|
Global Address Space Programming Interface
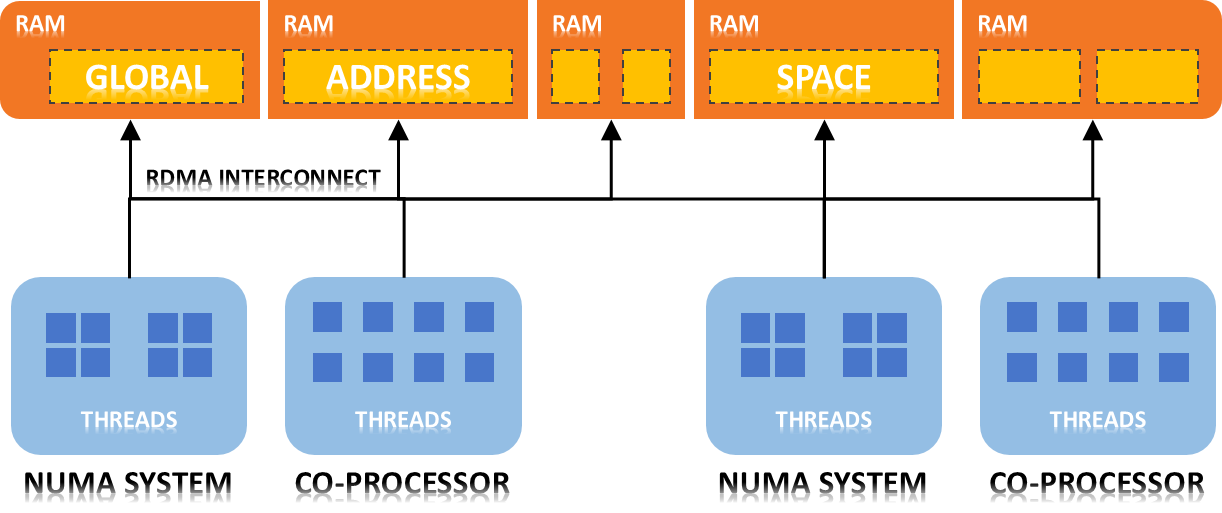
Global Address Space Programming Interface (GPI) is an application programming interface (API) for the development of scalable, asynchronous and fault tolerant parallel applications. It is an implementation of the partitioned global address space programming model. History GPI is developed by the Fraunhofer Institute for Industrial Mathematics (ITWM) since 2005 and was initially known as FVM (Fraunhofer Virtual Machine). In 2009 the name changed to Global Address Programming Interface or GPI. In 2011, Fraunhofer ITWM and its partners such as Fraunhofer SCAI, TUD, T-Systems SfR, DLR, KIT, FZJ, DWD and Scapos have initiated and launched the GASPI project to define a novel specification for an API (GASPI based on GPI) and to make this novel specification a reliable, scalable and universal tool for the HPC community. GPI-2 is the first open source implementation of this standard. The software is freely available to application developers and researchers, licenses for commercial ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fraunhofer Society
The Fraunhofer Society () is a German publicly-owned research organization with 76institutes spread throughout Germany, each focusing on different fields of applied science (as opposed to the Max Planck Society, which works primarily on Basic research, basic science). With some 30,800 employees, mainly scientists and engineers, and with an annual research budget of about €3.0billion, it is the biggest organization for applied research and development services in Europe. It is named after Joseph von Fraunhofer who, as a scientist, an engineer, and an entrepreneur, is said to have superbly exemplified the goals of the society. Some basic funding for the Fraunhofer Society is provided by the state (the German public, through the federal government together with the states or ''States of Germany, Länder'', "owns" the Fraunhofer Society), but more than 70% of the funding is earned through contract work, either for government-sponsored projects or from industry. Since the 1990s th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Linux
Linux ( ) is a family of open source Unix-like operating systems based on the Linux kernel, an kernel (operating system), operating system kernel first released on September 17, 1991, by Linus Torvalds. Linux is typically package manager, packaged as a Linux distribution (distro), which includes the kernel and supporting system software and library (computing), libraries—most of which are provided by third parties—to create a complete operating system, designed as a clone of Unix and released under the copyleft GPL license. List of Linux distributions, Thousands of Linux distributions exist, many based directly or indirectly on other distributions; popular Linux distributions include Debian, Fedora Linux, Linux Mint, Arch Linux, and Ubuntu, while commercial distributions include Red Hat Enterprise Linux, SUSE Linux Enterprise, and ChromeOS. Linux distributions are frequently used in server platforms. Many Linux distributions use the word "Linux" in their name, but the Free ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Application Programming Interface
An application programming interface (API) is a connection between computers or between computer programs. It is a type of software Interface (computing), interface, offering a service to other pieces of software. A document or standard that describes how to build such a connection or interface is called an ''API specification''. A computer system that meets this standard is said to ''implement'' or ''expose'' an API. The term API may refer either to the specification or to the implementation. In contrast to a user interface, which connects a computer to a person, an application programming interface connects computers or pieces of software to each other. It is not intended to be used directly by a person (the end user) other than a computer programmer who is incorporating it into software. An API is often made up of different parts which act as tools or services that are available to the programmer. A program or a programmer that uses one of these parts is said to ''call'' that ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Parallel Computing
Parallel computing is a type of computing, computation in which many calculations or Process (computing), processes are carried out simultaneously. Large problems can often be divided into smaller ones, which can then be solved at the same time. There are several different forms of parallel computing: Bit-level parallelism, bit-level, Instruction-level parallelism, instruction-level, Data parallelism, data, and task parallelism. Parallelism has long been employed in high-performance computing, but has gained broader interest due to the physical constraints preventing frequency scaling.S.V. Adve ''et al.'' (November 2008)"Parallel Computing Research at Illinois: The UPCRC Agenda" (PDF). Parallel@Illinois, University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign. "The main techniques for these performance benefits—increased clock frequency and smarter but increasingly complex architectures—are now hitting the so-called power wall. The computer industry has accepted that future performance inc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Partitioned Global Address Space
In computer science, partitioned global address space (PGAS) is a parallel programming model paradigm. PGAS is typified by communication operations involving a global memory address space abstraction that is logically partitioned, where a portion is local to each process, thread, or processing element. The novelty of PGAS is that the portions of the shared memory space may have an affinity for a particular process, thereby exploiting locality of reference in order to improve performance. A PGAS memory model is featured in various parallel programming languages and libraries, including: Coarray Fortran, Unified Parallel CSplit-C Fortress, Chapel, X10UPC++ [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Programming Model
A programming model is an execution model coupled to an API or a particular pattern of code. In this style, there are actually two execution models in play: the execution model of the base programming language and the execution model of the programming model. An example is Spark where Java is the base language, and Spark is the programming model. Execution may be based on what appear to be library calls. Other examples include the POSIX Threads library and Hadoop's MapReduce. In both cases, the execution model of the programming model is different from that of the base language in which the code is written. For example, the C programming language has no behavior in its execution model for input/output or thread behavior. But such behavior can be invoked from C syntax, by making what appears to be a call to a normal C library. What distinguishes a programming model from a normal library is that the behavior of the call cannot be understood in terms of the language the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fraunhofer Institute
The Fraunhofer Society () is a German publicly-owned research organization with 76institutes spread throughout Germany, each focusing on different fields of applied science (as opposed to the Max Planck Society, which works primarily on basic science). With some 30,800 employees, mainly scientists and engineers, and with an annual research budget of about €3.0billion, it is the biggest organization for applied research and development services in Europe. It is named after Joseph von Fraunhofer who, as a scientist, an engineer, and an entrepreneur, is said to have superbly exemplified the goals of the society. Some basic funding for the Fraunhofer Society is provided by the state (the German public, through the federal government together with the states or '' Länder'', "owns" the Fraunhofer Society), but more than 70% of the funding is earned through contract work, either for government-sponsored projects or from industry. Since the 1990s the organization has also internatio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Message Passing Interface
The Message Passing Interface (MPI) is a portable message-passing standard designed to function on parallel computing architectures. The MPI standard defines the syntax and semantics of library routines that are useful to a wide range of users writing portable message-passing programs in C, C++, and Fortran. There are several open-source MPI implementations, which fostered the development of a parallel software industry, and encouraged development of portable and scalable large-scale parallel applications. History The message passing interface effort began in the summer of 1991 when a small group of researchers started discussions at a mountain retreat in Austria. Out of that discussion came a Workshop on Standards for Message Passing in a Distributed Memory Environment, held on April 29–30, 1992 in Williamsburg, Virginia. Attendees at Williamsburg discussed the basic features essential to a standard message-passing interface and established a working group to continu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
GPI Overview
GPI may refer to: Economics * Gender Parity Index * Genuine progress indicator * Global Payments Innovation, a faster international payment service by SWIFT Education * George Padmore Institute, a British library and archives * Greenfield Park Primary International School, in Quebec, Canada Government and politics * Global Peace Index * Global Partnership Initiative of the United States State Department Materiel * United States national missile defense#Glide phase interceptors (GPIs) Medicine * Generic Product Identifier, a drug classification system * General paresis of the insane * Glucose-6-phosphate isomerase, an enzyme * Glycosylphosphatidylinositol, a glycolipid * Internal globus pallidus Science and technology * Gemini Planet Imager, a telescope instrument * General Purpose Input, an uncommitted digital signal pin on an integrated circuit or electronic circuit board used as an input and controllable by the user at runtime. * Gibson Plumage Index, an albatro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
GPI-Space
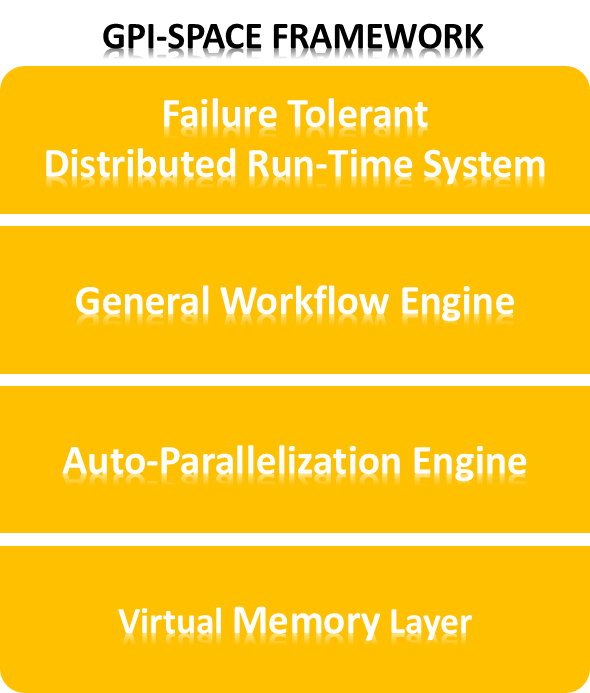
GPI-Space is a parallel programming development software, developed by the Fraunhofer Institute#Institutes, Fraunhofer Institute for Industrial Mathematics (ITWM). The main concept behind the software is separation of domain and High-performance computing, HPC knowledge and leaving each part to the respective experts while the GPI-Space as framework integrates both parts together. GPI-Space is making use of Global Address Space Programming Interface, GPI to solve big data problems more efficient than current solutions. GPI-Space was first introduced in a domain-specific version for geology, under the name SDPA (Seismic Development and Programming Architecture) at SEG 2010 in Houston. Core layers GPI Space comes with several layers, that make up the core of the parallel programming development software. Runtime engine The runtime engine is responsible to distribute the available jobs across the available systems. In a large scale High-performance computing, HPC Computer clust ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |