|
Helveticosaurus
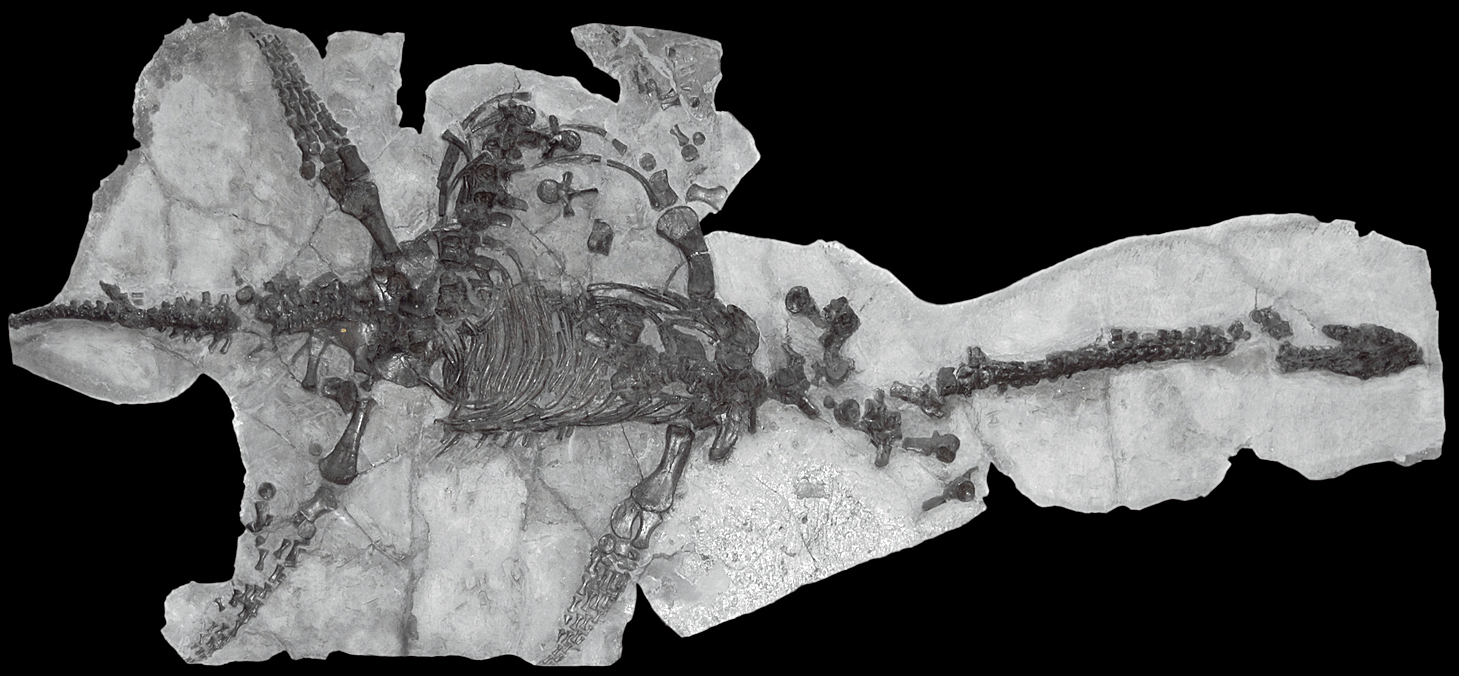
''Helveticosaurus'' is an extinct genus of diapsid marine reptile known from the Middle Triassic (Anisian-Ladinian boundary) of southern Switzerland. It contains a single species, ''Helveticosaurus zollingeri'', known from the nearly complete holotype T 4352 collected at Cava Tre Fontane of Monte San Giorgio, an area well known for its rich record of marine life during the Middle Triassic. Description and paleobiology ''Helveticosaurus'' is known from a nearly complete holotype which includes the premaxilla, maxilla, prefrontal, postfrontal, postorbital, squamosal, dentary and a postcranial skeleton. Several disarticulated elements are also known including teeth, portions of the snout and poscranial elements. ''Helveticosaurus'' is estimated to be about long from snout to tail. It possessed many features that were adaptations to a marine lifestyle in the shallow-sea environment that existed in Europe at the time when much of the continent was part of the Tethys Ocean. Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Helveticosauridae
Helveticosauridae is an extinct family of basal marine reptiles known from the Middle Triassic (Anisian-Ladinian boundary) of southern Switzerland and northern Italy. The type species of the family is '' Helveticosaurus zollingeri'', named by Bernhard Peyer in 1955 based on a single nearly complete specimen T 4352 collected at Cava Tre Fontane from the Anisian-Ladinian boundary of Monte San Giorgio, Switzerland. Peyer (1955) considered the species to be a very distinctive member of the order Placodontia, and thus erected Helveticosauridae as well as the superfamily Helveticosauroidea to contain it within Placodontia. Nosotti and Rieppel (2003) described '' Eusaurosphargis'' from the equivalent beds at Cava di Besano of the Besano Formation (Anisian-Ladinian boundary) of Italy. Their phylogenetic analysis recovered it as the sister taxon of ''Helveticosaurus'', and thus it was assigned to Helveticosauridae. Based on the description in the literature available for '' Saurosp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eusaurosphargis
''Eusaurosphargis'' is an extinct genus of a diapsid reptile, known from the Middle Triassic (Anisian and Ladinian age) Besano Formation of northern Italy and Prosanto Formation of south-eastern Switzerland. It contains a single species, ''Eusaurosphargis dalsassoi''. It was a small reptile, measuring long. Discovery The holotype of ''Eusaurosphargis dalsassoi'' (BES SC 390) is a partial skeleton of a single individual found disarticulated but in close association. BES SC 390 was collected from an oil shale at Cava di Besano of the Besano Formation (Grenzbitumenzone). These lagoonal beds are equivalent to those at Monte San Giorgio, dating to the Anisian-Ladinian boundary, probably to the latest Anisian at this location, of the early Middle Triassic, about 243 million years ago. Nicole Klein and Oliver J. Sichelschmidt (2014) described disarticulated remains they referred to ''Eusaurosphargis sp''. These remains were collected from the Dutch Winterswijk Qua ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sauropterygia
Sauropterygia ("lizard flippers") is an extinct taxon of diverse, aquatic diapsid reptiles that developed from terrestrial ancestors soon after the end-Permian extinction and flourished during the Triassic before all except for the Plesiosauria became extinct at the end of that period. The plesiosaurs would continue to diversify until the end of the Mesozoic, when they became extinct as part of the end-Cretaceous mass extinction. Sauropterygians are united by a radical adaptation of their pectoral girdle, adapted to support powerful flipper strokes. Some later sauropterygians, such as the pliosaurs, developed a similar mechanism in their pelvis. Other than being diapsids, their affinities to other reptiles have long been contentious. Sometimes suggested to be closely related to turtles, other proposals have considered them most closely related to Lepidosauromorpha or Archosauromorpha, and/or the marine reptile groups Thalattosauria and Ichthyosauromorpha. Origins an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Placodontia
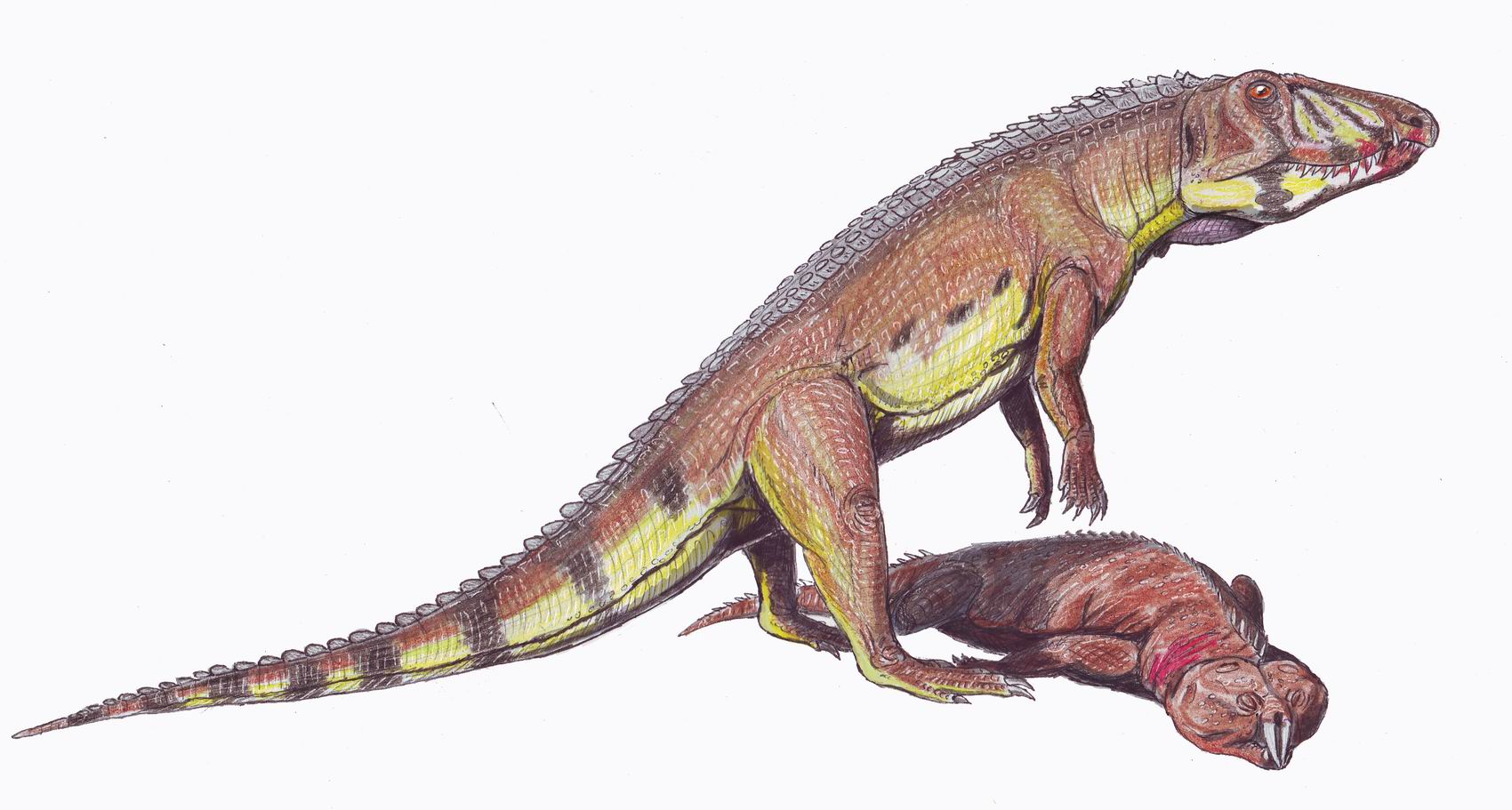
Placodonts ("Tablet (pharmacy), tablet tooth, teeth") are an Extinction, extinct order (biology), order of marine reptiles that lived during the Triassic period, becoming extinct at the end of the period. They were part of Sauropterygia, the group that includes Plesiosauria, plesiosaurs. Placodonts were generally between in length, with some of the largest measuring long. The first specimen was discovered in 1830. They have been found throughout central Europe, North Africa, the Middle East and China. Palaeobiology The earliest forms, like ''Placodus'', which lived in the early to middle Triassic, resembled barrel-bodied lizards superficially similar to the marine iguana of today, but larger. In contrast to the marine iguana, which feeds on algae, the placodonts ate Mollusca, molluscs and so their teeth were flat and tough to crush shells. In the earliest periods, their size was probably enough to keep away the top sea predators of the time: the sharks. However, as time passe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Archosauromorpha
Archosauromorpha ( Greek for "ruling lizard forms") is a clade of diapsid reptiles containing all reptiles more closely related to archosaurs (such as crocodilians and dinosaurs, including birds) than to lepidosaurs (such as tuataras, lizards, and snakes). Archosauromorphs first appeared during the late Middle Permian or Late Permian, though they became much more common and diverse during the Triassic period. Although Archosauromorpha was first named in 1946, its membership did not become well-established until the 1980s. Currently Archosauromorpha encompasses four main groups of reptiles: the stocky, herbivorous allokotosaurs and rhynchosaurs, the hugely diverse Archosauriformes, and a polyphyletic grouping of various long-necked reptiles including '' Protorosaurus'', tanystropheids, and '' Prolacerta''. Other groups including pantestudines (turtles and their extinct relatives) and the semiaquatic choristoderes have also been placed in Archosauromorpha by some authors ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Teeth
A tooth (: teeth) is a hard, calcified structure found in the jaws (or mouths) of many vertebrates and used to break down food. Some animals, particularly carnivores and omnivores, also use teeth to help with capturing or wounding prey, tearing food, for defensive purposes, to intimidate other animals often including their own, or to carry prey or their young. The roots of teeth are covered by gums. Teeth are not made of bone, but rather of multiple tissues of varying density and hardness that originate from the outermost embryonic germ layer, the ectoderm. The general structure of teeth is similar across the vertebrates, although there is considerable variation in their form and position. The teeth of mammals have deep roots, and this pattern is also found in some fish, and in crocodilians. In most teleost fish, however, the teeth are attached to the outer surface of the bone, while in lizards they are attached to the inner surface of the jaw by one side. In cartilaginous ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Taxonomic Rank
In biology, taxonomic rank (which some authors prefer to call nomenclatural rank because ranking is part of nomenclature rather than taxonomy proper, according to some definitions of these terms) is the relative or absolute level of a group of organisms (a ''taxon'') in a hierarchy that reflects evolutionary relationships. Thus, the most inclusive clades (such as Eukarya and Animalia) have the highest ranks, whereas the least inclusive ones (such as ''Homo sapiens'' or ''Bufo bufo'') have the lowest ranks. Ranks can be either relative and be denoted by an indented taxonomy in which the level of indentation reflects the rank, or absolute, in which various terms, such as species, genus, Family (biology), family, Order (biology), order, Class (biology), class, Phylum (biology), phylum, Kingdom (biology), kingdom, and Domain (biology), domain designate rank. This page emphasizes absolute ranks and the rank-based codes (the International Code of Zoological Nomenclature, Zoological Code, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Family (biology)
Family (, : ) is one of the eight major hierarchical taxonomic ranks in Linnaean taxonomy. It is classified between order and genus. A family may be divided into subfamilies, which are intermediate ranks between the ranks of family and genus. The official family names are Latin in origin; however, popular names are often used: for example, walnut trees and hickory trees belong to the family Juglandaceae, but that family is commonly referred to as the "walnut family". The delineation of what constitutes a family—or whether a described family should be acknowledged—is established and decided upon by active taxonomists. There are not strict regulations for outlining or acknowledging a family, yet in the realm of plants, these classifications often rely on both the vegetative and reproductive characteristics of plant species. Taxonomists frequently hold varying perspectives on these descriptions, leading to a lack of widespread consensus within the scientific community ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Basal (phylogenetics)
In phylogenetics, basal is the direction of the ''base'' (or root) of a phylogenetic tree#Rooted tree, rooted phylogenetic tree or cladogram. The term may be more strictly applied only to nodes adjacent to the root, or more loosely applied to nodes regarded as being close to the root. Note that extant taxa that lie on branches connecting directly to the root are not more closely related to the root than any other extant taxa. While there must always be two or more equally "basal" clades sprouting from the root of every cladogram, those clades may differ widely in taxonomic rank, Phylogenetic diversity, species diversity, or both. If ''C'' is a basal clade within ''D'' that has the lowest rank of all basal clades within ''D'', ''C'' may be described as ''the'' basal taxon of that rank within ''D''. The concept of a 'key innovation' implies some degree of correlation between evolutionary innovation and cladogenesis, diversification. However, such a correlation does not make a given ca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
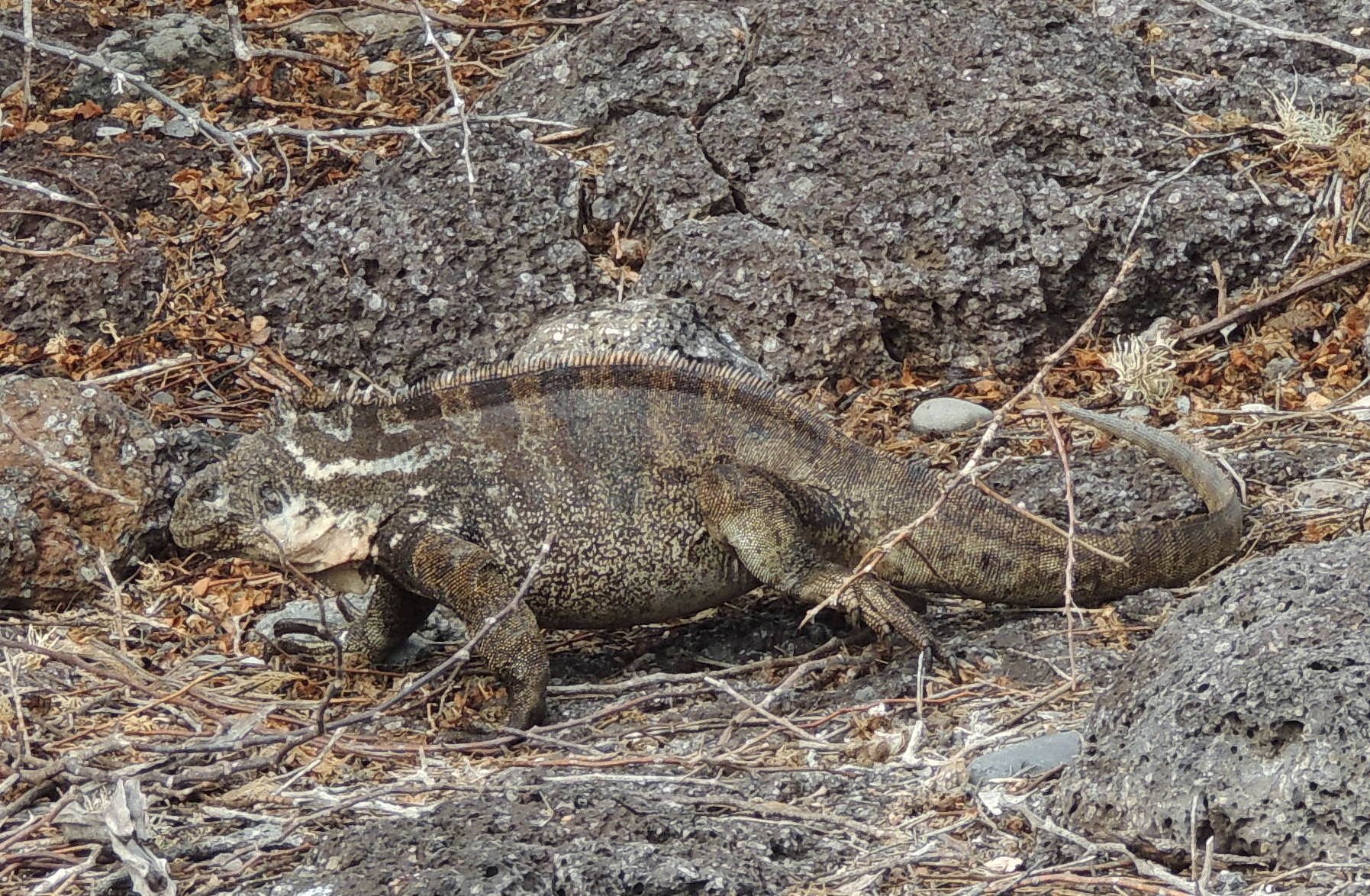
Marine Iguana
The marine iguana (''Amblyrhynchus cristatus''), also known as the sea iguana, saltwater iguana, or Galápagos marine iguana, is a species of Iguanidae, iguana found only on the Galápagos Islands (Ecuador). Unique among modern lizards, it is a marine reptile that has the ability to forage in the sea for algae, which make up almost all of its diet. Marine iguanas are the only extant lizard that spends time in a marine environment. Large males are able to dive to find this food source, while females and smaller males feed during low tide in the intertidal zone. They mainly live in Colony (biology), colonies on rocky shores where they bask after visiting the relatively cold water or intertidal zone, but can also be seen in marshes, mangrove swamps and beaches. Large males defend Territory (animal), territories for a short period, but smaller males have other breeding strategies. After mating, the female digs a nest hole in the soil where she lays her eggs, leaving them to hatch on th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |