|
Adikavi Pampa
Pampa (), also referred to by the honorific Ādikavi ("First Poet"), was a Kannada-language Jain poet whose works reflected his philosophical beliefs. He was a court poet of Vemulavada Chalukya king Arikesari II, who was a feudatory of the Rashtrakuta Emperor Krishna III. Pampa is best known for his epics or ''Pampa Bharata'', and the ''Ādi purāṇa'', both written in the '' champu'' style around . These works served as the model for all future ''champu'' works in Kannada. The works of Jain writers Pampa, Ponna and Ranna, collectively called the "Three gems of Kannada literature", heralded the 10th century era of medieval Kannada literature. Early life There are varying opinions about the early life and native language of Pampa. While it is commonly believed Pampa belonged to a Brahmin family that took to Jainism, their actual place of origin and native is debated. According to the trilingual inscription (in Sanskrit, Kannada and Telugu) installed by Pampa's younge ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
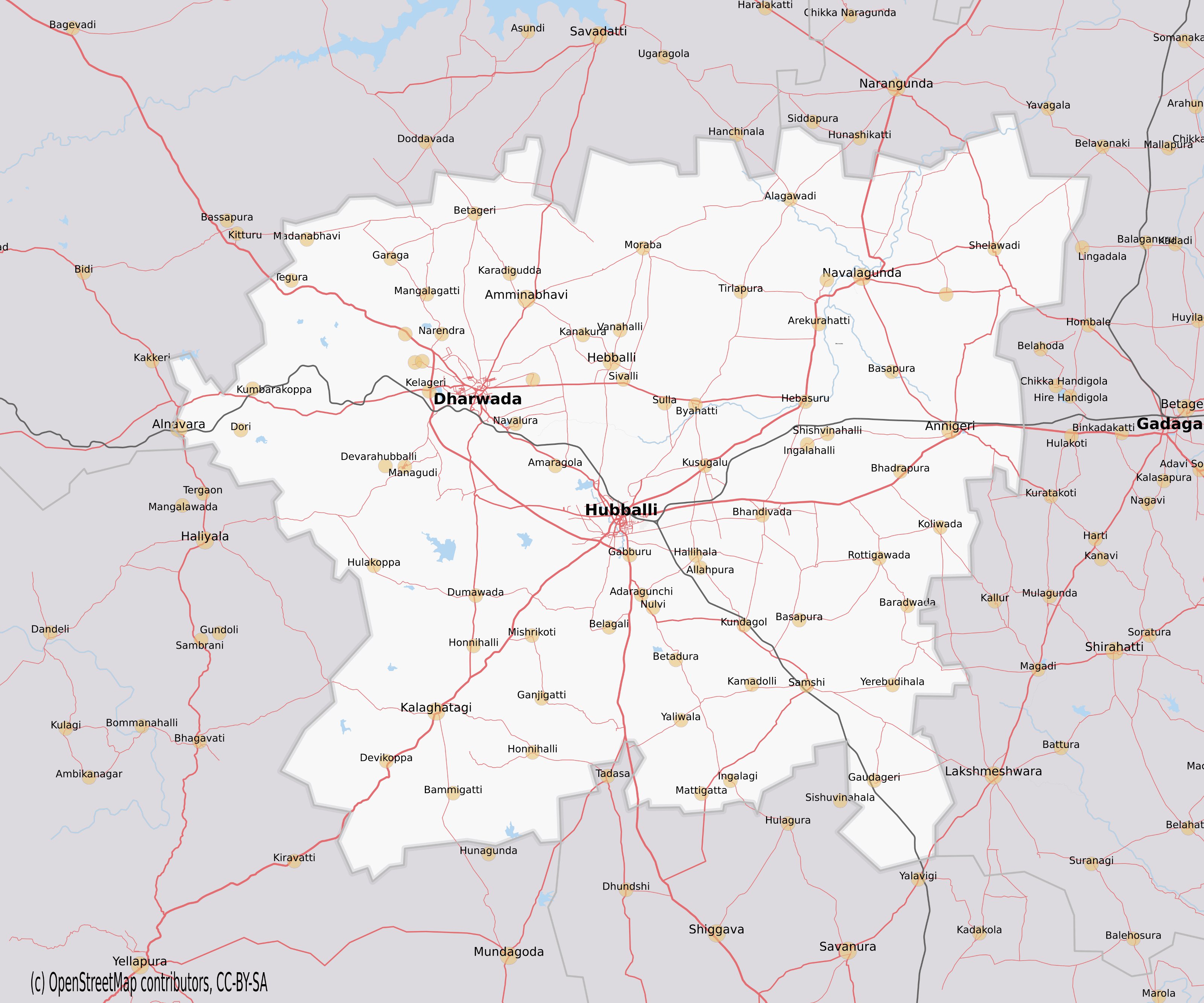
Annigeri
Annigeri is a taluk of Dharwad district in the state of Karnataka, India, located 20 km west of Gadag en route to Hubli and 35 km from Hubli. Introduction Annigeri ()is the place of birth of the famous Kannada poet Adikavi Pampa (). It is well known for the black stone temple built by the Western Chalukya Empire. known as Amruteshwara Temple. A temple of mythological figures supported by 76 columns, located in the Dharwad district, and has a derasar dedicated to Parshva, the 23rd Tirthankara in Jainism. Annigeri also has temples dedicated to Banashankari, Basappa, Gajina Basappa and Hanuman. There is an ancient Lingayati temple near the railway station. Annigeri has seven mosques and two Lingayatism, Lingayati Mathas. History Annigeri was an important political and cultural center in the past. Various kings like the Chalukya dynasty, Seuna Yadavas of Devagiri and the Hoysala Empire annexed the town, which once formed part of the kingdoms of the Kalachuris of Kalyani ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Telangana
Telangana is a States and union territories of India, state in India situated in the Southern India, south-central part of the Indian subcontinent on the high Deccan Plateau. It is the List of states and union territories of India by area, eleventh largest state by area and the List of states and union territories of India by population, twelfth most populated state in India, according to the 2011 Census of India, 2011 census. On 2 June 2014, the area was separated from the northwestern part of United Andhra Pradesh as the newly formed States and union territories of India, state of Telangana, with Hyderabad as its capital. Telugu language, Telugu, one of the classical languages of India, is the most widely spoken and the primary official language of Telangana state, whereas Urdu is recognised as the second official language. Additionally, several tribal languages such as Gondi, Kolami, Koya and Lambadi are spoken in different regions of the Telangana state. The economy of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Moksha (Jainism)
Sanskrit ' or Prakrit ''mokkha'' refers to the liberation or salvation of a soul from ''Saṃsāra (Jainism), saṃsāra'', the cycle of birth and death. It is a blissful state of existence of a soul, attained after the destruction of all Karma in Jainism, karmic bonds. A liberated soul is said to have attained its true and pristine nature of Unlimited bliss, Unlimited knowledge and Unlimited perception. Such a soul is called ''Siddha#Siddha in Jainism, siddha'' and is revered in Jainism. In Jainism, ''moksha'' is the highest and the noblest objective that a soul should strive to achieve. In fact, it is the only objective that a person should have; other objectives are contrary to the true nature of soul. With the right view, knowledge and efforts all souls can attain this state. That is why Jainism is also known as ' or the "path to liberation". According to the Sacred Jain Text, Tattvartha sutra: Bhavyata From the point of view of potentiality of , Jain texts bifurcates t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
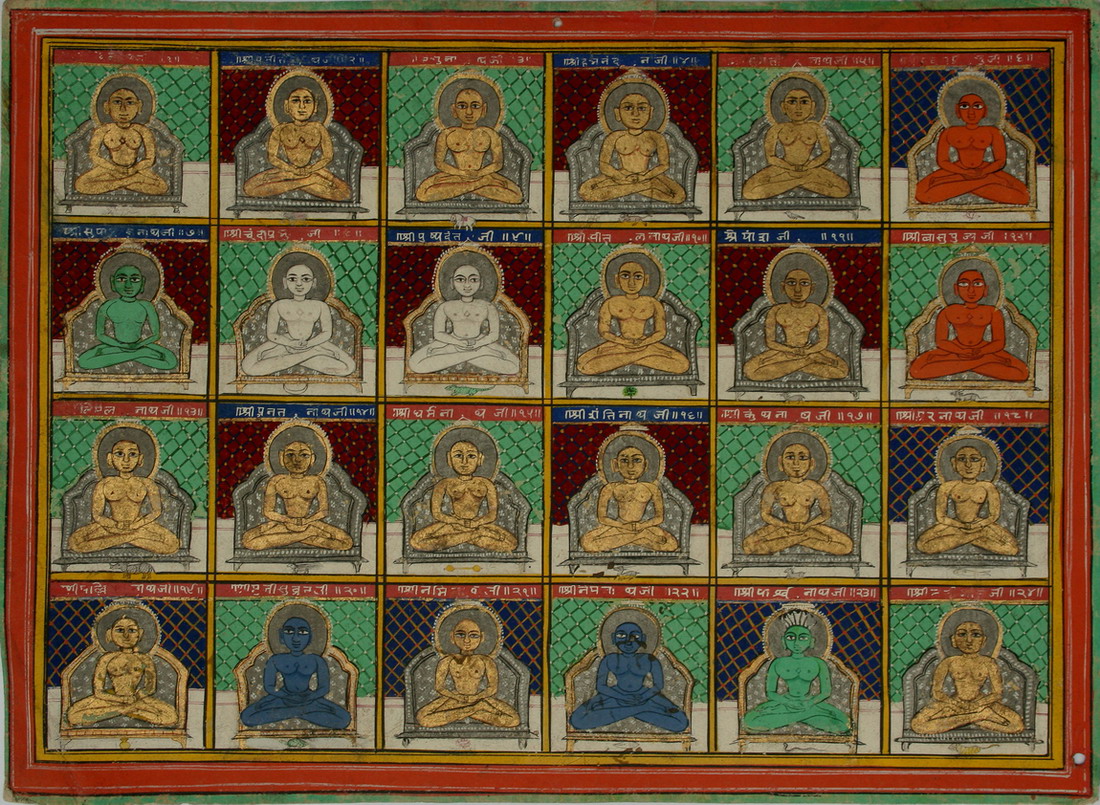
Rishabha
Rishabhanatha (Devanagari: ऋषभनाथ), also Rishabhadeva (Devanagari: ऋषभदेव, ), Rishabha (Devanagari: ऋषभ, ) or Ikshvaku (Devanagari: इक्ष्वाकु, ''Ikṣvāku''), is the first (Supreme preacher) of Jainism. He was the first of twenty-four teachers in the present half-cycle of time in Jain cosmology and called a "ford maker" because his teachings helped one cross the sea of interminable rebirths and deaths. The legends depict him as having lived millions of years ago. He was the spiritual successor of Sampratti Bhagwan, the last Tirthankara of the previous time cycle. He is also known as Ādinātha (), as well as Adishvara (first Jina), Yugadideva (first deva of the yuga), Prathamarajeshwara (first God-king) and Nabheya (son of Nabhi). He is also known as Ikshvaku, establisher of the Ikshvaku dynasty. Along with Mahavira, Parshvanath, Neminath, and Shantinath, Rishabhanatha is one of the five Tirthankaras that attract the most ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jainism
Jainism ( ), also known as Jain Dharma, is an Indian religions, Indian religion whose three main pillars are nonviolence (), asceticism (), and a rejection of all simplistic and one-sided views of truth and reality (). Jainism traces its spiritual ideas and history through the succession of twenty-four , supreme preachers of ''dharma''. The first in the current time cycle is Rishabhadeva, who tradition holds lived millions of years ago; the 23rd is Parshvanatha, traditionally dated to the 9th century Common Era, BCE; and the 24th is Mahāvīra, Mahavira, who lived . Jainism is considered an eternal ''dharma'' with the guiding every time cycle of the Jain cosmology, cosmology. Central to understanding Jain philosophy is the concept of ''bhedavijñāna'', or the clear distinction in the nature of the soul and non-soul entities. This principle underscores the innate purity and potential for liberation within every Jīva (Jainism), soul, distinct from the physical and menta ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tirthankara
In Jainism, a ''Tirthankara'' (; ) is a saviour and supreme preacher of the ''Dharma (Jainism), dharma'' (righteous path). The word ''tirthankara'' signifies the founder of a ''Tirtha (Jainism), tirtha'', a fordable passage across ''Saṃsāra (Jainism), saṃsāra'', the sea of interminable birth and death. According to Jains, ''tirthankaras'' are the supreme preachers of ''dharma'', who have conquered ''saṃsāra'' on their own and made a path for others to follow. After understanding the true nature of the self or soul, the ''Tīrthaṅkara'' attains ''kevala jnana'' (omniscience). A Tirthankara provides a bridge for others to follow them from ''saṃsāra'' to ''moksha'' (liberation). In Jain cosmology, the wheel of time is divided into two halves, Utsarpiṇī', the ascending time cycle, and ''avasarpiṇī'', the descending time cycle (said to be current now). In each half of the cycle, exactly 24 ''tirthankaras'' grace this part of the universe. There have been infini ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jinasena
Acharya Jinasena II (c. 9th century CE) was a monk and scholar in the ''Digambara'' tradition of Jainism. He was patronized by the Rashtrakuta Emperor Amoghavarsha I. He was the author of ''Adipurana'' and '' Mahapurana''.Early medieval developments (500–1100) Encyclopaedia Britannica Jinasena II was the disciple of '' Acharya Virasena'' and he completed the commentary '' Dhavala'' on '''', a revered text in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Uttara Kannada District
Uttara Kannada is a fifth largest district in the Indian state of Karnataka, It is bordered by the state of Goa and Belagavi districts to the north, Dharwad District and Haveri District to the east, Shivamogga District, and Udupi District to the south, and the Laccadive Sea to the west. Karwar is the district headquarters, and Sirsi is the major commercial center in the district. The district's agroclimatic divisions include the coastal plain consisting of Karwar, Ankola, Kumta, Honnavar, Bhatkal taluks and Malenadu consisting of Sirsi, Siddapur, Yellapur, Haliyal, Dandeli, Joida, Mundgod taluks. History The first known dynasty from Uttara Kannada District are Chutus of Banavasi. Uttara Kannada was the home of the Kadamba kingdom from the 350 to 525. They ruled from Banavasi. After the subjugation of the Kadambas by the Chalukyas, the district came under successive rule of empires like Chalukyas, Rashtrakutas, Hoysalas and Vijayanagar empire. Moroccan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Banavasi
Banavasi is an ancient temple town located near Sirsi in Karnataka. Banavasi was the ancient capital of the Kadamba dynasty that ruled all of modern-day Karnataka state. They were the first native empire to bring Kannada and Karnataka to prominence. It is away from its nearest large city Sirsi through SH 77. History Banavasi is one of the oldest town in the Karnataka state. It has grown up around the Madhukeshwara Temple built in the 5th century and dedicated to Shiva the supreme God in Shaivism, a major branch of Hinduism. 5th-century copper coin was discovered here with an inscription in the Kannada script The Kannada script ( IAST: ''Kannaḍa lipi''; obsolete: Kanarese or Canarese script in English) is an abugida of the Brahmic family, used to write Kannada, one of the Dravidian languages of South India especially in the state of Karnataka. I ..., one of the oldest such coins ever discovered. Adikavi Pampa, the first poet of Kannada, wrote his epics in Banav ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dharwad District
Dharwad or Dharawada is an administrative district of the state of Karnataka in southern India. The administrative headquarters of the district is the city of Dharwad, also known as Dharwar. Dharwad is located 425 km northwest of Bangalore and 421 km southeast of Pune, on the main highway between Chennai and Pune, the National Highway 4 (India, old numbering), National Highway 4 (NH4). Before 1997 the district had an area of 13738 km2. In 1997, the new districts of Gadag district, Gadag and Haveri district, Haveri were carved out of Dharwad's former territory, and a portion of Dharwad district was combined with lands formerly part of three other districts to create the new district of Davanagere. History Historical studies show that people from Lower Paleolithic, early Paleolithic age inhabited Dharwad district. The district was ruled by various dynasties from the 5th century onwards, Important among them are Badami Chalukya architecture, Badami and Kalyan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Varada
The Varada River (Verada River) is a river in central Karnataka, India. It originates in Varadamoola . It is a tributary of the Tungabhadra River. Geography The Varada river originates near Vardamoola in Sagara of Karnataka. It flows through the Western Ghats and enters the central districts of Karnataka, (Haveri and Bellary). The river joins the Tungabhadra River at Galaganath.Topographic ma"Davangere, India, ND-43-07, 1:250,000"Series U502, Army Map Service, November 1958 It is important to the wellbeing of the Kannada people along its course. Dams have been constructed along the river's course, providing water for irrigation and domestic purposes during summer. There are, however, no major irrigation projects on this river, although the government is considering one. Cultural significance The river has divine Divinity (from Latin ) refers to the quality, presence, or nature of that which is divine—a term that, before the rise of monotheism, evoked a bro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hampa Nagarajaiah
Hampa or Hompa () may refer to: Places * Hampa, East Azerbaijan * Hampa, West Azerbaijan Titles * Hompa, in the traditional leadership of Namibia a king of a tribe or clan {{Disambiguation, geo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |