|
Grigor I Mamikonian
Grigor I Mamikonian () was the presiding prince of Armenia in 662–685, when the country was under Arab domination. Grigor had been taken prisoner by the Arab governor of Syria, Mu'awiya, along with other Armenian nobles in 654/55, and was kept hostage at Damascus. In 661, when Mu'awiya entered into a civil war against Ali for control of the caliphate, and was seeking supporters in the provinces of the Arab empire, Grigor was released upon the request of the Armenian princes () and Patriarch Nerses III the Builder, and named as presiding prince of Armenia. He succeeded his brother Hamazasp IV Mamikonian, who had allied with the Byzantines when the latter had occupied Armenia in 657/58. Grigor is described by the medieval sources as a "benevolent man, distinguished by his spiritual qualities, just, calm and gentle". Grigor's rule was initially peaceful and prosperous, as Mu'awiya's Umayyad Caliphate held the Byzantines at bay. He is well remembered for his church foundations, an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Armenian Monarchs
This is a list of the monarchs of Armenia, rulers of the ancient Kingdom of Armenia (antiquity), Kingdom of Armenia (336 BC – AD 428), the medieval Bagratid Armenia, Kingdom of Armenia (884–1045), various lesser Armenian kingdoms (908–1170), and finally the Armenian Kingdom of Cilicia (1198–1375). The list also includes prominent vassal princes and lords who ruled during times without an Armenian kingdom, as well as later claimants to the position. Ancient Armenia (521 BC – AD 428) Early satraps (521–401 BC) * Hydarnes, Hydarnes I, satrap in the late 6th century BC?, granted Armenia by the Achaemenid Empire, Achaemenid king Darius the Great, Darius I as a semi-hereditary Satrap, satrapy * Hydarnes the Younger, Hydarnes II, satrap in the early 5th century BC? * Hydarnes (father of Stateira), Hydarnes III, satrap in the middle of the 5th century BC * Terituchmes, satrap in the second half of the 5th century BC Orontid dynasty (401–200 BC) Artaxiad dyna ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gregory The Illuminator
Gregory the Illuminator ( – ) was the founder and first official Catholicos of All Armenians, head of the Armenian Apostolic Church. He Christianization of Armenia, converted Armenia from Zoroastrianism in Armenia, Zoroastrianism to Christianity in the early fourth century (traditionally dated to 301), making Armenia the first state to adopt Christianity as its official religion. He is venerated as a saint in the Armenian Apostolic Church and in some other churches. Gregory is said to have been the son of a Parthian Empire, Parthian nobleman, Anak the Parthian, Anak, who assassinated the Arsacid dynasty of Armenia, Arsacid king of Armenia Khosrov II of Armenia, Khosrov II. The young Gregory was saved from the extermination of Anak's family and was raised as a Christian in Caesarea (Mazaca), Caesarea of Cappadocia, then part of the Roman Empire. Gregory returned to Armenia as an adult and entered the service of King Tiridates III of Armenia, Tiridates III, who had Gregory t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vassal Rulers Of The Umayyad Caliphate
A vassal or liege subject is a person regarded as having a mutual obligation to a lord or monarch, in the context of the feudal system in medieval Europe. While the subordinate party is called a vassal, the dominant party is called a suzerain. The rights and obligations of a vassal are called vassalage, while the rights and obligations of a suzerain are called suzerainty. The obligations of a vassal often included military support by knights in exchange for certain privileges, usually including land held as a tenant or fief. The term is also applied to similar arrangements in other feudal societies. In contrast, fealty (''fidelitas'') was sworn, unconditional loyalty to a monarch. European vassalage In fully developed vassalage, the lord and the vassal would take part in a commendation ceremony composed of two parts, the homage and the fealty, including the use of Christian sacraments to show its sacred importance. According to Eginhard's brief description, the ''commenda ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Princes Of Armenia
A prince is a male ruler (ranked below a king, grand prince, and grand duke) or a male member of a monarch's or former monarch's family. ''Prince'' is also a title of nobility (often highest), often hereditary, in some European states. The female equivalent is a princess. The English word derives, via the French word ''prince'', from the Latin noun , from (first) and (head), meaning "the first, foremost, the chief, most distinguished, noble ruler, prince". In a related sense, now not commonly used, all more or less sovereign rulers over a state, including kings, were "princes" in the language of international politics. They normally had another title, for example king or duke. Many of these were Princes of the Holy Roman Empire. Historical background The Latin word (older Latin *prīsmo-kaps, ), became the usual title of the informal leader of the Roman senate some centuries before the transition to empire, the ''princeps senatus''. Emperor Augustus established the forma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
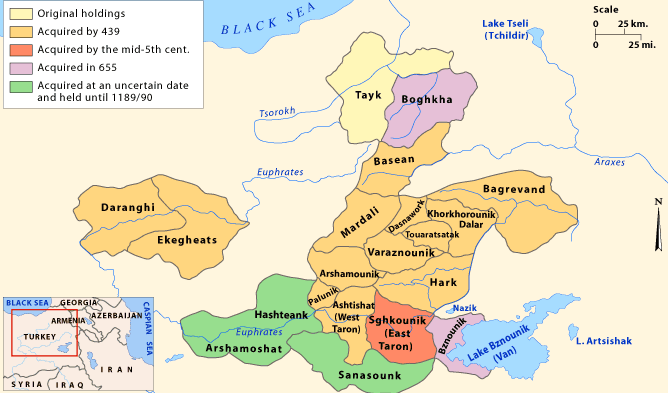
Mamikonian Family
Mamikonian or Mamikonean () was an Armenian aristocratic dynasty which dominated Armenia between the 4th and 8th centuries—through the late antique kingdom, Sasanian, Byzantine, and Arab dominations. They were the most notable noble house in early Christian Armenia after the ruling Arsacids and held the hereditary positions of (supreme commander of the army) and (royal tutor), allowing them to play the role of kingmaker for the later Armenian kings. They ruled over extensive territories, including the Armenian regions of Tayk, Taron, Sasun, and Bagrevand, among others. The Mamikonians had a reputation as supporters of the Roman (and later Byzantine) empire in Armenia against Sasanian Iran, although they also served as viceroys under Persian rule. Their influence over Armenian affairs began to decline at the end of the 6th century and suffered a final, decisive blow after a failed rebellion against Arab rule over Armenia in 774/75. Origin The origin of the Mamikonians i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Armenian Christians
Armenian Church is a multi-denominational concept. Thus it may refer to Armenian Apostolic, Armenian Catholic or Armenian Evangelical (Protestant) churches. It can also refer to individual Christian Armenian religious buildings in various locations. Institutions * Armenian Apostolic Church, founded in 1st century AD, adopted as state religion in 301 ** Mother See of Holy Etchmiadzin *** Armenian Patriarchate of Jerusalem *** Armenian Patriarchate of Constantinople ** Holy See of Cilicia (official name: Armenian Catholicosate of the Great House of Cilicia) * Armenian Catholic Church, founded in 1742 * Armenian Evangelical Church The Armenian Evangelical Church () was established on July 1, 1846, by thirty-seven men and three women in Constantinople. History In the 19th century there was an intellectual and spiritual awakening in Constantinople. This awakening and enlig ..., founded in 1846 Armenian church buildings * Armenian Church, Brăila, Romania * Armenian Church, Bucha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
7th-century People From The Umayyad Caliphate
The 7th century is the period from 601 through 700 in accordance with the Julian calendar in the Christian Era. The spread of Islam and the Muslim conquests began with the unification of Arabia by the Islamic prophet Muhammad starting in 622. After Muhammad's death in 632, Islam expanded beyond the Arabian Peninsula under the Rashidun Caliphate (632–661) and the Umayyad Caliphate (661–750). The Muslim conquest of Persia in the 7th century led to the downfall of the Sasanian Empire. Also conquered during the 7th century were Syria, Palestine, Armenia, Egypt, and North Africa. The Byzantine Empire suffered setbacks during the rapid expansion of the Caliphate and a mass incursion of Slavs in the Balkans which reduced its territorial limits. The decisive victory at the Siege of Constantinople in the 670s led the empire to retain Asia Minor, which ensured the existence of the empire. In the Iberian Peninsula, the 7th century was known as the ''Siglo de Concilios'' (century o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
685 Deaths
__NOTOC__ Year 685 ( DCLXXXV) was a common year starting on Sunday of the Julian calendar. The denomination 685 for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years. Events By place Byzantine Empire * July 10 – Emperor Constantine IV dies of dysentery at Constantinople after a 17-year reign, and is succeeded by his 16-year-old son Justinian II. Europe * Kuber, brother of Asparukh of Bulgaria, defeats the Avars in Syrmia (Pannonia). He leads his followers of around 70,000 people to Macedonia (modern North Macedonia). Britain * May 20 – Battle of Dun Nechtain: The Picts under King Bridei III revolt against their Northumbrian overlords. Cuthbert, bishop of Lindisfarne, advises King Ecgfrith of Northumbria (Bridei's cousin) not to invade Pictland (modern Scotland). Undeterred, Ecgfrith marches his army north to engage the enemy near Dunnichen. The Picts, possib ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Medieval Armenia
Medieval Armenia refers to the history of Armenia during the Middle Ages. It follows Ancient Armenia and covers a period of approximately eight centuries, beginning with the Muslim conquest of Armenia in the 7th century. Key events during this period includes the rebirth of an Armenian Kingdom under the Bagratid dynasty, followed by the arrival of the Seljuk Turks. During this period, a portion of the Armenian people migrate to Cilicia to seek refuge from invasions, while the remnants in Eastern Armenia see the establishment of Zakarid Armenia under the Kingdom of Georgia. This period also marks the emergence of the royal dynasty in Artsakh. In Cilicia, Armenians establish a crusader state, the Armenian Kingdom of Cilicia, which would be the last fully independent Armenian state throughout the following centuries until the establishment of modern-day Armenia. The arrival of the Mongol Empire in the area, followed by the rise and fall of several other Turko-Mongol confeder ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |