|
Glycerone
Dihydroxyacetone (; DHA), also known as glycerone, is a simple saccharide (a triose) with formula . DHA is primarily used as an ingredient in sunless tanning products. It is often derived from plant sources such as sugar beets and sugar cane, and by the fermentation of glycerin. Chemistry DHA is a hygroscopic white crystalline powder. It has a sweet cooling taste and a characteristic odor. It is the simplest of all ketoses and has no chiral center. The normal form is a dimer (2,5-bis(hydroxymethyl)-1,4-dioxane-2,5-diol). The dimer slowly dissolves in water, whereupon it converts to the monomer. These solutions are stable at pH's between 4 and 6. In more basic solution, it degrades to brown product. : This skin browning effect is attributed to a Maillard reaction. DHA condenses with the amino acid residues in the protein keratin, the major component of the skin surface. When injected, no pigmentation occurs, consistent with a role for oxygen in color development. The res ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dihydroxyacetone Phosphate
Dihydroxyacetone phosphate (DHAP, also glycerone phosphate in older texts) is the anion with the formula HOCH2C(O)CH2OPO32-. This anion is involved in many metabolic pathways, including the Calvin cycle in plants and glycolysis.Nelson, D. L.; Cox, M. M. "Lehninger, Principles of Biochemistry" 3rd Ed. Worth Publishing: New York, 2000. . It is the phosphate ester of dihydroxyacetone. Role in glycolysis Dihydroxyacetone phosphate lies in the glycolysis metabolic pathway, and is one of the two products of breakdown of fructose 1,6-bisphosphate, along with glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate. It is rapidly and reversibly isomerised to glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate. ''The numbering of the carbon atoms indicates the fate of the carbons according to their position in fructose 6-phosphate.'' Role in other pathways In the Calvin cycle, DHAP is one of the products of the sixfold reduction of 1,3-bisphosphoglycerate by NADPH. It is also used in the synthesis of sedoheptulose 1,7-bispho ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glycolysis
Glycolysis is the metabolic pathway that converts glucose () into pyruvic acid, pyruvate and, in most organisms, occurs in the liquid part of cells (the cytosol). The Thermodynamic free energy, free energy released in this process is used to form the high-energy molecules adenosine triphosphate (ATP) and NADH, reduced nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NADH). Glycolysis is a sequence of ten reactions catalyzed by enzymes. The wide occurrence of glycolysis in other species indicates that it is an ancient metabolic pathway. Indeed, the reactions that make up glycolysis and its parallel pathway, the pentose phosphate pathway, can occur in the Great Oxygenation Event, oxygen-free conditions of the Archean oceans, also in the absence of enzymes, catalyzed by metal ions, meaning this is a plausible prebiotic pathway for abiogenesis. The most common type of glycolysis is the ''Embden–Meyerhof–Parnas (EMP) pathway'', which was discovered by Gustav Embden, Otto Meyerhof, and Jakub Kar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sunless Tanning
Sunless tanning refers to the effect of a sun tanning, suntan without exposure to the Sun. Sunless tanning involves the use of #Oral agents, oral agents (carotenids), or creams, lotions or sprays applied to the skin. Skin-applied products may be #Skin-reactive agents, skin-reactive agents or #Bronzers, temporary bronzers (colorants). Sunless tanning has emerged as an alternative to UV exposure (from sunlight or indoor tanning), which has been linked to increased risk of skin cancer. The chemical compound dihydroxyacetone (DHA) is used in sunless tanning products in concentrations of 3%-5%. DHA concentration is adjusted to provide darker and lighter shades of tan. The reaction of keratin protein present in skin and DHA is responsible for the production of pigmentation. Oral agents (carotenoids) A safe and effective method of sunless tanning is consumption of certain carotenoids—antioxidants found in some fruits and vegetables such as carrots and tomatoes—which can result ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Saccharide
A carbohydrate () is a biomolecule composed of carbon (C), hydrogen (H), and oxygen (O) atoms. The typical hydrogen-to-oxygen atomic ratio is 2:1, analogous to that of water, and is represented by the empirical formula (where ''m'' and ''n'' may differ). This formula does not imply direct covalent bonding between hydrogen and oxygen atoms; for example, in , hydrogen is covalently bonded to carbon, not oxygen. While the 2:1 hydrogen-to-oxygen ratio is characteristic of many carbohydrates, exceptions exist. For instance, uronic acids and deoxy-sugars like fucose deviate from this precise stoichiometric definition. Conversely, some compounds conforming to this definition, such as formaldehyde and acetic acid, are not classified as carbohydrates. The term is predominantly used in biochemistry, functioning as a synonym for saccharide (), a group that includes sugars, starch, and cellulose. The saccharides are divided into four chemical groups: monosaccharides, disaccharides, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phosphorylation
In biochemistry, phosphorylation is described as the "transfer of a phosphate group" from a donor to an acceptor. A common phosphorylating agent (phosphate donor) is ATP and a common family of acceptor are alcohols: : This equation can be written in several ways that are nearly equivalent that describe the behaviors of various protonated states of ATP, ADP, and the phosphorylated product. As is clear from the equation, a phosphate group per se is not transferred, but a phosphoryl group (PO3-). Phosphoryl is an electrophile. This process and its inverse, dephosphorylation, are common in biology. Text was copied from this source, which is available under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License. Protein phosphorylation often activates (or deactivates) many enzymes. During respiration Phosphorylation is essential to the processes of both anaerobic and aerobic respiration, which involve the production of adenosine triphosphate (ATP), the "high-energy" exc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Structural Isomer
In chemistry, a structural isomer (or constitutional isomer in the IUPAC nomenclature) of a compound is a compound that contains the same number and type of atoms, but with a different connectivity (i.e. arrangement of bonds) between them. The term metamer was formerly used for the same concept. For example, butanol , methyl propyl ether , and diethyl ether have the same molecular formula but are three distinct structural isomers. The concept applies also to polyatomic ions with the same total charge. A classical example is the cyanate ion and the fulminate ion . It is also extended to ionic compounds, so that (for example) ammonium cyanate and urea are considered structural isomers,William F. Bynum, E. Janet Browne, Roy Porter (2014)''Dictionary of the History of Science'' page 218. and so are methylammonium formate and ammonium acetate . Structural isomerism is the most radical type of isomerism. It is opposed to stereoisomerism, in which the atoms and bon ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Catalytic Cycle
In chemistry, a catalytic cycle is a multistep reaction mechanism that involves a catalyst. The catalytic cycle is the main method for describing the role of catalysts in biochemistry, organometallic chemistry, bioinorganic chemistry, materials science, etc. Since catalysts are regenerated, catalytic cycles are usually written as a sequence of chemical reactions in the form of a loop. In such loops, the initial step entails binding of one or more reactants by the catalyst, and the final step is the release of the product and regeneration of the catalyst. Articles on the Monsanto process, the Wacker process, and the Heck reaction show catalytic cycles. A catalytic cycle is not necessarily a full reaction mechanism. For example, it may be that the intermediates have been detected, but it is not known by which mechanisms the actual elementary reactions occur. Precatalysts Precatalysts are not catalysts but are ''precursors'' to catalysts. Precatalysts are converted in the r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
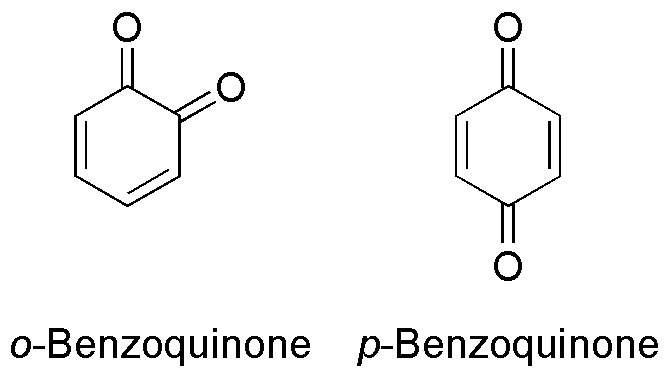
Benzoquinone
Benzoquinone (C6H4O2) is a quinone with a single benzene ring. There are 2 (out of 3 hypothetical) benzoquinones: * 1,4-Benzoquinone, most commonly, right image (also ''para''-benzoquinone, ''p''-benzoquinone, ''para''-quinone, or just quinone) * 1,2-Benzoquinone, less commonly, left image (also ''ortho''-benzoquinone, ''o''-benzoquinone, ''ortho''-quinone) *1,3-benzoquinone "does not exist, because its structure would be nonplanar and highly strained", though derivatives are known. An alkylated ''p''-benzoquinone has been found in the rhizomes of '' Iris kemaonensis''. See also * Arene substitution pattern Arene substitution patterns are part of organic chemistry IUPAC nomenclature and pinpoint the position of substituents other than hydrogen in relation to each other on an aromatic hydrocarbon. ''Ortho'', ''meta'', and ''para'' substitution * ... References {{Chemistry index ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Catalysts
Catalysis () is the increase in reaction rate, rate of a chemical reaction due to an added substance known as a catalyst (). Catalysts are not consumed by the reaction and remain unchanged after it. If the reaction is rapid and the catalyst recycles quickly, very small amounts of catalyst often suffice; mixing, surface area, and temperature are important factors in reaction rate. Catalysts generally react with one or more reactants to form reaction intermediate, intermediates that subsequently give the final reaction product, in the process of regenerating the catalyst. The rate increase occurs because the catalyst allows the reaction to occur by an alternative mechanism which may be much faster than the noncatalyzed mechanism. However the noncatalyzed mechanism does remain possible, so that the total rate (catalyzed plus noncatalyzed) can only increase in the presence of the catalyst and never decrease. Catalysis may be classified as either homogeneous catalysis, homogeneou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Palladium
Palladium is a chemical element; it has symbol Pd and atomic number 46. It is a rare and lustrous silvery-white metal discovered in 1802 by the English chemist William Hyde Wollaston. He named it after the asteroid Pallas (formally 2 Pallas), which was itself named after the epithet of the Greek goddess Athena, acquired by her when she slew Pallas. Palladium, platinum, rhodium, ruthenium, iridium and osmium form together a group of elements referred to as the platinum group metals (PGMs). They have similar chemical properties, but palladium has the lowest melting point and is the least dense of them. More than half the supply of palladium and its congener platinum is used in catalytic converters, which convert as much as 90% of the harmful gases in automobile exhaust (hydrocarbons, carbon monoxide, and nitrogen dioxide) into nontoxic substances (nitrogen, carbon dioxide and water vapor). Palladium is also used in electronics, dentistry, medicine, hydrogen purification ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Catalyst
Catalysis () is the increase in rate of a chemical reaction due to an added substance known as a catalyst (). Catalysts are not consumed by the reaction and remain unchanged after it. If the reaction is rapid and the catalyst recycles quickly, very small amounts of catalyst often suffice; mixing, surface area, and temperature are important factors in reaction rate. Catalysts generally react with one or more reactants to form intermediates that subsequently give the final reaction product, in the process of regenerating the catalyst. The rate increase occurs because the catalyst allows the reaction to occur by an alternative mechanism which may be much faster than the noncatalyzed mechanism. However the noncatalyzed mechanism does remain possible, so that the total rate (catalyzed plus noncatalyzed) can only increase in the presence of the catalyst and never decrease. Catalysis may be classified as either homogeneous, whose components are dispersed in the same phase (usual ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ferrous
In chemistry, iron(II) refers to the chemical element, element iron in its +2 oxidation number, oxidation state. The adjective ''ferrous'' or the prefix ''ferro-'' is often used to specify such compounds, as in ''ferrous chloride'' for iron(II) chloride (). The adjective ''ferric'' is used instead for iron(III) salts, containing the cation Fe3+. The word ''wikt:ferrous, ferrous'' is derived from the Latin word , meaning "iron". In salt (chemistry), ionic compounds (salts), such an atom may occur as a separate cation (positive ion) abbreviated as Fe2+, although more precise descriptions include other ligands such as water and halides. Iron(II) centres occur in coordination complexes, such as in the anion ferrocyanide, , where six cyanide ligands are bound the metal centre; or, in organometallic compounds, such as the ferrocene , where two cyclopentadienyl anions are bound to the FeII centre. Ferrous ions in biology All known forms of life require iron. Many proteins in living ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |