|
Gustavus Adolphus Golden Gusties
Gustavus Adolphus College ( ) is a private liberal arts college in St. Peter, Minnesota, United States. It was founded in 1862 by Swedish Americans led by Eric Norelius and is affiliated with the Evangelical Lutheran Church in America. Gustavus was named for Gustavus Adolphus, the Monarchy of Sweden, King of Sweden from 1611 to 1632. Its residential campus includes a 125-acre arboretum. History Founding in 1862, Eric Norelius founded the college's predecessor, a Lutheran parochial school in Red Wing. It offered classes for grade-school children; collegiate courses were not offered until nearly a decade later, but the college uses the earlier date as the year it was founded. Originally named Minnesota Elementarskola (''elementary school'' in Swedish), it moved the following year to East Union, an unincorporated town in Dahlgren Township. In 1865, on the 1,000th anniversary of the death of St. Ansgar, known as the "Apostle of the North", the institution was renamed and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Private College
Private universities and private colleges are higher education institutions not operated, owned, or institutionally funded by governments. However, they often receive tax breaks, public student loans, and government grants. Depending on the country, private universities may be subject to government regulations. Private universities may be contrasted with public universities and national universities which are either operated, owned or institutionally funded by governments. Additionally, many private universities operate as nonprofit organizations. Across the world, different countries have different regulations regarding accreditation for private universities and as such, private universities are more common in some countries than in others. Some countries do not have any private universities at all. Africa Egypt Egypt currently has 21 public universities with about two million students and 23 private universities with 60,000 students. Egypt has many private universities in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dahlgren Township, Carver County, Minnesota
Dahlgren Township is a rural township in Carver County, Minnesota, United States. The township's economy is based on commercial agriculture around dairying, livestock and cash grain farming. The population was 854 as of the 2020 census. History Dahlgren Township was organized in 1864, and named for John A. Dahlgren, a United States Navy admiral. Geography According to the United States Census Bureau, the township has a total area of , of which is land and (1.22%) is water. The west edge of the city of Carver is located within the township geographically but is a separate entity. Township 115 North, Range 24 West, Fifth Principal Meridian of the Public Land Survey System. Lakes * Ave Lake * E Union Lake * Gaystock Lake * Maria Lake (northeast quarter) * Miller Lake Adjacent townships * Laketown Township (north) * San Francisco Township (south) * Hancock Township (southwest) * Benton Township (west) * Waconia Township (northwest) Unincorporated communities * Augus ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Uppsala University
Uppsala University (UU) () is a public university, public research university in Uppsala, Sweden. Founded in 1477, it is the List of universities in Sweden, oldest university in Sweden and the Nordic countries still in operation. Initially founded in the 15th century, the university rose to significance during the rise of Swedish Empire, Sweden as a great power at the end of the 16th century and was then given relative financial stability with a large donation from Monarchy of Sweden, King Gustavus Adolphus of Sweden, Gustavus Adolphus in the early 17th century. Uppsala also has an important historical place in Swedish national culture, and national identity, identity for the Swedish establishment: in historiography, religion, literature, politics, and music. Many aspects of Swedish academic culture in general, such as the white student cap, originated in Uppsala. It shares some peculiarities, such as the student nation system, with Lund University and the University of Helsink ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jack Ohle
Jack Ohle (pronounced OH-lee) was the President of Gustavus Adolphus College from July 2008 to June 2014. He was previously the President of Wartburg College in Waverly, Iowa, from 1998. Both institutions are part of the Evangelical Lutheran Church in America (ECLA) Colleges and Universities, and Ohle has chaired the executive committee of the Council of Presidents of ELCA Colleges and Universities. Professional appointments Ohle graduated from Ohio Northern University with a Bachelor of Arts in social work in 1969. After completing some graduate work at Hamma School of Theology, Ohle earned a Master of Arts degree in higher education administration from Bowling Green State University. After completing his MA, he went on administrative positions at Ohio Northern University and Muskingum College. Afterward, he became vice president for advancement at Nebraska Wesleyan University where he worked for ten years. He then worked as vice president for institutional advancement and late ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
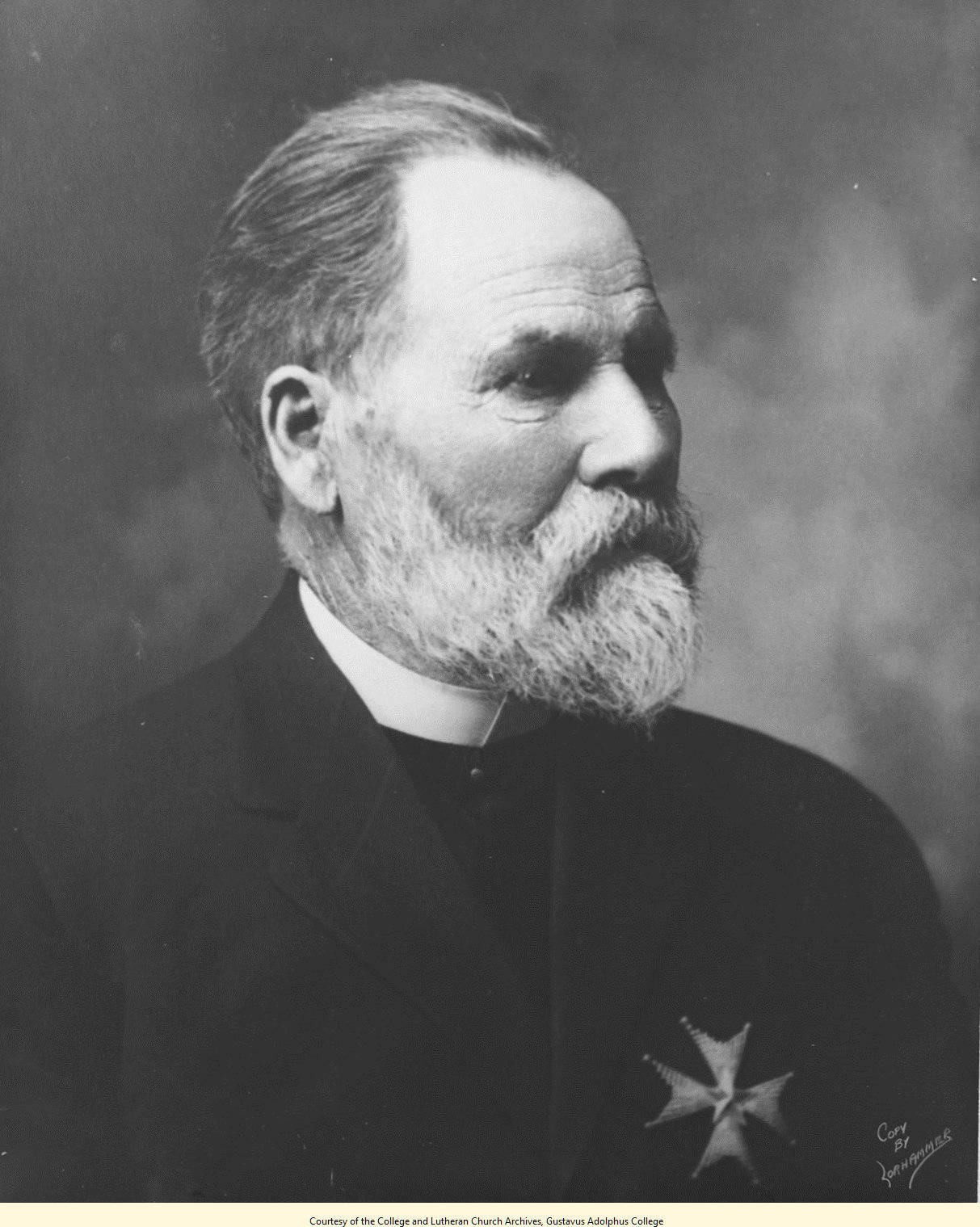
Andrew Jackson (pastor)
Andrew Jackson (February 11, 1828 – July 23, 1901) was a Swedish-American Lutheran minister who served as president of the Minnesota Conference of the Augustana Evangelical Lutheran Church. Biography Andrew Jackson was born to Olaf Jakobson and Petronella Olofsdotter in the parish of Valla on the island of Tjörn in the province of Bohuslän, Sweden. Jackson had 11 siblings: seven brothers and four sisters. His education began at formal school in Marstrand in Västra Götaland and from there he attended high school and college in Gothenborg, Gothenborg, Sweden. During school vacations he worked as a private tutor, and while working for one of his clients, Captain Klase, he was inspired and encouraged to go to sea in 1852. He boarded a ship bound for New York City, but upon arrival there deserted his ship to sign on with another crew. He had signed on under the common Swedish surname Dahlin, but subsequently changed his last name to Jackson. H later took a train to Galesburg, I ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nobel Laureates
The Nobel Prizes (, ) are awarded annually by the Royal Swedish Academy of Sciences, the Swedish Academy, the Karolinska Institutet, and the Norwegian Nobel Committee to individuals and organizations who make outstanding contributions in the fields of chemistry, physics, literature, peace, and physiology or medicine. They were established by the 1895 will of Alfred Nobel, which dictates that the awards should be administered by the Nobel Foundation. An additional prize in memory of Alfred Nobel was established in 1968 by Sveriges Riksbank (Sweden's central bank) for outstanding contributions to the field of economics. Each recipient, a Nobelist or '' laureate'', receives a gold medal, a diploma, and a sum of money which is decided annually by the Nobel Foundation. Prize Different organisations are responsible for awarding the individual prizes; the Royal Swedish Academy of Sciences awards the Prizes in Physics, Chemistry, and Economics; the Swedish Academy awards the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alfred Nobel
Alfred Bernhard Nobel ( ; ; 21 October 1833 – 10 December 1896) was a Swedish chemist, inventor, engineer, and businessman. He is known for inventing dynamite, as well as having bequeathed his fortune to establish the Nobel Prizes. He also made several other important contributions to science, holding 355 patents during his life. Born into the prominent Nobel family in Stockholm, Nobel displayed an early aptitude for science and learning, particularly in chemistry and languages; he became fluent in six languages and filed his first patent at the age of 24. He embarked on many business ventures with his family, most notably owning the company Bofors, which was an iron and steel producer that he had developed into a major manufacturer of cannons and other armaments. Nobel's most famous invention, dynamite, was an explosive made using nitroglycerin, which was patented in 1867. He further invented gelignite in 1875 and ballistite in 1887. Upon his death, Nobel donated his fortun ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nobel Foundation
The Nobel Foundation () is a private institution founded on 29 June 1900 to manage the finances and administration of the Nobel Prizes. The foundation is based on the last will of Alfred Nobel, the inventor of dynamite. It also holds Nobel Symposia on important breakthroughs in science and topics of cultural or social significance. History Alfred Nobel (; born 21 October 1833, in Stockholm, Sweden) was a chemist, engineer, innovator, armaments manufacturer and the inventor of dynamite. He owned Bofors, a major armaments manufacturer, which he had redirected from its original business as an iron and steel mill. Nobel held 355 different patents, dynamite being the most famous. Nobel amassed a sizeable personal fortune during his lifetime, thanks mostly to this invention. In 1896 Nobel died of a stroke in his villa in Sanremo, San Remo, Italy where he had lived his final years.AFP"Alfred Nobel's last will and testament", ''The Local''(5 October 2009): accessed 14 January 2009. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nobel Conference
The Nobel Conference is an academic conference held annually at Gustavus Adolphus College in St. Peter, Minnesota. Founded in 1963, the conference links a general audience with scientists with topics related to the natural and social sciences. The conference is open to the general public. History Gustavus Adolphus College was founded by Swedish immigrants in 1862 and throughout its history, has continued to honor its Swedish heritage. As the College prepared to build a new science hall in the early 1960s, College officials asked the Nobel Foundation for permission to name the building the Alfred Nobel Hall of Science as a memorial to the great Swedish inventor and philanthropist. Permission was granted, and the facility's dedication ceremony in 1963 included 26 Nobel laureates and officials from the Nobel Foundation. Following the 1963 Nobel Prize ceremonies in Stockholm, College representatives met with Nobel Foundation officials, asking them to endorse an annual science confe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
V-12 Navy College Training Program
The V-12 Navy College Training Program was designed to supplement the force of commissioned officers in the United States Navy during World War II. Between July 1, 1943, and June 30, 1946, more than 125,000 participants were enrolled in 131 colleges and universities in the United States. Numerous participants attended classes and lectures at their respective colleges and earned completion degrees for their studies. Some even returned from their naval obligations to earn a degree from the colleges where they were previously stationed. The V-12 program's goal was to produce officers, not unlike the Army Specialized Training Program (ASTP), which sought to turn out more than 200,000 technically trained personnel in such fields as engineering, foreign languages, and medicine. Running from 1942 to 1944, the ASTP recruits were expected but not required to become officers at the end of their training. History The V-12 program was founded to generate a large number of officers for both t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lutheran Church In America
The Lutheran Church in America (LCA) was an American and Canadian Lutheran church body that existed from 1962 to 1987. It was headquartered in New York City and its publishing house was Fortress Press. The LCA's immigrant heritage came mostly from Germany, Sweden, present-day Czech Republic, present-day Slovakia, Denmark, and Finland, and its demographic focus was on the East Coast (centered on Pennsylvania), with large numbers in the Midwest and some presence in the Southern Atlantic states. Theologically, the LCA was often considered the most liberal and ecumenical branch in American Lutheranism, although there were tendencies toward conservative pietism in some rural and small-town congregations. In church governance, the LCA was clerical and centralized, in contrast to the congregationalist or "low church" strain in American Protestant Christianity. With some notable exceptions, LCA churches tended to be more formalistically liturgical than their counterparts in the Ameri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Augustana Evangelical Lutheran Church
The Augustana Evangelical Lutheran Church (previously the Augustana Lutheran Synod and also Scandinavian Evangelical Lutheran Augustana Synod in North America and Swedish Evangelical Lutheran Augustana Synod in North America) was a Lutheran church body in the United States that was one of the churches that merged into the Lutheran Church in America (LCA) in 1962. It had its roots among the Swedish immigrants in the 19th century. In 1961, just before its merger into the LCA, the Augustana Synod had 1,353 pastors, 1,219 congregations, and 619,040 members. Formation The Scandinavian Evangelical Lutheran Augustana Synod in North America was established in 1860. The organizing meeting was held at the Jefferson Prairie Settlement, near Clinton, Wisconsin on June 5–8. A group of Swedish Lutheran pastors including Jonas Swensson, Lars Paul Esbjörn, Tuve Hasselquist, Eric Norelius, and Erland Carlsson pioneered development of the Augustana Synod. ''Augustana'' is a shortened v ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |