|
Govinda IV
Govinda IV (reigned 930–936 CE) was the younger brother of Amoghavarsha II. He became the Rashtrakuta emperor in 930 as described in the Kalasa record of Chikmagalur. He was a very unpopular ruler who indulged in licentious acts. Control over Kannauj was lost during his rule. The Chalukyas of Vengi defeated him and much territory was lost. Finally, his own vassals including King Arikesari of Vemulavada revolted against him and placed Amoghavarsha III on the throne in 935. This is known from the records of Kannada poet Adikavi Pampa, who was patronised by King Arikesari.Kamath 2001, p. 82 Govinda IV patronised Kannada poet Ravinagabhatta. Name and Attestations A Kannada Kannada () is a Dravidian language spoken predominantly in the state of Karnataka in southwestern India, and spoken by a minority of the population in all neighbouring states. It has 44 million native speakers, and is additionally a ... form of his name, ''Gojjiga'', is attested in c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rashtrakuta Empire
The Rashtrakuta Empire was a royal Indian polity ruling large parts of the Indian subcontinent between the 6th and 10th centuries. The earliest known Rashtrakuta inscription is a 7th-century copper plate grant detailing their rule from Manapur, a city in Central or West India. Other ruling Rashtrakuta clans from the same period mentioned in inscriptions were the kings of Achalapur and the rulers of Kannauj. Several controversies exist regarding the origin of these early Rashtrakutas, their native homeland and their language. The Elichpur clan was a feudatory of the Badami Chalukyas, and during the rule of Dantidurga, it overthrew Chalukya Kirtivarman II and went on to build an empire with the Gulbarga region in modern Karnataka as its base. This clan came to be known as the Rashtrakutas of Manyakheta, rising to power in South India in 753 AD. At the same time the Pala dynasty of Bengal and the Prathihara dynasty of Gurjaratra were gaining force in eastern and northweste ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Adikavi Pampa
Pampa (), also referred to by the honorific Ādikavi ("First Poet"), was a Kannada-language Jain poet whose works reflected his philosophical beliefs. He was a court poet of Vemulavada Chalukya king Arikesari II, who was a feudatory of the Rashtrakuta Emperor Krishna III. Pampa is best known for his epics or ''Pampa Bharata'', and the ''Ādi purāṇa'', both written in the '' champu'' style around . These works served as the model for all future ''champu'' works in Kannada. The works of Jain writers Pampa, Ponna and Ranna, collectively called the "Three gems of Kannada literature", heralded the 10th century era of medieval Kannada literature. Early life There are varying opinions about the early life and native language of Pampa. While it is commonly believed Pampa belonged to a Brahmin family that took to Jainism, their actual place of origin and native is debated. According to the trilingual inscription (in Sanskrit, Kannada and Telugu) installed by Pampa's younge ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rashtrakuta Emperors
The Rashtrakuta Empire was a royal Indian polity ruling large parts of the Indian subcontinent between the 6th and 10th centuries. The earliest known Rashtrakuta inscription is a 7th-century copper plate grant detailing their rule from Manapur, a city in Central or West India. Other ruling Rashtrakuta clans from the same period mentioned in inscriptions were the kings of Achalapur and the rulers of Kannauj. Several controversies exist regarding the origin of these early Rashtrakutas, their native homeland and their language. The Elichpur clan was a feudatory of the Badami Chalukyas, and during the rule of Dantidurga, it overthrew Chalukya Kirtivarman II and went on to build an empire with the Gulbarga region in modern Karnataka as its base. This clan came to be known as the Rashtrakutas of Manyakheta, rising to power in South India in 753 AD. At the same time the Pala dynasty of Bengal and the Prathihara dynasty of Gurjaratra were gaining force in eastern and northwestern ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
10th-century Indian Monarchs
1 (one, unit, unity) is a number, numeral, and glyph. It is the first and smallest positive integer of the infinite sequence of natural numbers. This fundamental property has led to its unique uses in other fields, ranging from science to sports, where it commonly denotes the first, leading, or top thing in a group. 1 is the unit of counting or measurement, a determiner for singular nouns, and a gender-neutral pronoun. Historically, the representation of 1 evolved from ancient Sumerian and Babylonian symbols to the modern Arabic numeral. In mathematics, 1 is the multiplicative identity, meaning that any number multiplied by 1 equals the same number. 1 is by convention not considered a prime number. In digital technology, 1 represents the "on" state in binary code, the foundation of computing. Philosophically, 1 symbolizes the ultimate reality or source of existence in various traditions. In mathematics The number 1 is the first natural number after 0. Each natural number, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hindu Monarchs
Hindus (; ; also known as Sanātanīs) are people who religiously adhere to Hinduism, also known by its endonym Sanātana Dharma.Jeffery D. Long (2007), A Vision for Hinduism, IB Tauris, , pp. 35–37 Historically, the term has also been used as a geographical, cultural, and later religious identifier for people living in the Indian subcontinent. It is assumed that the term ''"Hindu"'' traces back to Avestan scripture Vendidad which refers to land of seven rivers as Hapta Hendu which itself is a cognate to Sanskrit term ''Sapta Sindhuḥ''. (The term ''Sapta Sindhuḥ'' is mentioned in Rig Veda and refers to a North western Indian region of seven rivers and to India as a whole.) The Greek cognates of the same terms are "''Indus''" (for the river) and "''India''" (for the land of the river). Likewise the Hebrew cognate ''hōd-dū'' refers to India mentioned in Hebrew BibleEsther 1:1. The term "''Hindu''" also implied a geographic, ethnic or cultural identifier for people ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bhima III
Bhima (, ), also known as Bhimasena (, ), is a hero and one of the most prominent characters in the Hindu epic ''Mahabharata''. As the second of the five Pandava brothers, Bhima was born to Kunti—the wife of King Pandu—fathered by Vayu, the wind god, which bestowed upon him superhuman strength from birth. His rivalry with the Kauravas, especially Duryodhana, defined much of his life, with this tension ultimately erupting in the Kurukshetra War, where Bhima killed all hundred Kaurava brothers. Bhima's life was filled with extraordinary episodes that showcased his strength and bravery. From childhood, where he was poisoned, to his victories over formidable foes like Bakasura, Hidimba, and Jarasandha, Bhima's adventures are integral to the ''Mahabharata''’s storyline. His raw, earthy nature is reflected in the brutal slaying of his enemies, his immense appetite and his marriage with Hidimbi, a rakshasi (a demoness), who bore him a son, Ghatotkacha, a powerful warrior who woul ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amma I
Amma or AMMA may refer to: Acronym * Amhara Mass Media Agency (created in 1993), a media organisation in Amhara Region in Ethiopia * All Malaysia Malayalee Association * American Mask Manufacturers Association * American Medical Marijuana Association * Association of Malayalam Movie Artists * Assistant Masters' and Mistresses' Association, former British trade union People * Anasuya Devī (1923–1985), Indian spiritual guru * J. Jayalalithaa (1948–2016), Former Chief Minister of Tamil Nadu * Mata Amritanandamayi (born 1953), Indian spiritual guru known as "the hugging saint" * Amma Sri Karunamayi (born 1958), Indian spiritual guru * Amma Asante (born 1969), British screenwriter and director * Amma Asante (politician) (born 1972), Dutch politician * Kollakkayil Devaki Amma (born ), Indian forester Film * ''Amma'' (1949 film), a Sri Lankan film * ''Amma'' (1952 film), an Indian Malayalam film * ''Amma'' (1968 film), an Indian Kannada film * ''Amma'' (1976 film) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eastern Chalukyas
Eastern Chalukyas, also known as the Chalukyas of Vengi, were a dynasty that ruled parts of South India between the 7th and 12th centuries. They started out as governors of the Chalukyas of Badami in the Deccan region. Subsequently, they became a sovereign power, and ruled the Vengi region of present-day Andhra Pradesh until . They continued ruling the region as feudatories of the Medieval Cholas until 1189 CE. Originally, the capital of the Eastern Chalukyas was located at Pishtapura (modern-day Pitapuram). It was subsequently moved to Vengi (present-day Pedavegi, near Eluru) and then to Rajamahendravaram (now Rajahmundry). Throughout their history, the Eastern Chalukyas were the cause of many wars between the more powerful Cholas and Western Chalukyas over the control of the strategically important Vengi country. The five centuries of the Eastern Chalukya rule of Vengi saw not only the consolidation of this region into a unified whole, but also saw the efflorescence ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sangli
Sangli (ISO 15919, ISO: ''Sāṁgalī''; ) is a metropolitan town and the headquarters of Sangli District in Maharashtra, in south-western India. It has earned the nickname "Turmeric City of India" for being the hub of the Asia's largest production and trade of this spice. Sangli is situated on the banks of river Krishna and houses many Sugar refinery, sugar factories. A significant city in South-Western India, it lies 376 km from Mumbai, 230 km from Pune and 638 km from Bangalore. The city has a significant healthcare hub, including its twin City Miraj. Sangli-Miraj combined has more than 1000+ Hospitals and Clinics. Sangli is known as Turmeric city for its global turmeric trade as well grapes, raisins, jaggery and the most significant number of sugar factories in India, with district area having has more than 30 sugar factories. The Sangli region boasts the largest raisin market in Asia. Sangli-Miraj-Kupwad municipal corporation (SMKMC) along with its Urban Aggl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
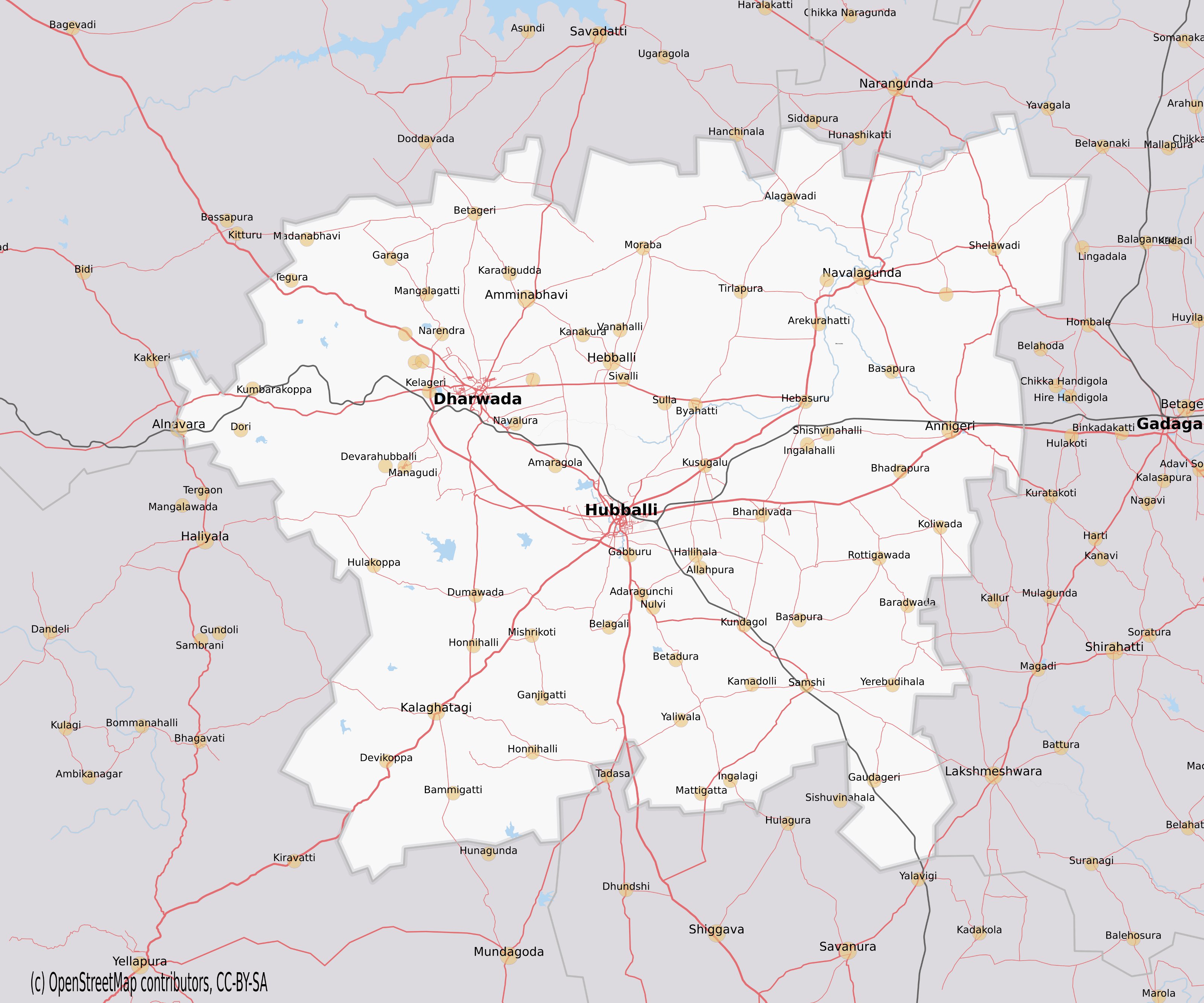
Dharwad District
Dharwad or Dharawada is an administrative district of the state of Karnataka in southern India. The administrative headquarters of the district is the city of Dharwad, also known as Dharwar. Dharwad is located 425 km northwest of Bangalore and 421 km southeast of Pune, on the main highway between Chennai and Pune, the National Highway 4 (India, old numbering), National Highway 4 (NH4). Before 1997 the district had an area of 13738 km2. In 1997, the new districts of Gadag district, Gadag and Haveri district, Haveri were carved out of Dharwad's former territory, and a portion of Dharwad district was combined with lands formerly part of three other districts to create the new district of Davanagere. History Historical studies show that people from Lower Paleolithic, early Paleolithic age inhabited Dharwad district. The district was ruled by various dynasties from the 5th century onwards, Important among them are Badami Chalukya architecture, Badami and Kalyan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dharwad
Dharwad (), also known as Dharwar, is a city located in the northwestern part of the Indian state of Karnataka. It is the headquarters of the Dharwad district of Karnataka and forms a contiguous urban area with the city of Hubballi. It was merged with Hubballi in 1962 to form the twin cities of Hubballi–Dharwad, Hubballi-Dharwad. It covers an area of and is located northwest of Bangalore, on National Highway 48 (India), NH-48, between Bangalore and Pune. In 2016, Hubli-Dharwad was selected for solar city / green city master plans. In 2017, government of India included Hubli-Dharwad city for a Smart Cities Mission, smart city project, a flagship scheme for overall development of infrastructure in the twin-cities. Etymology The word "Dharwad" is derived from the Sanskrit word 'dwarawata', 'dwara', meaning "door" and 'wata' or 'wada' meaning "town." It means a place of rest in a long travel or a small habitation. For centuries, Dharwad acted as a resting place for travelers and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kannada
Kannada () is a Dravidian language spoken predominantly in the state of Karnataka in southwestern India, and spoken by a minority of the population in all neighbouring states. It has 44 million native speakers, and is additionally a second or third language for 15 million speakers in Karnataka. It is the official and administrative language of Karnataka. It also has scheduled status in India and has been included among the country's designated classical languages.Kuiper (2011), p. 74R Zydenbos in Cushman S, Cavanagh C, Ramazani J, Rouzer P, ''The Princeton Encyclopedia of Poetry and Poetics: Fourth Edition'', p. 767, Princeton University Press, 2012, Kannada was the court language of a number of dynasties and empires of South India, Central India and the Deccan Plateau, namely the Kadamba dynasty, Western Ganga dynasty, Nolamba dynasty, Chalukya dynasty, Rashtrakutas, Western Chalukya Empire, Seuna dynasty, kingdom of Mysore, Nayakas of Keladi, Ho ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |