|
Great Wings
The greater wing of the sphenoid bone, or alisphenoid, is a bony process of the sphenoid bone, positioned in the skull behind each eye. There is one on each side, extending from the side of the body of the sphenoid and curving upward, laterally, and backward. Structure The greater wings of the sphenoid are two strong processes of bone, which arise from the sides of the body, and are curved upward, laterally, and backward; the posterior part of each projects as a triangular process that fits into the angle between the squamous and the petrous part of the temporal bone and presents at its apex a downward-directed process, the spine of sphenoid bone. Cerebral surface The superior or cerebral surface of each greater wing ig. 1forms part of the middle cranial fossa; it is deeply concave, and presents depressions for the convolutions of the temporal lobe of the brain. It has a number of foramina (holes) in it: * The foramen rotundum is a circular aperture at its anterior and medial ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sphenoid Bone
The sphenoid bone is an unpaired bone of the neurocranium. It is situated in the middle of the skull towards the front, in front of the basilar part of occipital bone, basilar part of the occipital bone. The sphenoid bone is one of the seven bones that articulate to form the orbit (anatomy), orbit. Its shape somewhat resembles that of a butterfly, bat or wasp with its wings extended. The name presumably originates from this shape, since () means in Ancient Greek. Structure It is divided into the following parts: * a median portion, known as the body of sphenoid bone, containing the sella turcica, which houses the pituitary gland as well as the paired paranasal sinuses, the sphenoidal sinuses * two Greater wing of sphenoid bone, greater wings on the lateral side of the body and two Lesser wing of sphenoid bone, lesser wings from the anterior side. * Pterygoid processes of the sphenoides, directed downwards from the junction of the body and the greater wings. Two sphenoidal co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Middle Meningeal Vessels
The middle meningeal artery (') is typically the third branch of the maxillary artery#First portion, first portion of the maxillary artery. After branching off the maxillary artery in the infratemporal fossa, it runs through the foramen spinosum to supply the dura mater (the outer meningeal layer) and the calvaria (skull), calvaria. The middle meningeal artery is the largest of the three (paired) arteries that supply the meninges, the others being the anterior meningeal artery and the posterior meningeal artery. The anterior branch of the middle meningeal artery runs beneath the pterion. It is vulnerable to injury at this point, where the skull is thin. Rupture of the artery may give rise to an epidural hematoma. In the dry cranium, the middle meningeal, which runs within the dura mater surrounding the brain, makes a deep groove in the calvarium. The middle meningeal artery is intimately associated with the auriculotemporal nerve, which wraps around the artery making the two easi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Frontal Bone
In the human skull, the frontal bone or sincipital bone is an unpaired bone which consists of two portions.'' Gray's Anatomy'' (1918) These are the vertically oriented squamous part, and the horizontally oriented orbital part, making up the bony part of the forehead, part of the bony orbital cavity holding the eye, and part of the bony part of the nose respectively. The name comes from the Latin word ''frons'' (meaning "forehead"). Structure The frontal bone is made up of two main parts. These are the squamous part, and the orbital part. The squamous part marks the vertical, flat, and also the biggest part, and the main region of the forehead. The orbital part is the horizontal and second biggest region of the frontal bone. It enters into the formation of the roofs of the orbital and nasal cavities. Sometimes a third part is included as the nasal part of the frontal bone, and sometimes this is included with the squamous part. The nasal part is between the brow ridges, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pterygomaxillary Fissure
The pterygomaxillary fissure is a fissure of the human skull. It is vertical, and descends at right angles from the medial end of the inferior orbital fissure. It is a triangular interval, formed by the divergence of the maxilla from the pterygoid process of the sphenoid. It connects the infratemporal with the pterygopalatine fossa, and transmits the terminal part of the maxillary artery The maxillary artery (eg, internal maxillary artery) supplies deep structures of the face. It branches from the external carotid artery just deep to the neck of the mandible. Structure The maxillary artery, the larger of the two terminal branches .... The posterior superior alveolar nerve of the maxillary nerve goes from the pterygopalatine fossa to the infratemporal region via this fissure. The pterygopalatine plates are separated laterally from the posterior surface of the body of the maxilla by the pterygomaxillary fissure. In older texts, the pterygomaxillary fissure is sometimes call ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tensor Veli Palatini
The tensor veli palatini muscle (tensor palati or tensor muscle of the velum palatinum) is a thin, triangular muscle of the head that tenses the soft palate and opens the Eustachian tube to equalise pressure in the middle ear. Structure The tensor veli palatini muscle is thin and triangular in shape. Origin It arises from the scaphoid fossa of the pterygoid process of the sphenoid anteriorly, the (medial aspect of the) spine of sphenoid bone posteriorly, and - between the aforementioned anterior and posterior attachments - from the anterolateral aspect of the membranous wall of the pharyngotympanic tube. At the muscle's origin, some of its muscle fibres may be continuous with those of the tensor tympani muscle. Insertion Inferiorly, the muscle converges to form a tendon of attachment. This tendon winds medially around the pterygoid hamulus (with a small bursa interposed between the two) to insert into the palatine aponeurosis and into the bony surface posterior to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sphenomandibular Ligament
The sphenomandibular ligament (internal lateral ligament) is one of the three ligaments of the temporomandibular joint. It is situated medially to - and generally separate from - the articular capsule of the joint. Superiorly, it is attached to the spine of the sphenoid bone; inferiorly, it is attached to the lingula of mandible. The SML acts to limit inferior-ward movement of the mandible. The SML is derived from Meckel's cartilage. Anatomy The SML is a tough,'flat, thin band. It broadens inferiorly, measuring about 12 mm in width on average at the point of its inferior attachment. It is derived from the perichondrium of Meckel's cartilage. Attachments Superiorly, the SML is attached to the spine of the sphenoid bone (spina angularis by a narrow attachment. Inferiorly, it is attached at to lingula of mandible and the inferior margin of the mandibular foramen. Anatomical relations The lateral pterygoid muscle, auriculotemporal nerve, and the maxillary artery and m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chorda Tympani Nerve
Chorda tympani is a branch of the facial nerve that carries gustatory (taste) sensory innervation from the front of the tongue and parasympathetic ( secretomotor) innervation to the submandibular and sublingual salivary glands. Chorda tympani has a complex course from the brainstem, through the temporal bone and middle ear, into the infratemporal fossa, and ending in the oral cavity. Structure Chorda tympani fibers emerge from the pons of the brainstem as part of the intermediate nerve of the facial nerve. The facial nerve exits the cranial cavity through the internal acoustic meatus and enters the facial canal. In the facial canal, the chorda tympani branches off the facial nerve and enters the lateral wall of the tympanic cavity inside the middle ear where it runs across the tympanic membrane (from posterior to anterior) and medial to the neck of the malleus. The chorda then exits the skull by descending through the petrotympanic fissure into the infratemporal fossa ju ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sphenoidal Spine
The sphenoidal spine (Latin: "''spina angularis''") is a downwardly directed process at the apex of the great wings of the sphenoid bone that serves as the origin of the sphenomandibular ligament. Additional images File:Spine of sphenoid bone.png, Base of skull. Inferior surface. Spine of sphenoid bone marked with black circle References External links * - "Schematic view of key landmarks of the infratemporal fossa The infratemporal fossa is an irregularly shaped cavity that is a part of the skull. It is situated below and medial to the zygomatic arch. It is not fully enclosed by bone in all directions. It contains superficial muscles, including the lower ...." * Bones of the head and neck {{musculoskeletal-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
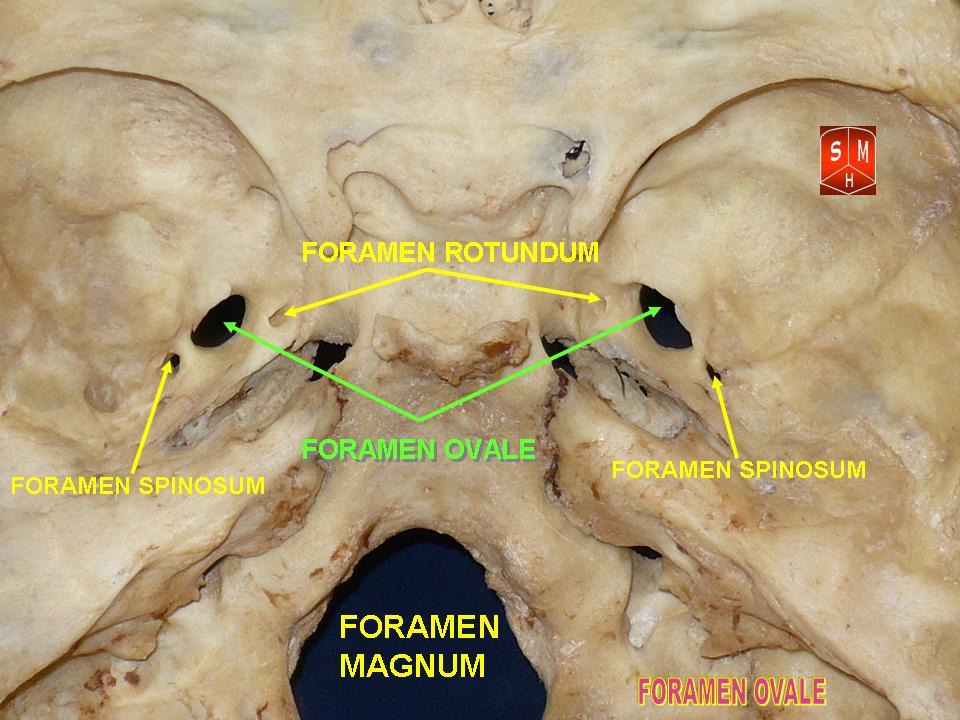
Foramen Ovale (skull)
The foramen ovale (En: oval window) is a hole in the posterior part of the sphenoid bone, posterolateral to the foramen rotundum. It is one of the larger of the several holes (the foramina) in the skull. It transmits the mandibular nerve, a branch of the trigeminal nerve. Structure The foramen ovale is an opening in the greater wing of the sphenoid bone. The foramen ovale is one of two cranial foramina in the greater wing, the other being the foramen spinosum. The foramen ovale is posterolateral to the foramen rotundum and anteromedial to the foramen spinosum. Posterior and medial to the foramen is the opening for the carotid canal. Contents The following structures pass through foramen ovale: * mandibular nerve (CN V) (a branch of the trigeminal nerve (CN V)) *accessory meningeal artery * lesser petrosal nerve (a branch of the glossopharyngeal nerve) * an emissary vein connecting the cavernous sinus with the pterygoid plexus * (occasionally) meningeal branch o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lateral Pterygoid Muscle
The lateral pterygoid muscle (or external pterygoid muscle) is a muscle of mastication. It has two heads. It lies superior to the medial pterygoid muscle. It is supplied by pterygoid branches of the maxillary artery, and the lateral pterygoid nerve (from the mandibular nerve, CN V3). It depresses and protrudes the mandible. When each muscle works independently, they can move the mandible side to side. Structure The lateral pterygoid muscle has an upper head and a lower head. * The upper head originates on the infratemporal surface and infratemporal crest of the greater wing of the sphenoid bone. It inserts onto the articular disc and fibrous capsule of the temporomandibular joint. * The lower head originates on the lateral surface of the lateral pterygoid plate. It inserts onto the pterygoid fovea at the neck of the condyloid process of the mandible. It lies superior to the medial pterygoid muscle. Blood supply The lateral pterygoid muscle is supplied by pterygoid b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Infratemporal Fossa
The infratemporal fossa is an irregularly shaped cavity that is a part of the skull. It is situated below and medial to the zygomatic arch. It is not fully enclosed by bone in all directions. It contains superficial muscles, including the lower part of the temporalis muscle, the lateral pterygoid muscle, and the medial pterygoid muscle. It also contains important blood vessels such as the middle meningeal artery, the pterygoid plexus, and the retromandibular vein, and nerves such as the mandibular nerve (CN V3) and its branches. Structure Boundaries The boundaries of the infratemporal fossa occur: * ''anteriorly'', by the infratemporal surface of the maxilla, and the ridge which descends from its zygomatic process. This contains the alveolar canal. * ''posteriorly'', by the tympanic part of the temporal bone, and the spina angularis of the sphenoid. * ''superiorly'', by the greater wing of the sphenoid below the infratemporal crest, and by the under surface of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Temporalis
In anatomy, the temporalis muscle, also known as the temporal muscle, is one of the muscles of mastication (chewing). It is a broad, fan-shaped convergent muscle on each side of the head that fills the temporal fossa, superior to the zygomatic arch so it covers much of the temporal bone.Illustrated Anatomy of the Head and Neck, Fehrenbach and Herring, Elsevier, 2012, page 98 ''Temporal'' refers to the head's temples. Structure In humans, the temporalis muscle arises from the temporal fossa and the deep part of temporal fascia. This is a very broad area of attachment. It passes medial to the zygomatic arch. It forms a tendon which inserts onto the coronoid process of the mandible, with its insertion extending into the retromolar fossa posterior to the most distal mandibular molar.Human Anatomy, Jacobs, Elsevier, 2008, page 194 In other mammals, the muscle usually spans the dorsal part of the skull all the way up to the medial line. There, it may be attached to a sagittal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |