Foramen Ovale (skull) on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The foramen ovale (En: oval window) is a hole in the posterior part of the
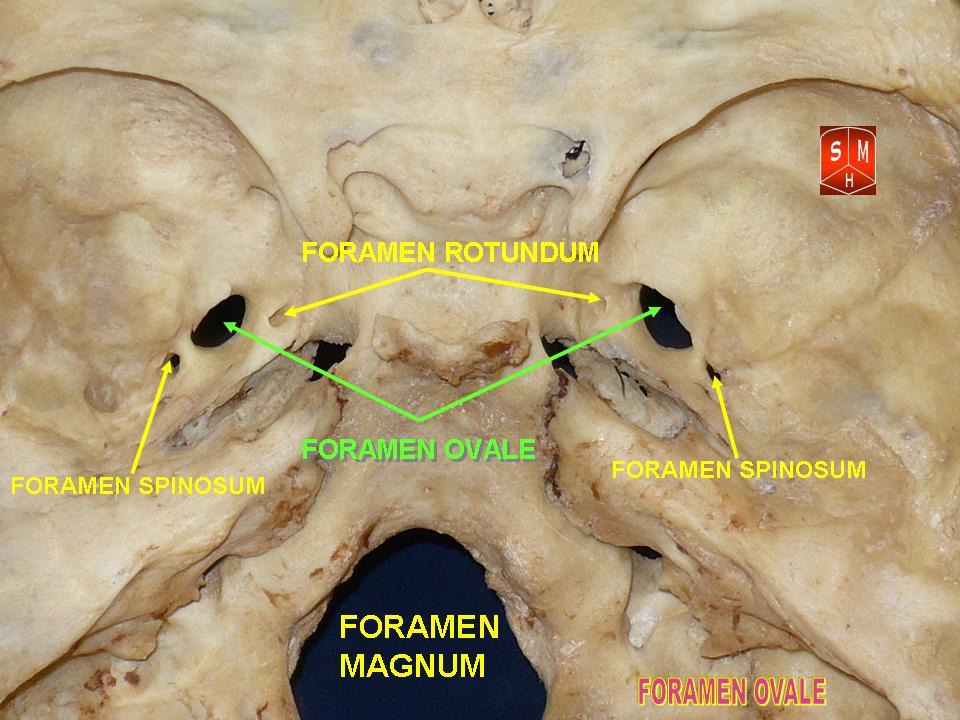 The
The
Adult skull as seen from beneath at uiuc.edu
{{Authority control Foramina of the skull
sphenoid bone
The sphenoid bone is an unpaired bone of the neurocranium. It is situated in the middle of the skull towards the front, in front of the basilar part of occipital bone, basilar part of the occipital bone. The sphenoid bone is one of the seven bon ...
, posterolateral to the foramen rotundum. It is one of the larger of the several holes (the foramina
In anatomy and osteology, a foramen (; : foramina, or foramens ; ) is an opening or enclosed gap within the dense connective tissue (bones and deep fasciae) of extant and extinct amniote animals, typically to allow passage of nerves, arter ...
) in the skull. It transmits the mandibular nerve
In neuroanatomy, the mandibular nerve (V) is the largest of the three divisions of the trigeminal nerve, the fifth Cranial nerves, cranial nerve (CN V). Unlike the other divisions of the trigeminal nerve (ophthalmic nerve, maxillary nerve) which ...
, a branch of the trigeminal nerve
In neuroanatomy, the trigeminal nerve (literal translation, lit. ''triplet'' nerve), also known as the fifth cranial nerve, cranial nerve V, or simply CN V, is a cranial nerve responsible for Sense, sensation in the face and motor functions ...
.
Structure
 The
The foramen
In anatomy and osteology, a foramen (; : foramina, or foramens ; ) is an opening or enclosed gap within the dense connective tissue (bones and deep fasciae) of extant and extinct amniote animals, typically to allow passage of nerves, artery, ...
ovale is an opening in the greater wing of the sphenoid bone
The sphenoid bone is an unpaired bone of the neurocranium. It is situated in the middle of the skull towards the front, in front of the basilar part of occipital bone, basilar part of the occipital bone. The sphenoid bone is one of the seven bon ...
. The foramen ovale is one of two cranial foramina in the greater wing, the other being the foramen spinosum. The foramen ovale is posterolateral to the foramen rotundum and anteromedial to the foramen spinosum. Posterior and medial to the foramen is the opening for the carotid canal
The carotid canal is a passage in the petrous part of the temporal bone of the skull through which the internal carotid artery and its internal carotid (nervous) plexus pass from the neck into (the middle cranial fossa of) the cranial cavity.
...
.
Contents
The following structures pass through foramen ovale: * mandibular nerve (CN V) (a branch of the trigeminal nerve (CN V)) *accessory meningeal artery
Accessory may refer to:
* Accessory (legal term), a person who assists a criminal
In anatomy
* Accessory bone
* Accessory breast
* Accessory kidney
* Accessory muscle
* Accessory nucleus, in anatomy, a cranial nerve nucleus
* Accessory nerve
* ...
* lesser petrosal nerve (a branch of the glossopharyngeal nerve
The glossopharyngeal nerve (), also known as the ninth cranial nerve, cranial nerve IX, or simply CN IX, is a cranial nerve that exits the brainstem from the sides of the upper Medulla oblongata, medulla, just anterior (closer to the nose) to t ...
)
* an emissary vein connecting the cavernous sinus
The cavernous sinus within the human head is one of the dural venous sinuses creating a cavity called the lateral sellar compartment bordered by the temporal bone of the skull and the sphenoid bone, lateral to the sella turcica.
Structure
The ...
with the pterygoid plexus
* (occasionally) meningeal branch of the mandibular nerve
Variation
In a study conducted on 100 skulls, the foramen ovale was divided into 2 or 3 components in 4.5% of the cases. The borders of the foramen in some skulls were also irregular and rough. This may suggest, based on radiological images, the presence of morbid changes, which might be the sole anatomical variation in the foramina ovalia of humans. In newborn, the foramen ovale is about 3.85 mm and in the adults about 7.2 mm in length. The average maximal length is about 7.48 mm and its average minimal length is 4.17 mm in the adult. The width extends from 1.81 mm in the newborn to 3.7 mm in adults.Development
Similar to other foramina, the foramen ovale differs in shape and size throughout life. In a study using over 350 skulls, the earliest perfect ring-shaped formation of the foramen ovale was observed in the 7th month of fetal life, and the latest in 3 years after birth.Clinical significance
The foramen ovale is used as the entry point into the skull when conducting a Percutaneous Rhizotomy using either radio-frequency ablation, balloon compression or glycerol injection. These are performed to treat trigeminal neuralgia. In the procedure, the electrode is introduced through the cheek of an anesthetized patient and radiologically guided into the foramen ovale, with the intention of partially or fully ablating one or more of the divisions (typically the Mandibular) to relieve pain. This entry point is also used to surgically place local electrodes directly on the surface of the mesial temporal lobe, in order to observe neural activity of patients with suspected focal epilepsy.History
Etymology
The name "foramen ovale" comes from theLatin
Latin ( or ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic languages, Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally spoken by the Latins (Italic tribe), Latins in Latium (now known as Lazio), the lower Tiber area aroun ...
"oval hole / window".
See also
*Foramina of the skull
This article lists Foramen, foramina that occur in the human body.
__TOC__
Skull
The human skull has numerous openings (foramen, foramina), through which cranial nerves, arteries, veins, and other structures pass. These foramina vary in siz ...
References
External links
* * () *Adult skull as seen from beneath at uiuc.edu
{{Authority control Foramina of the skull