|
Good–Turing Frequency Estimation
Good–Turing frequency estimation is a statistical technique for estimating the probability of encountering an object of a hitherto unseen species, given a set of past observations of objects from different species. In drawing balls from an urn, the 'objects' would be balls and the 'species' would be the distinct colours of the balls (finite but unknown in number). After drawing R_\text red balls, R_\text black balls and R_\text green balls, we would ask what is the probability of drawing a red ball, a black ball, a green ball or one of a previously unseen colour. Historical background Good–Turing frequency estimation was developed by Alan Turing and his assistant I. J. Good as part of their methods used at Bletchley Park for cracking German ciphers for the Enigma machine during World War II. Turing at first modelled the frequencies as a multinomial distribution, but found it inaccurate. Good developed smoothing algorithms to improve the estimator's accuracy. The discovery ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Statistical
Statistics (from German language, German: ', "description of a State (polity), state, a country") is the discipline that concerns the collection, organization, analysis, interpretation, and presentation of data. In applying statistics to a scientific, industrial, or social problem, it is conventional to begin with a statistical population or a statistical model to be studied. Populations can be diverse groups of people or objects such as "all people living in a country" or "every atom composing a crystal". Statistics deals with every aspect of data, including the planning of data collection in terms of the design of statistical survey, surveys and experimental design, experiments. When census data (comprising every member of the target population) cannot be collected, statisticians collect data by developing specific experiment designs and survey sample (statistics), samples. Representative sampling assures that inferences and conclusions can reasonably extend from the sample ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
AT&T
AT&T Inc., an abbreviation for its predecessor's former name, the American Telephone and Telegraph Company, is an American multinational telecommunications holding company headquartered at Whitacre Tower in Downtown Dallas, Texas. It is the world's List of telecommunications companies, third largest telecommunications company by revenue and the List of mobile network operators in the United States, third largest wireless carrier in the United States behind T-Mobile US, T-Mobile and Verizon. As of 2023, AT&T was ranked 32nd on the Fortune 500, ''Fortune'' 500 rankings of the largest United States corporations, with revenues of $122.4 billion. The modern company to bear the AT&T name began its history as the American District Telegraph Company, formed in St. Louis in 1878. After expanding services to Arkansas, Kansas, Oklahoma and Texas through a series of mergers, it became the Southwestern Bell Telephone Company in 1920. Southwestern Bell was a subsidiary of AT&T Corporation, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Categorical Data
In statistics, a categorical variable (also called qualitative variable) is a variable (research), variable that can take on one of a limited, and usually fixed, number of possible values, assigning each individual or other unit of observation to a particular group or nominal category on the basis of some qualitative property. In computer science and some branches of mathematics, categorical variables are referred to as enumerations or enumerated types. Commonly (though not in this article), each of the possible values of a categorical variable is referred to as a level. The probability distribution associated with a random variable, random categorical variable is called a categorical distribution. Categorical data is the statistical data type consisting of categorical variables or of data that has been converted into that form, for example as grouped data. More specifically, categorical data may derive from observations made of qualitative data that are summarised as counts or cros ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1953 Introductions
Events January * January 6 – The Asian Socialist Conference opens in Rangoon, Burma. * January 12 – Estonian émigrés found a Estonian government-in-exile, government-in-exile in Oslo. * January 14 ** Marshal Josip Broz Tito is chosen President of Socialist Federal Republic of Yugoslavia, Yugoslavia. ** The Central Intelligence Agency, CIA-sponsored Robertson Panel first meets to discuss the Unidentified flying object, UFO phenomenon. * January 15 ** Georg Dertinger, foreign minister of East Germany, is arrested for spying. ** British security forces in West Germany arrest 7 members of the Naumann Circle, a clandestine Neo-Nazi organization. * January 19 – 71.1% of all television sets in the United States are tuned into ''I Love Lucy'', to watch Lucy give birth to Little Ricky, which is more people than those who tune into Dwight Eisenhower's inauguration the next day. This record is never broken. * January 24 ** Mau Mau Uprising: Rebels in Kenya kill th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pseudocount
In statistics, additive smoothing, also called Laplace smoothing or Lidstone smoothing, is a technique used to smooth count data, eliminating issues caused by certain values having 0 occurrences. Given a set of observation counts \mathbf = \langle x_1, x_2, \ldots, x_d \rangle from a d-dimensional multinomial distribution with N trials, a "smoothed" version of the counts gives the estimator : \hat\theta_i = \frac \qquad (i = 1, \ldots, d), where the smoothed count \hat x_i = N \hat\theta_i, and the "pseudocount" ''α'' > 0 is a smoothing parameter, with ''α'' = 0 corresponding to no smoothing (this parameter is explained in below). Additive smoothing is a type of shrinkage estimator, as the resulting estimate will be between the empirical probability ( relative frequency) x_i/N and the uniform probability 1/d. Common choices for ''α'' are 0 (no smoothing), (the Jeffreys prior), or 1 (Laplace's rule of succession), but the parameter may also be set empir ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ewens Sampling Formula
In population genetics, Ewens's sampling formula describes the probabilities associated with counts of how many different alleles are observed a given number of times in the sample. Definition Ewens's sampling formula, introduced by Warren Ewens, states that under certain conditions (specified below), if a random sample of ''n'' gametes is taken from a population and classified according to the gene at a particular locus then the probability that there are ''a''1 alleles represented once in the sample, and ''a''2 alleles represented twice, and so on, is :\operatorname(a_1,\dots,a_n; \theta)=\prod_^n, for some positive number ''θ'' representing the population mutation rate, whenever a_1, \ldots, a_n is a sequence of nonnegative integers such that :a_1+2a_2+3a_3+\cdots+na_n=\sum_^ i a_i = n.\, The phrase "under certain conditions" used above is made precise by the following assumptions: * The sample size ''n'' is small by comparison to the size of the whole population; and * ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
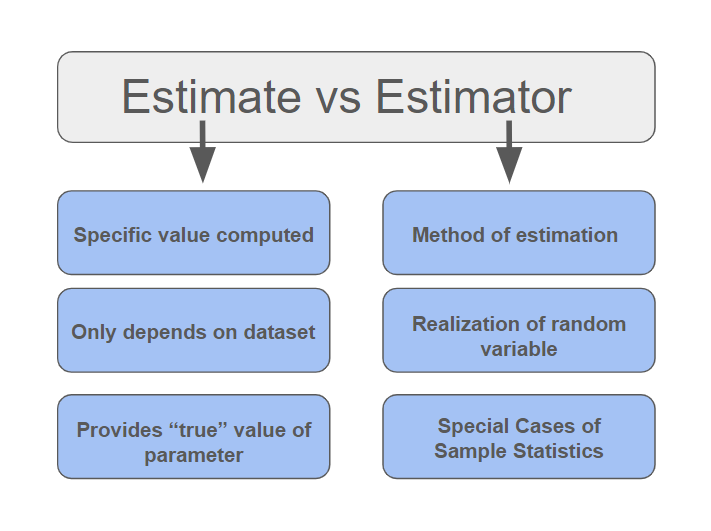
Estimator
In statistics, an estimator is a rule for calculating an estimate of a given quantity based on Sample (statistics), observed data: thus the rule (the estimator), the quantity of interest (the estimand) and its result (the estimate) are distinguished. For example, the sample mean is a commonly used estimator of the population mean. There are point estimator, point and interval estimators. The point estimators yield single-valued results. This is in contrast to an interval estimator, where the result would be a range of plausible values. "Single value" does not necessarily mean "single number", but includes vector valued or function valued estimators. ''Estimation theory'' is concerned with the properties of estimators; that is, with defining properties that can be used to compare different estimators (different rules for creating estimates) for the same quantity, based on the same data. Such properties can be used to determine the best rules to use under given circumstances. Howeve ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bernoulli Distribution
In probability theory and statistics, the Bernoulli distribution, named after Swiss mathematician Jacob Bernoulli, is the discrete probability distribution of a random variable which takes the value 1 with probability p and the value 0 with probability q = 1-p. Less formally, it can be thought of as a model for the set of possible outcomes of any single experiment that asks a yes–no question. Such questions lead to outcome (probability), outcomes that are Boolean-valued function, Boolean-valued: a single bit whose value is success/yes and no, yes/Truth value, true/Binary code, one with probability ''p'' and failure/no/false (logic), false/Binary code, zero with probability ''q''. It can be used to represent a (possibly biased) coin toss where 1 and 0 would represent "heads" and "tails", respectively, and ''p'' would be the probability of the coin landing on heads (or vice versa where 1 would represent tails and ''p'' would be the probability of tails). In particular, unfair co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cornell University
Cornell University is a Private university, private Ivy League research university based in Ithaca, New York, United States. The university was co-founded by American philanthropist Ezra Cornell and historian and educator Andrew Dickson White in 1865. Since its founding, Cornell University has been a Mixed-sex education, co-educational and nonsectarian institution. As of fall 2024, the student body included 16,128 undergraduate and 10,665 graduate students from all 50 U.S. states and 130 countries. The university is organized into eight Undergraduate education, undergraduate colleges and seven Postgraduate education, graduate divisions on its main Ithaca campus. Each college and academic division has near autonomy in defining its respective admission standards and academic curriculum. In addition to its primary campus in Ithaca, Cornell University administers three satellite campuses, including two in New York City, the Weill Cornell Medicine, medical school and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
C (programming Language)
C (''pronounced'' '' – like the letter c'') is a general-purpose programming language. It was created in the 1970s by Dennis Ritchie and remains very widely used and influential. By design, C's features cleanly reflect the capabilities of the targeted Central processing unit, CPUs. It has found lasting use in operating systems code (especially in Kernel (operating system), kernels), device drivers, and protocol stacks, but its use in application software has been decreasing. C is commonly used on computer architectures that range from the largest supercomputers to the smallest microcontrollers and embedded systems. A successor to the programming language B (programming language), B, C was originally developed at Bell Labs by Ritchie between 1972 and 1973 to construct utilities running on Unix. It was applied to re-implementing the kernel of the Unix operating system. During the 1980s, C gradually gained popularity. It has become one of the most widely used programming langu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Simple Linear Regression
In statistics, simple linear regression (SLR) is a linear regression model with a single explanatory variable. That is, it concerns two-dimensional sample points with one independent variable and one dependent variable (conventionally, the ''x'' and ''y'' coordinates in a Cartesian coordinate system) and finds a linear function (a non-vertical straight line) that, as accurately as possible, predicts the dependent variable values as a function of the independent variable. The adjective ''simple'' refers to the fact that the outcome variable is related to a single predictor. It is common to make the additional stipulation that the ordinary least squares (OLS) method should be used: the accuracy of each predicted value is measured by its squared '' residual'' (vertical distance between the point of the data set and the fitted line), and the goal is to make the sum of these squared deviations as small as possible. In this case, the slope of the fitted line is equal to the corre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Empirical Bayes Method
Empirical Bayes methods are procedures for statistical inference in which the prior probability distribution is estimated from the data. This approach stands in contrast to standard Bayesian methods, for which the prior distribution is fixed before any data are observed. Despite this difference in perspective, empirical Bayes may be viewed as an approximation to a fully Bayesian treatment of a hierarchical model wherein the parameters at the highest level of the hierarchy are set to their most likely values, instead of being integrated out. Introduction Empirical Bayes methods can be seen as an approximation to a fully Bayesian treatment of a hierarchical Bayes model. In, for example, a two-stage hierarchical Bayes model, observed data y = \ are assumed to be generated from an unobserved set of parameters \theta = \ according to a probability distribution p(y\mid\theta)\,. In turn, the parameters \theta can be considered samples drawn from a population characterised b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |