|
Grippia
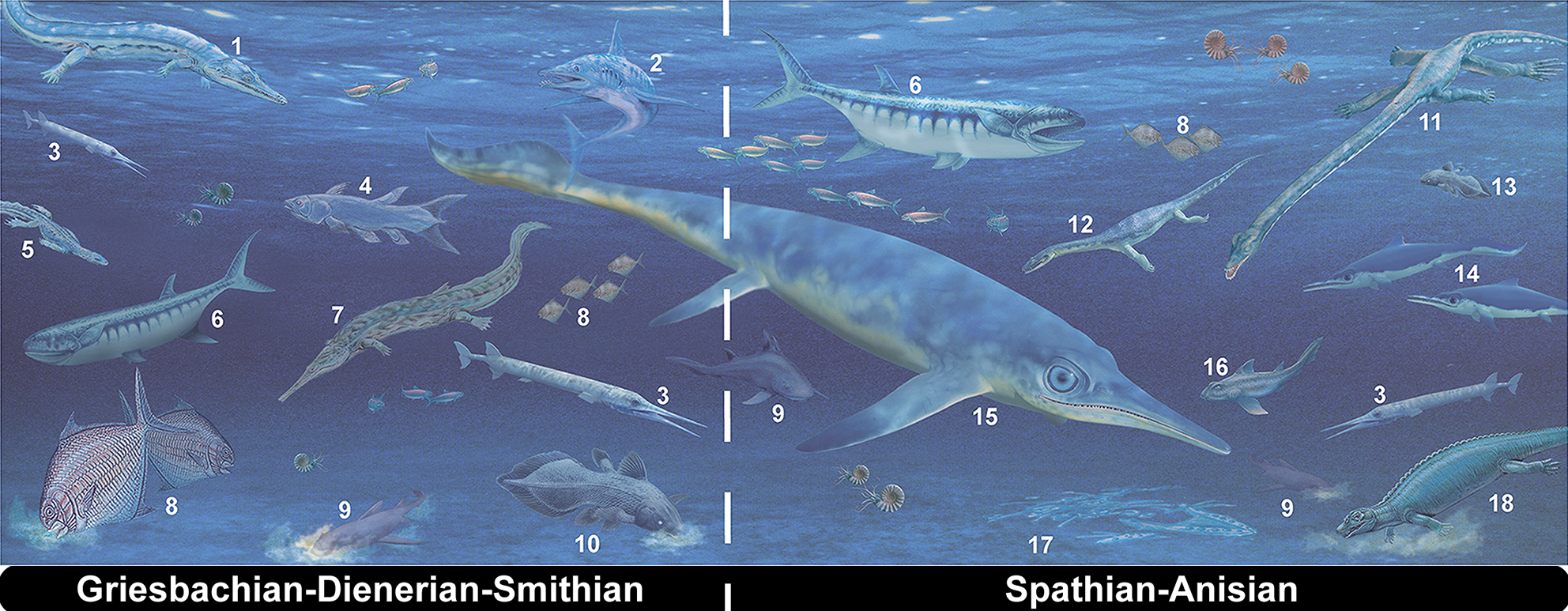
''Grippia'' is a genus of early ichthyopterygian, an extinct group of reptiles that resembled dolphins. Its only species is ''Grippia longirostris''. It was a relatively small ichthyopterygian, measuring around long. Fossil remains from Svalbard from the specimen SVT 203 were originally assigned to ''G. longirostris'' but are now thought to have belonged to a non-ichthyopterygian diapsid related to '' Helveticosaurus''. Discovery Fossils have been found along the coasts of Greenland, China, Japan, Norway, and Canada ( Sulfur Mountain Formation); of Early Triassic age. No complete skeletons have ever been found. However, well-preserved remains have been found, with the most notable ones including: *The Marine Ironstone found in Agardh Bay Norway. This specimen consists of a partial skull fossil; however, it was lost during World War II and presumably destroyed. *Previously, the Vega Phroso Siltstone Member of the Sulphur Mountain Formation in British Columbia. This specimen co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gulosaurus
''Gulosaurus'' is an extinct genus of basal grippidian ichthyopterygian known from the Early Triassic Vega-Phroso Siltstone Member of the Sulphur Mountain Formation of east-central British Columbia, Canada. ''Gulosaurus'' was first named by Robin S. Cuthbertson, Anthony P. Russell and Jason S. Anderson in 2013 and the type species is ''Gulosaurus helmi''. The name means 'Helm's wolverine lizard' and refers to the Wolverine Nordic and Mountain Society, who maintain the area around Wapiti Lake where it was found, and to Dr Charles Helm, who is a leading paleontologist around this same area. Originally ''Gulosaurus'' was thought to be either '' Grippia longirostris'' or '' Parvinatator wapitiensis,'' but as the fossil was incomplete it was uncertain which. In 2013, the other half of the fossil, including its skull, was discovered and this proved it to be a new species entirely, closely related to ''Grippia'' and very similar. Features Overall, ''Gulosaurus'' was similar t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Helveticosaurus
''Helveticosaurus'' is an extinct genus of diapsid marine reptile known from the Middle Triassic (Anisian-Ladinian boundary) of southern Switzerland. It contains a single species, ''Helveticosaurus zollingeri'', known from the nearly complete holotype T 4352 collected at Cava Tre Fontane of Monte San Giorgio, an area well known for its rich record of marine life during the Middle Triassic. Description and paleobiology ''Helveticosaurus'' is known from a nearly complete holotype which includes the premaxilla, maxilla, prefrontal, postfrontal, postorbital, squamosal, dentary and a postcranial skeleton. Several disarticulated elements are also known including teeth, portions of the snout and poscranial elements. ''Helveticosaurus'' is estimated to be about long from snout to tail. It possessed many features that were adaptations to a marine lifestyle in the shallow-sea environment that existed in Europe at the time when much of the continent was part of the Tethys Ocean. Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ichthyopterygia
Ichthyopterygia ("fish flippers") was a designation introduced by Richard Owen, Sir Richard Owen in 1840 to designate the Jurassic ichthyosaurs that were known at the time, but the term is now used more often for both true Ichthyosauria and their more primitive early and middle Triassic ancestors. Basal (phylogenetics), Basal ichthyopterygians (prior to and ancestral to true Ichthyosauria) were mostly small (a meter or less in length) with elongated bodies and long, spool-shaped vertebrae, indicating that they swam in a sinuous, eel-like manner. This allowed for quick movements and maneuverability that were advantages in shallow-water hunting. Even at this early stage, they were already very specialised animals with proper flippers, and would have been incapable of movement on land. These animals seem to have been widely distributed around the coast of the northern half of Pangea, as they are known from the Olenekian (Early Triassic) and early Anisian (early Middle Triassic) of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sulfur Mountain Formation
The Sulphur Mountain Formation is a Formation (geology), geologic formation of Early Triassic, Early to Middle Triassic age. It is present on the western edge of the Western Canadian Sedimentary Basin, Western Canada Sedimentary Basin in the foothills and Canadian Rockies, Rocky Mountains of western Alberta and northeastern British Columbia. It includes marine fossils from the time shortly after the Permian-Triassic extinction event.Noad, Jon, 2017. Field trip to examine Montney Formation analogs: Exposures of the Sulphur Mountain Formation around Canmore and Kananaskis, western Alberta, Canada. In: J.C.C. Hseih, ed., Geologic field trips of the Canadian Rockies: 2017 meeting of the GSA Rocky Mountain Section, Geological Society of America, Field Guide 48, p. 137-152; doi: 10.1130/2017.0048(05). The Sulphur Mountain Formation was first described as a stratigraphic unit, member of the Spray River Formation by P.S. Warren in 1945, who named it for Sulphur Mountain (Alberta), Sulphu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Early Triassic
The Early Triassic is the first of three epochs of the Triassic Period of the geologic timescale. It spans the time between 251.9 Ma and Ma (million years ago). Rocks from this epoch are collectively known as the Lower Triassic Series, which is a unit in chronostratigraphy. The Early Triassic is the oldest epoch of the Mesozoic Era. It is preceded by the Lopingian Epoch (late Permian, Paleozoic Era) and followed by the Middle Triassic Epoch. The Early Triassic is divided into the Induan and Olenekian ages. The Induan is subdivided into the Griesbachian and Dienerian subages and the Olenekian is subdivided into the Smithian and Spathian subages. The Lower Triassic series is coeval with the Scythian Stage, which is today not included in the official timescales but can be found in older literature. In Europe, most of the Lower Triassic is composed of Buntsandstein, a lithostratigraphic unit of continental red beds. The Early Triassic and partly also the Middle Trias ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Germany
Germany, officially the Federal Republic of Germany, is a country in Central Europe. It lies between the Baltic Sea and the North Sea to the north and the Alps to the south. Its sixteen States of Germany, constituent states have a total population of over 84 million in an area of , making it the most populous member state of the European Union. It borders Denmark to the north, Poland and the Czech Republic to the east, Austria and Switzerland to the south, and France, Luxembourg, Belgium, and the Netherlands to the west. The Capital of Germany, nation's capital and List of cities in Germany by population, most populous city is Berlin and its main financial centre is Frankfurt; the largest urban area is the Ruhr. Settlement in the territory of modern Germany began in the Lower Paleolithic, with various tribes inhabiting it from the Neolithic onward, chiefly the Celts. Various Germanic peoples, Germanic tribes have inhabited the northern parts of modern Germany since classical ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bombing Raid
Strategic bombing is a systematically organized and executed military attack from the air which can utilize strategic bombers, long- or medium-range missiles, or nuclear-armed fighter-bomber aircraft to attack targets deemed vital to the enemy's war-making capability. It is a military strategy used in total war with the goal of defeating the enemy by destroying its morale, its economic ability to produce and transport materiel to the theatres of military operations, or both. The term terror bombing is used to describe the strategic bombing of civilian targets without military value, in the hope of damaging an enemy's morale. One of the strategies of war is to demoralize the enemy so that peace or surrender becomes preferable to continuing the conflict. Strategic bombing has been used to this end. The phrase "terror bombing" entered the English lexicon towards the end of World War II and many strategic bombing campaigns and individual raids have been described as terror bombing ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Species
A species () is often defined as the largest group of organisms in which any two individuals of the appropriate sexes or mating types can produce fertile offspring, typically by sexual reproduction. It is the basic unit of Taxonomy (biology), classification and a taxonomic rank of an organism, as well as a unit of biodiversity. Other ways of defining species include their karyotype, DNA sequence, morphology (biology), morphology, behaviour, or ecological niche. In addition, palaeontologists use the concept of the chronospecies since fossil reproduction cannot be examined. The most recent rigorous estimate for the total number of species of eukaryotes is between 8 and 8.7 million. About 14% of these had been described by 2011. All species (except viruses) are given a binomial nomenclature, two-part name, a "binomen". The first part of a binomen is the name of a genus to which the species belongs. The second part is called the specific name (zoology), specific name or the specific ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Body Of Vertebra
Each vertebra (: vertebrae) is an irregular bone with a complex structure composed of bone and some hyaline cartilage, that make up the vertebral column or spine, of vertebrates. The proportions of the vertebrae differ according to their spinal segment and the particular species. The basic configuration of a vertebra varies; the vertebral body (also ''centrum'') is of bone and bears the load of the vertebral column. The upper and lower surfaces of the vertebra body give attachment to the intervertebral discs. The posterior part of a vertebra forms a vertebral arch, in eleven parts, consisting of two pedicles (pedicle of vertebral arch), two laminae, and seven processes. The laminae give attachment to the ligamenta flava (ligaments of the spine). There are vertebral notches formed from the shape of the pedicles, which form the intervertebral foramina when the vertebrae articulate. These foramina are the entry and exit conduits for the spinal nerves. The body of the vertebra an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ribs
The rib cage or thoracic cage is an endoskeletal enclosure in the thorax of most vertebrates that comprises the ribs, vertebral column and sternum, which protect the vital organs of the thoracic cavity, such as the heart, lungs and great vessels and support the shoulder girdle to form the core (anatomy), core part of the axial skeleton. A typical human skeleton, human thoracic cage consists of 12 pairs of ribs and the adjoining costal cartilages, the sternum (along with the manubrium and xiphoid process), and the 12 thoracic vertebrae articulating with the ribs. The thoracic cage also provides attachments for extrinsic skeletal muscles of the neck, upper limbs, upper abdomen and back, and together with the overlying skin and associated fascia and muscles, makes up the thoracic wall. In tetrapods, the rib cage intrinsically holds the muscles of respiration (thoracic diaphragm, diaphragm, intercostal muscles, etc.) that are crucial for active inhalation and forced exhalation, and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Basal (anatomy)
Standard anatomical terms of location are used to describe unambiguously the anatomy of humans and other animals. The terms, typically derived from Latin or Greek roots, describe something in its standard anatomical position. This position provides a definition of what is at the front ("anterior"), behind ("posterior") and so on. As part of defining and describing terms, the body is described through the use of anatomical planes and axes. The meaning of terms that are used can change depending on whether a vertebrate is a biped or a quadruped, due to the difference in the neuraxis, or if an invertebrate is a non-bilaterian. A non-bilaterian has no anterior or posterior surface for example but can still have a descriptor used such as proximal or distal in relation to a body part that is nearest to, or furthest from its middle. International organisations have determined vocabularies that are often used as standards for subdisciplines of anatomy. For example, '' Terminolog ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |