|
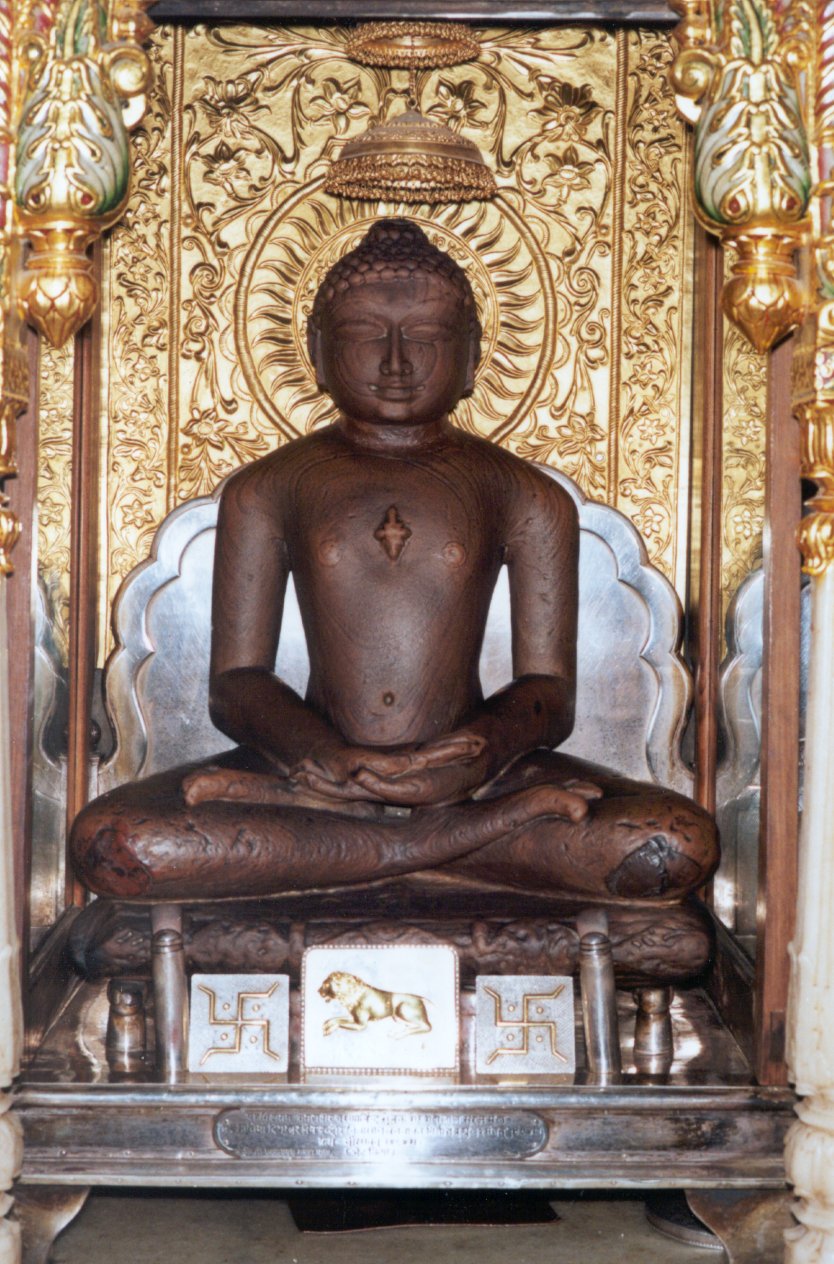
Virasena
Acharya Virasena (792-853 CE), also spelt as Veerasena, was a Digambara monk and belonged to the lineage of Acharya Kundakunda. He was an Indian mathematician and Jain philosopher and scholar. He was also known as a famous orator and an accomplished poet. His most reputed work is the Jain treatise '' Dhavala''. The late Dr. Hiralal Jain places the completion of this treatise in 816 AD. Virasena was a noted mathematician. He gave the derivation of the volume of a frustum by a sort of infinite procedure. He worked with the concept of ''ardhachheda'': the number of times a number can be divided by 2. This coincides with the binary logarithm when applied to powers of two, but gives the 2-adic order rather than the logarithm for other integers. Virasena gave the approximate formula ''C'' = 3''d'' + (16''d''+16)/113 to relate the circumference of a circle, ''C'', to its diameter, ''d''. For large values of ''d'', this gives the approximation π ≈ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jinasena
Acharya Jinasena II (c. 9th century CE) was a monk and scholar in the ''Digambara'' tradition of Jainism. He was patronized by the Rashtrakuta Emperor Amoghavarsha I. He was the author of ''Adipurana'' and '' Mahapurana''.Early medieval developments (500–1100) Encyclopaedia Britannica Jinasena II was the disciple of '' Acharya Virasena'' and he completed the commentary '' Dhavala'' on '''', a revered text in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Digambara Acharyas
''Digambara'' (; "sky-clad") is one of the two major schools of Jainism, the other being ''Śvetāmbara'' (white-clad). The Sanskrit word ''Digambara'' means "sky-clad", referring to their traditional monastic practice of neither possessing nor wearing any clothes. Nakedness was the ideal practice of lord Mahavira and his immediate followers. Mahavira emphasized the importance of nakedness for monks. It symbolizes complete detachment and is an ideal form of conduct. Mahavira believed that renouncing clothes made the body immune to external influences like heat and cold, increasing resilience. Without clothes, a monk would avoid the distractions of acquiring, maintaining, and washing garments, allowing him to focus on spiritual growth and self-discipline. Digambara and Śvetāmbara traditions have had historical differences ranging from their dress code, their temples and iconography, attitude towards female monastics, their legends, and the texts they consider as important. Di ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Digambara
''Digambara'' (; "sky-clad") is one of the two major Jain schools and branches, schools of Jainism, the other being ''Śvetāmbara'' (white-clad). The Sanskrit word ''Digambara'' means "sky-clad", referring to their traditional monastic practice of neither possessing nor wearing any clothes. Nakedness was the ideal practice of lord Mahavira and his immediate followers. Mahavira emphasized the importance of nakedness for monks. It symbolizes complete detachment and is an ideal form of conduct. Mahavira believed that renouncing clothes made the body immune to external influences like heat and cold, increasing resilience. Without clothes, a monk would avoid the distractions of acquiring, maintaining, and washing garments, allowing him to focus on spiritual growth and self-discipline. Digambara and Śvetāmbara traditions have had historical differences ranging from their dress code, their temples and iconography, attitude towards female monastics, their legends, and the texts the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shatakhandagama
The (Prakrit: "Scripture in Six Parts") is the only canonical piece of literature of Digambara sect of Jainism. According to Digambara tradition, the original teachings of lord Mahavira were passed on orally from Ganadhar, the chief disciple of Mahavira to his disciples and so on as they had the capability of listening and remembering it for always. But as the centuries passed there was downfall in these capabilities and so Ācārya Puṣpadanta and Bhūtabali penned down the teachings of Mahavira in ''Ṣaṭkhaṇḍāgama''. Therefore the ''Ṣaṭkhaṇḍāgama'' is the most revered Digambara text that has been given the status of '' āgama''. The importance of the ''Ṣaṭkhaṇḍāgama'' to the Digambaras can be judged by the fact that, the day its ''Dhavalā'' commentary was completed, it is commemorated on the ''Śrūta Pañcamī'', a day when all the Jain scriptures are venerated. The ''Ṣaṭkhaṇḍāgama'', the first ''āgama'', is also called the "Prathama ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Indian Mathematics
Indian mathematics emerged in the Indian subcontinent from 1200 BCE until the end of the 18th century. In the classical period of Indian mathematics (400 CE to 1200 CE), important contributions were made by scholars like Aryabhata, Brahmagupta, Bhaskara II, Varāhamihira, and Madhava of Sangamagrama, Madhava. The Decimal, decimal number system in use today: "The measure of the genius of Indian civilisation, to which we owe our modern (number) system, is all the greater in that it was the only one in all history to have achieved this triumph. Some cultures succeeded, earlier than the Indian, in discovering one or at best two of the characteristics of this intellectual feat. But none of them managed to bring together into a complete and coherent system the necessary and sufficient conditions for a number-system with the same potential as our own." was first recorded in Indian mathematics. Indian mathematicians made early contributions to the study of the concept of 0 (number), ze ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dhavala
The (Prakrit: "Scripture in Six Parts") is the only canonical piece of literature of Digambara sect of Jainism. According to Digambara tradition, the original teachings of lord Mahavira were passed on orally from Ganadhar, the chief disciple of Mahavira to his disciples and so on as they had the capability of listening and remembering it for always. But as the centuries passed there was downfall in these capabilities and so Ācārya Puṣpadanta and Bhūtabali penned down the teachings of Mahavira in ''Ṣaṭkhaṇḍāgama''. Therefore the ''Ṣaṭkhaṇḍāgama'' is the most revered Digambara text that has been given the status of '' āgama''. The importance of the ''Ṣaṭkhaṇḍāgama'' to the Digambaras can be judged by the fact that, the day its ''Dhavalā'' commentary was completed, it is commemorated on the ''Śrūta Pañcamī'', a day when all the Jain scriptures are venerated. The ''Ṣaṭkhaṇḍāgama'', the first ''āgama'', is also called the "Prathama ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Binary Logarithm
In mathematics, the binary logarithm () is the exponentiation, power to which the number must be exponentiation, raised to obtain the value . That is, for any real number , :x=\log_2 n \quad\Longleftrightarrow\quad 2^x=n. For example, the binary logarithm of is , the binary logarithm of is , the binary logarithm of is , and the binary logarithm of is . The binary logarithm is the logarithm to the base and is the inverse function of the power of two function. There are several alternatives to the notation for the binary logarithm; see the #Notation, Notation section below. Historically, the first application of binary logarithms was in music theory, by Leonhard Euler: the binary logarithm of a frequency ratio of two musical tones gives the number of octaves by which the tones differ. Binary logarithms can be used to calculate the length of the representation of a number in the binary numeral system, or the number of bits needed to encode a message in infor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kashtha Sangha
Kashtha Sangha (काष्ठा संघ) was a Digambar Jain monastic order once dominant in several regions of North and Western India. It is considered to be a branch of Mula Sangh itself. It is said to have originated from a town named Kashtha. Origin The origin of Kashtha Sangha is often attributed to Lohacharya in several texts and inscriptions from Delhi region. The Kashtasangh Gurvavali identifies Lohacharya as the last person who knew Acharanga in the Digambara tradition, who lived until the 683rd year of the nirvana of Lord Mahavira. the Darshanasara of Devasena (VS 990) attributes the origin to Kumarasena in Vikram Samvat 753. Acharya Chandrasena initiated Aryanandi. Aryanandi initiated Virasena and Jayasena. Virasena initiated six disciples who were Dasharayguru, Jinasena, Vinayasena, Shripal, Padmasena and Devasena. Dasharayguru and Jinasena initiated Gunabhadra who later initiated Lokasena. Vinayasena initiated Kumarasena who started the Kashtha San ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amoghavarsha
Amoghavarsha I (also known as Amoghavarsha Nrupatunga I) (r. 814 – 878 CE) is considered by many historians to be the greatest emperor of the Rashtrakuta dynasty. His reign of 64 years is one of the longest precisely dated monarchical reigns on record. Many Kannada and Sanskrit scholars prospered during his rule, including the great Indian mathematician Mahaviracharya who wrote ''Ganita-sara-samgraha'', Jinasena, Virasena, Shakatayan and Sri Vijaya (a Kannada language theorist). Amoghavarsha I was an accomplished poet and scholar. He wrote (or co-authored) the '' Kavirajamarga'', the earliest extant literary work in Kannada,Sastri (1955), p. 355. and ''Prashnottara Ratnamalika'', a religious work in Sanskrit. During his rule he held titles such as ''Nrupathunga'', ''Atishadhavala'', ''Veeranarayana'', ''Rattamarthanda'' and ''Srivallabha''. He moved the Rashtrakuta regnal capital from Mayurkhandi in the present-day Bidar district to Manyakheta in the present-day Kal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
853 Deaths
__NOTOC__ Year 853 ( DCCCLIII) was a common year starting on Sunday of the Julian calendar. Events By place Byzantine Empire * May 22 – A Byzantine fleet (85 ships and 5,000 men) sacks and destroys the port city of Damietta, located on the Nile Delta in Egypt. A large quantity of weapons and supplies intended for the Emirate of Crete are captured. Europe * Danish Vikings attempt to subjugate the Curonians on the shoreline of the Baltic Sea, but they are repulsed. King Olof leads Swedish Vikings in retaliation, and attacks the towns of Seeburg and Apuolė (modern Courland). * Viking marauders in Gaul sail eastward from Nantes without opposition, and reach Tours. The monasteries at Saint-Florent-le-Vieil and Marmoutier are ravaged. * King Charles the Bald bribes Boris I, ruler ('' khan'') of the Bulgarian Empire, to form an alliance against his brother Louis the German, with Rastislav of Moravia.. * Gauzbert, count of Maine, is killed during an ambush by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
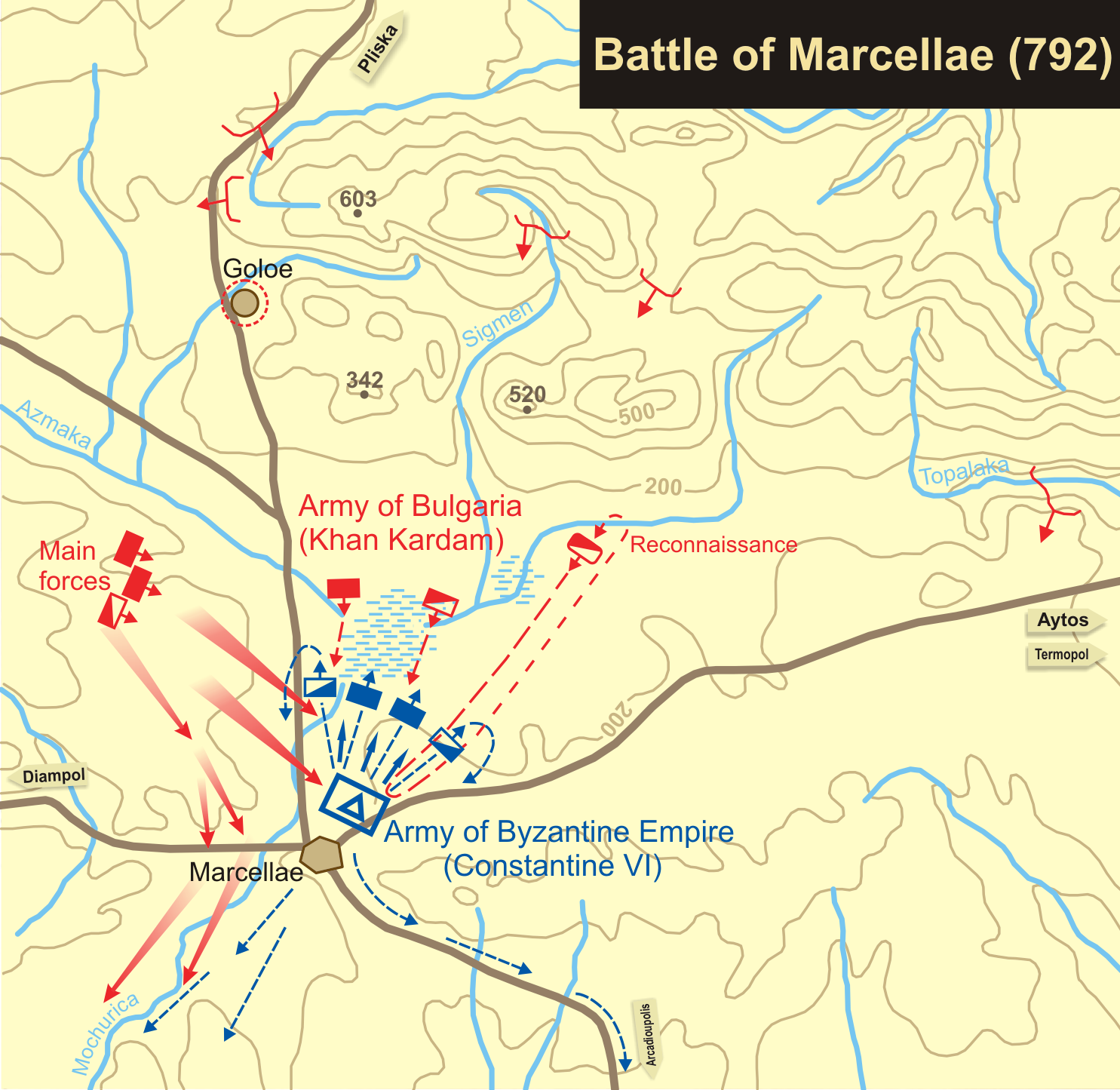
792 Births
__NOTOC__ Year 792 ( DCCXCII) was a leap year starting on Sunday of the Julian calendar, the 792nd year of the Common Era (CE) and Anno Domini (AD) designations, the 792nd year of the 1st millennium, the 92nd year of the 8th century, and the 3rd year of the 790s decade. The denomination 792 for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years. Events By place Byzantine Empire * Spring – Emperor Constantine VI suppresses a rebellion, and restores his mother Irene to her former position as co-empress of the Byzantine Empire. The rival factions in Constantinople continue their intrigues against Constantine. * Battle of Marcellae: Constantine VI leads a Byzantine expeditionary force into northern Thrace. At the border castle of Marcellae, near the modern town of Karnobat (Bulgaria), the Bulgarians under Kardam defeat the Byzantines. Europe * The Westphalians rise up ag ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |