academy Of Sciences
The National Academy of Sciences (NAS) is a United States nonprofit, NGO, non-governmental organization. NAS is part of the National Academies of Sciences, Engineering, and Medicine, along with the National Academy of Engineering (NAE) and the National Academy of Medicine (NAM). As a national academy, new members of the organization are elected annually by current members, based on their distinguished and continuing achievements in original research. Election to the National Academy is one of the highest honors in the scientific field in the United States. Member of the National Academy of Sciences, Members of the National Academy of Sciences serve ''pro bono'' as "advisers to the nation" on science, engineering, and medicine. The group holds a congressional charter under Title 36 of the United States Code. Congress legislated and President Abraham Lincoln signed an Act of Congress (1863) establishing the National Academy of Sciences as an independent, trusted nongovernmen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lynx X-ray Observatory
The Lynx X-ray Observatory (''Lynx'') is a NASA-funded Large strategic science missions, Large Mission Concept Study commissioned as part of the National Academy of Sciences 2020 Astronomy and Astrophysics Decadal Survey. The concept study phase is complete as of August 2019, and the ''Lynx'' final report has been submitted to the Decadal Survey for prioritization. If launched, ''Lynx'' would be the most powerful X-ray astronomy observatory constructed to date, enabling order-of-magnitude advances in capability over the current Chandra X-ray Observatory and XMM-Newton space telescopes. Background In 2016, following recommendations laid out in the so-called Enduring Quests and Daring Visions, Astrophysics Roadmap of 2013, NASA established four space telescope concept studies for future Large strategic science missions. In addition to ''Lynx'' (originally called X-ray Surveyor in thRoadmap document'','' they are the Habitable Exoplanet Imaging Mission (HabEx), the Large Ultra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Origins Space Telescope
Origins Space Telescope (''Origins'') is a concept study for a far-infrared survey space telescope mission.Preparing for the 2020 Decadal Survey Large Mission Concepts (PDF) Paul Hertz, NASA A preliminary concept in pre-formulation, it was presented to the in 2019 for a possible selection to N ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nancy Grace Roman Space Telescope
The Nancy Grace Roman Space Telescope (shortened as the Roman Space Telescope, Roman, or RST) is a NASA infrared space telescope in development and scheduled to launch to a Sun–Earth L2 orbit by May 2027. It is named after former NASA Chief of Astronomy Nancy Grace Roman. The Roman Space Telescope is based on an existing wide field of view primary mirror and will carry two scientific instruments. The Wide-Field Instrument (WFI) is a 300.8-megapixel multi-band visible and near-infrared camera, providing a sharpness of images comparable to that achieved by the Hubble Space Telescope over a 0.28 square degree field of view, 100 times larger than imaging cameras on the Hubble. The Coronagraphic Instrument (CGI) is a high-contrast, small field of view camera and spectrometer covering visible and near-infrared wavelengths using novel starlight-suppression technology. Stated objectives include a search for extra-solar planets using gravitational microlensing, along wi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
James Webb Space Telescope
The James Webb Space Telescope (JWST) is a space telescope designed to conduct infrared astronomy. As the largest telescope in space, it is equipped with high-resolution and high-sensitivity instruments, allowing it to view objects too old, List of the most distant astronomical objects, distant, or faint for the Hubble Space Telescope. This enables investigations across many fields of astronomy and cosmology, such as observation of the Population III star, first stars and the Galaxy formation and evolution, formation of the first galaxies, and detailed atmospheric characterization of potentially habitable exoplanets. Although the Webb's mirror diameter is 2.7 times larger than that of the Hubble Space Telescope, it produces images of comparable optical resolution, resolution because it observes in the longer-wavelength infrared spectrum. The longer the wavelength of the spectrum, the larger the information-gathering surface required (mirrors in the infrared spectrum or antenna a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Large Strategic Science Missions
NASA's large strategic science missions or large strategic missions, formerly known as Flagship missions or Flagship-class missions, are the costliest and most capable NASA science spacecraft. Flagship missions exist within all four divisions of NASA's Science Mission Directorate (SMD): the astrophysics, Earth science, heliophysics and planetary science divisions. "Large" refers to the budget of each mission, typically the most expensive mission in the scientific discipline. Within the Astrophysics Division and the Planetary Science Division, the large strategic missions are usually in excess of US$1 billion. Within Earth Science Division and Heliophysics Division, the large strategic missions are usually in excess of US$500 million.Powering Science: NASA's Large Strategic Science Missions (20 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Large Ultraviolet Optical Infrared Surveyor
The Large Ultraviolet Optical Infrared Surveyor, commonly known as LUVOIR (), is a multi-wavelength space telescope concept being developed by NASA under the leadership of a Science and Technology Definition Team. It is one of four large astrophysics space mission concepts studied in preparation for the National Academy of Sciences 2020 Astronomy and Astrophysics Decadal Survey. While LUVOIR is a concept for a general-purpose observatory, it has the key science goal of characterizing a wide range of exoplanets, including those that might be habitable. An additional goal is to enable a broad range of astrophysics, from the reionization epoch, through galaxy formation and evolution, to star and planet formation. Powerful imaging and spectroscopy observations of Solar System bodies would also be possible. LUVOIR would be a Large Strategic Science Mission and was considered for a development start sometime in the 2020s. The LUVOIR Study Team, under Study Scientist Aki Roberge, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |